
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Phosphoric diester hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of an sh2 domain of phospholipasE C-gamma1 complexed with a high affinity binding peptide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
PhospholipasE C gamma-1, c-terminal sh2 domain. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. Phosphopeptide from pdgf. Chain: b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Cattle. Organism_taxid: 9913. Organism_taxid: 9913
|
|
NMR struc:
|
 |
18 models
|
 |
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.M.Pascal,A.U.Singer,G.Gish,T.Yamazaki,S.E.Shoelson,T.Pawson, L.E.Kay,J.D.Forman-Kay
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.M.Pascal
et al.
(1994).
Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of an SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1 complexed with a high affinity binding peptide.
Cell,
77,
461-472.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Aug-94
|
Release date:
|
26-Jan-95
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.3.1.4.11
- phosphoinositide phospholipase C.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
myo-Inositol Phosphate Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate) + H2O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
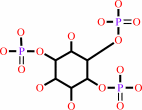 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
|
+
|
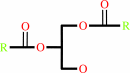 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain B:
E.C.2.7.10.1
- receptor protein-tyrosine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Cell
77:461-472
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of an SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1 complexed with a high affinity binding peptide.
|
|
S.M.Pascal,
A.U.Singer,
G.Gish,
T.Yamazaki,
S.E.Shoelson,
T.Pawson,
L.E.Kay,
J.D.Forman-Kay.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The solution structure of the C-terminal SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1
(PLC-gamma 1), in complex with a phosphopeptide corresponding to its Tyr-1021
high affinity binding site on the platelet-derived growth factor receptor, has
been determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The topology of the
SH2-phosphopeptide complex is similar to previously reported Src and Lck SH2
complexes. However, the binding site for residues C-terminal to the
phosphotyrosine (pTyr) is an extended groove that contacts peptide residues at
the +1 to +6 positions relative to the pTyr. This striking difference from Src
and Lck reflects the fact that the PLC-gamma 1 complex involves binding of a
phosphopeptide with predominantly hydrophobic residues C-terminal to the pTyr
and therefore serves as a prototype for a second class of SH2-phosphopeptide
interactions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Neumayr,
T.Rudas,
and
O.Steinhauser
(2010).
Global and local Voronoi analysis of solvation shells of proteins.
|
| |
J Chem Phys,
133,
084108.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Pati,
G.U.Gurudutta,
O.P.Kalra,
and
A.Mukhopadhyay
(2010).
The structural insights of stem cell factor receptor (c-Kit) interaction with tyrosine phosphatase-2 (Shp-2): An in silico analysis.
|
| |
BMC Res Notes,
3,
14.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Everett,
T.D.Bunney,
Y.Yoon,
F.Rodrigues-Lima,
R.Harris,
P.C.Driscoll,
K.Abe,
H.Fuchs,
M.H.de Angelis,
P.Yu,
W.Cho,
and
M.Katan
(2009).
Characterization of phospholipase C gamma enzymes with gain-of-function mutations.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
23083-23093.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Min,
R.E.Joseph,
D.B.Fulton,
and
A.H.Andreotti
(2009).
Itk tyrosine kinase substrate docking is mediated by a nonclassical SH2 domain surface of PLCgamma1.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
21143-21148.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hanke,
and
M.Mann
(2009).
The phosphotyrosine interactome of the insulin receptor family and its substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2.
|
| |
Mol Cell Proteomics,
8,
519-534.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.H.Scheuermann,
D.R.Tomchick,
M.Machius,
Y.Guo,
R.K.Bruick,
and
K.H.Gardner
(2009).
Artificial ligand binding within the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain of the HIF2 transcription factor.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
450-455.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kaushansky,
A.Gordus,
B.Chang,
J.Rush,
and
G.MacBeath
(2008).
A quantitative study of the recruitment potential of all intracellular tyrosine residues on EGFR, FGFR1 and IGF1R.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
4,
643-653.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Schedlbauer,
R.Auer,
K.Ledolter,
M.Tollinger,
K.Kloiber,
R.Lichtenecker,
S.Ruedisser,
U.Hommel,
W.Schmid,
R.Konrat,
and
G.Kontaxis
(2008).
