 |
PDBsum entry 2oxe

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of the human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Pancreatic lipase-related protein 2. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Tissue: pancreas. Gene: pnliprp2, plrp2. Expressed in: spodoptera frugiperda. Expression_system_taxid: 7108.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.224
|
R-free:
|
0.261
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.R.Walker,T.Davis,A.Seitova,P.J.Finerty Jr.,C.Butler-Cole, I.Kozieradzki,J.Weigelt,M.Sundstrom,C.H.Arrowsmith,A.M.Edwards, A.Bochkarev,S.Dhe-Paganon,Structural Genomics Consortium (Sgc)
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Eydoux
et al.
(2008).
Structure of human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 with the lid in an open conformation.
Biochemistry,
47,
9553-9564.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Feb-07
|
Release date:
|
27-Mar-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P54317
(LIPR2_HUMAN) -
Pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
469 a.a.
435 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.26
- galactolipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-3-O-(beta-D-galactosyl)-sn-glycerol + 2 H2O = 3-beta-D- galactosyl-sn-glycerol + 2 a fatty acid + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1,2-diacyl-3-O-(beta-D-galactosyl)-sn-glycerol
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
=
|
3-beta-D- galactosyl-sn-glycerol
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 64.71% similarity
|
+
|
2
×
a fatty acid
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.3
- triacylglycerol lipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a triacylglycerol + H2O = a diacylglycerol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
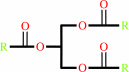 triacylglycerol
triacylglycerol
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
=
|
diacylglycerol
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 43.75% similarity
|
+
|
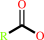 2
×
fatty acid
2
×
fatty acid
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:9553-9564
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 with the lid in an open conformation.
|
|
C.Eydoux,
S.Spinelli,
T.L.Davis,
J.R.Walker,
A.Seitova,
S.Dhe-Paganon,
A.De Caro,
C.Cambillau,
F.Carrière.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Access to the active site of pancreatic lipase (PL) is controlled by a surface
loop, the lid, which normally undergoes conformational changes only upon
addition of lipids or amphiphiles. Structures of PL with their lids in the open
and functional conformation have required cocrystallization with amphiphiles.
Here we report two crystal structures of wild-type and unglycosylated human
pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 (HPLRP2) with the lid in an open
conformation in the absence of amphiphiles. These structures solved
independently are strikingly similar, with some residues of the lid being poorly
defined in the electron-density map. The open conformation of the lid is however
different from that previously observed in classical liganded PL, suggesting
different kinetic properties for HPLRP2. Here we show that the HPLRP2 is
directly inhibited by E600, does not present interfacial activation, and acts
preferentially on substrates forming monomers or small aggregates (micelles)
dispersed in solution like monoglycerides, phospholipids and galactolipids,
whereas classical PL displays reverse properties and a high specificity for
unsoluble substrates like triglycerides and diglycerides forming oil-in-water
interfaces. These biochemical properties imply that the lid of HPLRP2 is likely
to spontaneously adopt in solution the open conformation observed in the crystal
structure. This open conformation generates a large cavity capable of
accommodating the digalactose polar head of galactolipids, similar to that
previously observed in the active site of the guinea pig PLRP2, but absent from
the classical PL. Most of the structural and kinetic properties of HPLRP2 were
found to be different from those of rat PLRP2, the structure of which was
previously obtained with the lid in a closed conformation. Our findings
illustrate the essential role of the lid in determining the substrate
specificity and the mechanism of action of lipases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Labar,
C.Bauvois,
F.Borel,
J.L.Ferrer,
J.Wouters,
and
D.M.Lambert
(2010).
Crystal structure of the human monoacylglycerol lipase, a key actor in endocannabinoid signaling.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
218-227.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Brownlee,
D.J.Forster,
M.D.Wilcox,
P.W.Dettmar,
C.J.Seal,
and
J.P.Pearson
(2010).
Physiological parameters governing the action of pancreatic lipase.
|
| |
Nutr Res Rev,
23,
146-154.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