Direct methods and residue type specific isotope labeling in NMR structure determination and model-driven sequential assignment.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
42,
111-127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.P.Monteiro,
R.J.Arai,
and
L.R.Travassos
(2008).
Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and protein tyrosine nitration in redox signaling.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
10,
843-889.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Reddi,
G.Ying,
L.Duan,
G.Chen,
M.Dimri,
P.Douillard,
B.J.Druker,
M.Naramura,
V.Band,
and
H.Band
(2007).
Binding of Cbl to a phospholipase Cgamma1-docking site on platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta provides a dual mechanism of negative regulation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
29336-29347.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Spuches,
H.J.Argiros,
K.H.Lee,
L.L.Haas,
S.C.Pero,
D.N.Krag,
P.P.Roller,
D.E.Wilcox,
and
B.A.Lyons
(2007).
Calorimetric investigation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated peptide ligand binding to the human Grb7-SH2 domain.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
20,
245-252.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.DeBell,
L.Graham,
I.Reischl,
C.Serrano,
E.Bonvini,
and
B.Rellahan
(2007).
Intramolecular regulation of phospholipase C-gamma1 by its C-terminal Src homology 2 domain.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
27,
854-863.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Fischer,
K.Kloiber,
J.Häusler,
K.Ledolter,
R.Konrat,
and
W.Schmid
(2007).
Synthesis of a 13C-methyl-group-labeled methionine precursor as a useful tool for simplifying protein structural analysis by NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
610-612.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Liu,
K.Jablonowski,
M.Raina,
M.Arcé,
T.Pawson,
and
P.D.Nash
(2006).
The human and mouse complement of SH2 domain proteins-establishing the boundaries of phosphotyrosine signaling.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
22,
851-868.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Schröder,
T.Rudas,
S.Boresch,
and
O.Steinhauser
(2006).
Simulation studies of the protein-water interface. I. Properties at the molecular resolution.
|
| |
J Chem Phys,
124,
234907.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Rudas,
C.Schröder,
S.Boresch,
and
O.Steinhauser
(2006).
Simulation studies of the protein-water interface. II. Properties at the mesoscopic resolution.
|
| |
J Chem Phys,
124,
234908.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Wen,
J.Yan,
and
M.Zhang
(2006).
Structural characterization of the split pleckstrin homology domain in phospholipase C-gamma1 and its interaction with TRPC3.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
12060-12068.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Matoba,
T.Kumagai,
A.Yamamoto,
H.Yoshitsu,
and
M.Sugiyama
(2006).
Crystallographic evidence that the dinuclear copper center of tyrosinase is flexible during catalysis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
8981-8990.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Poulin,
F.Sekiya,
and
S.G.Rhee
(2005).
Intramolecular interaction between phosphorylated tyrosine-783 and the C-terminal Src homology 2 domain activates phospholipase C-gamma1.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
4276-4281.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ivancic,
A.M.Spuches,
E.C.Guth,
M.A.Daugherty,
D.E.Wilcox,
and
B.A.Lyons
(2005).
Backbone nuclear relaxation characteristics and calorimetric investigation of the human Grb7-SH2/erbB2 peptide complex.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1556-1569.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Radtke,
S.Haan,
A.Jörissen,
H.M.Hermanns,
S.Diefenbach,
T.Smyczek,
H.Schmitz-Vandeleur,
P.C.Heinrich,
I.Behrmann,
and
C.Haan
(2005).
The Jak1 SH2 domain does not fulfill a classical SH2 function in Jak/STAT signaling but plays a structural role for receptor interaction and up-regulation of receptor surface expression.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
25760-25768.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.J.Scharf,
J.Witney,
R.Daly,
and
B.A.Lyons
(2004).
Solution structure of the human Grb14-SH2 domain and comparison with the structures of the human Grb7-SH2/erbB2 peptide complex and human Grb10-SH2 domain.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
2541-2546.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Cuadrado,
L.F.Garcia-Fernandez,
L.Gonzalez,
Y.Suarez,
A.Losada,
V.Alcaide,
T.Martinez,
J.M.Fernandez-Sousa,
J.M.Sanchez-Puelles,
and
A.Munoz
(2003).
Aplidin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells via glutathione depletion and sustained activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Src, JNK, and p38 MAPK.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
241-250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Wojciechowski,
T.Grycuk,
J.M.Antosiewicz,
and
B.Lesyng
(2003).
Prediction of secondary ionization of the phosphate group in phosphotyrosine peptides.
|
| |
Biophys J,
84,
750-756.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.De Souza,
L.J.Fabri,
A.Nash,
D.J.Hilton,
N.A.Nicola,
and
M.Baca
(2002).
SH2 domains from suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 and protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 have similar binding specificities.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9229-9236.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Donaldson,
G.Gish,
T.Pawson,
L.E.Kay,
and
J.D.Forman-Kay
(2002).
Structure of a regulatory complex involving the Abl SH3 domain, the Crk SH2 domain, and a Crk-derived phosphopeptide.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
14053-14058.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hörtner,
U.Nielsch,
L.M.Mayr,
P.C.Heinrich,
and
S.Haan
(2002).
A new high affinity binding site for suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 on the erythropoietin receptor.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
2516-2526.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Saito,
and
B.C.Berk
(2002).
Angiotensin II-mediated signal transduction pathways.
|
| |
Curr Hypertens Rep,
4,
167-171.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Poulin,
F.Sekiya,
and
S.G.Rhee
(2000).
Differential roles of the Src homology 2 domains of phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1) in platelet-derived growth factor-induced activation of PLC-gamma1 in intact cells.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
6411-6416.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Y.Lee,
B.Y.Ahn,
and
K.S.Kim
(2000).
A thioredoxin from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii has a glutaredoxin-like fold but thioredoxin-like activities.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
6652-6659.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yoshizumi,
J.Abe,
J.Haendeler,
Q.Huang,
and
B.C.Berk
(2000).
Src and Cas mediate JNK activation but not ERK1/2 and p38 kinases by reactive oxygen species.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
11706-11712.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Forman-Kay,
and
T.Pawson
(1999).
Diversity in protein recognition by PTB domains.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
9,
690-695.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.E.DeBell,
B.A.Stoica,
M.C.Verí,
A.Di Baldassarre,
S.Miscia,
L.J.Graham,
B.L.Rellahan,
M.Ishiai,
T.Kurosaki,
and
E.Bonvini
(1999).
Functional independence and interdependence of the Src homology domains of phospholipase C-gamma1 in B-cell receptor signal transduction.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
19,
7388-7398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.S.Ji,
A.Chattopadhyay,
M.Vecchi,
and
G.Carpenter
(1999).
Physiological requirement for both SH2 domains for phospholipase C-gamma1 function and interaction with platelet-derived growth factor receptors.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
19,
4961-4970.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Williams
(1999).
Mammalian phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
255-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Li,
G.Gish,
D.Yang,
A.J.Coffey,
J.D.Forman-Kay,
I.Ernberg,
L.E.Kay,
and
T.Pawson
(1999).
Novel mode of ligand binding by the SH2 domain of the human XLP disease gene product SAP/SH2D1A.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
9,
1355-1362.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhang,
A.Chattopadhyay,
Q.S.Ji,
J.D.Owen,
P.J.Ruest,
G.Carpenter,
and
S.K.Hanks
(1999).
Focal adhesion kinase promotes phospholipase C-gamma1 activity.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
9021-9026.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Ottinger,
M.C.Botfield,
and
S.E.Shoelson
(1998).
Tandem SH2 domains confer high specificity in tyrosine kinase signaling.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
729-735.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Bradshaw,
R.A.Grucza,
J.E.Ladbury,
and
G.Waksman
(1998).
Probing the "two-pronged plug two-holed socket" model for the mechanism of binding of the Src SH2 domain to phosphotyrosyl peptides: a thermodynamic study.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
9083-9090.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Gardner,
and
L.E.Kay
(1998).
The use of 2H, 13C, 15N multidimensional NMR to study the structure and dynamics of proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
27,
357-406.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kay,
D.R.Muhandiram,
G.Wolf,
S.E.Shoelson,
and
J.D.Forman-Kay
(1998).
Correlation between binding and dynamics at SH2 domain interfaces.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
5,
156-163.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kay
(1998).
Protein dynamics from NMR.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
5,
513-517.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Rui,
and
C.Carter-Su
(1998).
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates the association of SH2-Bbeta with PDGF receptor and phosphorylation of SH2-Bbeta.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
21239-21245.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Jansson,
G.Andersson,
M.Uhlén,
B.Nilsson,
and
J.Kördel
(1998).
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF)binding protein 1 binding epitope on IGF-I probed by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy and mutational analysis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
24701-24707.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Katan
(1998).
Families of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C: structure and function.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1436,
5.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Y.Bai,
P.Dieter,
C.Peschel,
S.W.Morris,
and
J.Duyster
(1998).
Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of large-cell anaplastic lymphoma is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that utilizes phospholipase C-gamma to mediate its mitogenicity.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
18,
6951-6961.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.K.Sawyer
(1998).
Src homology-2 domains: structure, mechanisms, and drug discovery.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
47,
243-261.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Mikita,
C.Daniel,
P.Wu,
and
U.Schindler
(1998).
Mutational analysis of the STAT6 SH2 domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
17634-17642.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.U.Singer,
and
J.D.Forman-Kay
(1997).
pH titration studies of an SH2 domain-phosphopeptide complex: unusual histidine and phosphate pKa values.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
6,
1910-1919.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Gay,
P.Furet,
C.García-Echeverría,
J.Rahuel,
P.Chène,
H.Fretz,
J.Schoepfer,
and
G.Caravatti
(1997).
Dual specificity of Src homology 2 domains for phosphotyrosine peptide ligands.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
5712-5718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.McNemar,
M.E.Snow,
W.T.Windsor,
A.Prongay,
P.Mui,
R.Zhang,
J.Durkin,
H.V.Le,
and
P.C.Weber
(1997).
Thermodynamic and structural analysis of phosphotyrosine polypeptide binding to Grb2-SH2.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
10006-10014.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.M.Farschon,
C.Couture,
T.Mustelin,
and
D.D.Newmeyer
(1997).
Temporal phases in apoptosis defined by the actions of Src homology 2 domains, ceramide, Bcl-2, interleukin-1beta converting enzyme family proteases, and a dense membrane fraction.
|
| |
J Cell Biol,
137,
1117-1125.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Tall,
G.Dormán,
P.Garcia,
L.Runnels,
S.Shah,
J.Chen,
A.Profit,
Q.M.Gu,
A.Chaudhary,
G.D.Prestwich,
and
M.J.Rebecchi
(1997).
Phosphoinositide binding specificity among phospholipase C isozymes as determined by photo-cross-linking to novel substrate and product analogs.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
7239-7248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kuriyan,
and
D.Cowburn
(1997).
Modular peptide recognition domains in eukaryotic signaling.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
26,
259-288.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Gardner,
M.K.Rosen,
and
L.E.Kay
(1997).
Global folds of highly deuterated, methyl-protonated proteins by multidimensional NMR.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
1389-1401.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Ali,
P.P.Sayeski,
L.B.Dirksen,
D.J.Hayzer,
M.B.Marrero,
and
K.E.Bernstein
(1997).
Dependence on the motif YIPP for the physical association of Jak2 kinase with the intracellular carboxyl tail of the angiotensin II AT1 receptor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
23382-23388.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.S.Charifson,
L.M.Shewchuk,
W.Rocque,
C.W.Hummel,
S.R.Jordan,
C.Mohr,
G.J.Pacofsky,
M.R.Peel,
M.Rodriguez,
D.D.Sternbach,
and
T.G.Consler
(1997).
Peptide ligands of pp60(c-src) SH2 domains: a thermodynamic and structural study.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
6283-6293.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Shoelson
(1997).
SH2 and PTB domain interactions in tyrosine kinase signal transduction.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
1,
227-234.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.D.Mulhern,
G.L.Shaw,
C.J.Morton,
A.J.Day,
and
I.D.Campbell
(1997).
The SH2 domain from the tyrosine kinase Fyn in complex with a phosphotyrosyl peptide reveals insights into domain stability and binding specificity.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
1313-1323.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.D.Singer,
H.A.Brown,
and
P.C.Sternweis
(1997).
Regulation of eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase D.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
66,
475-509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Wand,
and
S.W.Englander
(1996).
Protein complexes studied by NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
7,
403-408.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Breeze,
B.V.Kara,
D.G.Barratt,
M.Anderson,
J.C.Smith,
R.W.Luke,
J.R.Best,
and
S.A.Cartlidge
(1996).
Structure of a specific peptide complex of the carboxy-terminal SH2 domain from the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
15,
3579-3589.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Law,
K.A.Chandran,
S.P.Sidorenko,
and
E.A.Clark
(1996).
Phospholipase C-gamma1 interacts with conserved phosphotyrosyl residues in the linker region of Syk and is a substrate for Syk.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
16,
1305-1315.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.W.Ward,
K.H.Gough,
M.Rashke,
S.S.Wan,
G.Tribbick,
and
J.Wang
(1996).
Systematic mapping of potential binding sites for Shc and Grb2 SH2 domains on insulin receptor substrate-1 and the receptors for insulin, epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
5603-5609.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Hall,
E.J.Williams,
S.E.Moore,
F.S.Walsh,
A.Prochiantz,
and
P.Doherty
(1996).
Inhibition of FGF-stimulated phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and neurite outgrowth by a cell-membrane permeable phosphopeptide.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
6,
580-587.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Rahuel,
B.Gay,
D.Erdmann,
A.Strauss,
C.Garcia-Echeverría,
P.Furet,
G.Caravatti,
H.Fretz,
J.Schoepfer,
and
M.G.Grütter
(1996).
Structural basis for specificity of Grb2-SH2 revealed by a novel ligand binding mode.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
3,
586-589.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Thornton,
W.T.Mueller,
P.McConnell,
G.Zhu,
A.R.Saltiel,
and
V.Thanabal
(1996).
Nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 Src homology 2 domain.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
11852-11864.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Claesson-Welsh
(1996).
Mechanism of action of platelet-derived growth factor.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
28,
373-385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kay,
D.R.Muhandiram,
N.A.Farrow,
Y.Aubin,
and
J.D.Forman-Kay
(1996).
Correlation between dynamics and high affinity binding in an SH2 domain interaction.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
361-368.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Anafi,
M.K.Rosen,
G.D.Gish,
L.E.Kay,
and
T.Pawson
(1996).
A potential SH3 domain-binding site in the Crk SH2 domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
21365-21374.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.van der Geer,
S.Wiley,
G.D.Gish,
V.K.Lai,
R.Stephens,
M.F.White,
D.Kaplan,
and
T.Pawson
(1996).
Identification of residues that control specific binding of the Shc phosphotyrosine-binding domain to phosphotyrosine sites.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
93,
963-968.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Williams,
and
M.Katan
(1996).
Structural views of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C: signalling the way ahead.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
1387-1394.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.T.Nolte,
M.J.Eck,
J.Schlessinger,
S.E.Shoelson,
and
S.C.Harrison
(1996).
Crystal structure of the PI 3-kinase p85 amino-terminal SH2 domain and its phosphopeptide complexes.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
3,
364-374.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Réty,
K.Fütterer,
R.A.Grucza,
C.M.Munoz,
W.A.Frazier,
and
G.Waksman
(1996).
pH-Dependent self-association of the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain of the Src homologous and collagen-like (SHC) protein.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
405-413.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Itoh,
K.Miura,
H.Miki,
and
T.Takenawa
(1996).
Beta-tubulin binds Src homology 2 domains through a region different from the tyrosine-phosphorylated protein-recognizing site.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
27931-27935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Hemmann,
C.Gerhartz,
B.Heesel,
J.Sasse,
G.Kurapkat,
J.Grötzinger,
A.Wollmer,
Z.Zhong,
J.E.Darnell,
L.Graeve,
P.C.Heinrich,
and
F.Horn
(1996).
Differential activation of acute phase response factor/Stat3 and Stat1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. II. Src homology SH2 domains define the specificity of stat factor activation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
12999-13007.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.L.Günther,
Y.Liu,
D.Sanford,
W.W.Bachovchin,
and
B.Schaffhausen
(1996).
NMR analysis of interactions of a phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase SH2 domain with phosphotyrosine peptides reveals interdependence of major binding sites.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
15570-15581.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.J.Metzler,
B.Leiting,
K.Pryor,
L.Mueller,
and
B.T.Farmer
(1996).
The three-dimensional solution structure of the SH2 domain from p55blk kinase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
6201-6211.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Eriksson,
E.Nånberg,
L.Rönnstrand,
U.Engström,
U.Hellman,
E.Rupp,
G.Carpenter,
C.H.Heldin,
and
L.Claesson-Welsh
(1995).
Demonstration of functionally different interactions between phospholipase C-gamma and the two types of platelet-derived growth factor receptors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
7773-7781.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Gronenborn,
and
G.M.Clore
(1995).
Structures of protein complexes by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,
30,
351-385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Schaffhausen
(1995).
SH2 domain structure and function.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1242,
61-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Heldin
(1995).
Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction.
|
| |
Cell,
80,
213-223.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.MacLean,
A.M.Sefler,
G.Zhu,
S.J.Decker,
A.R.Saltiel,
J.Singh,
D.McNamara,
E.M.Dobrusin,
and
T.K.Sawyer
(1995).
Differentiation of peptide molecular recognition by phospholipase C gamma-1 Src homology-2 domain and a mutant Tyr phosphatase PTP1bC215S.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
13-20.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Y.Noh,
S.H.Shin,
and
S.G.Rhee
(1995).
Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C and mitogenic signaling.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1242,
99.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Alonso,
M.Koegl,
N.Mazurenko,
and
S.A.Courtneidge
(1995).
Sequence requirements for binding of Src family tyrosine kinases to activated growth factor receptors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
9840-9848.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.B.Cohen,
R.Ren,
and
D.Baltimore
(1995).
Modular binding domains in signal transduction proteins.
|
| |
Cell,
80,
237-248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Siligardi,
and
A.F.Drake
(1995).
The importance of extended conformations and, in particular, the PII conformation for the molecular recognition of peptides.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
37,
281-292.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Larose,
G.Gish,
and
T.Pawson
(1995).
Construction of an SH2 domain-binding site with mixed specificity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
3858-3862.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.Zhou,
R.P.Meadows,
T.M.Logan,
H.S.Yoon,
W.S.Wade,
K.S.Ravichandran,
S.J.Burakoff,
and
S.W.Fesik
(1995).
Solution structure of the Shc SH2 domain complexed with a tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide from the T-cell receptor.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
7784-7788.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Lee,
and
S.G.Rhee
(1995).
Significance of PIP2 hydrolysis and regulation of phospholipase C isozymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Cell Biol,
7,
183-189.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Narula,
R.W.Yuan,
S.E.Adams,
O.M.Green,
J.Green,
T.B.Philips,
L.D.Zydowsky,
M.C.Botfield,
M.Hatada,
and
E.R.Laird
(1995).
Solution structure of the C-terminal SH2 domain of the human tyrosine kinase Syk complexed with a phosphotyrosine pentapeptide.
|
| |
Structure,
3,
1061-1073.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Songyang,
G.Gish,
G.Mbamalu,
T.Pawson,
and
L.C.Cantley
(1995).
A single point mutation switches the specificity of group III Src homology (SH) 2 domains to that of group I SH2 domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
26029-26032.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Songyang,
and
L.C.Cantley
(1995).
Recognition and specificity in protein tyrosine kinase-mediated signalling.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
20,
470-475.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yu,
and
S.L.Schreiber
(1994).
Signalling an interest.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
1,
417-420.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yoakim,
W.Hou,
Z.Songyang,
Y.Liu,
L.Cantley,
and
B.Schaffhausen
(1994).
Genetic analysis of a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase SH2 domain reveals determinants of specificity.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
14,
5929-5938.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

