 |
PDBsum entry 2nu8

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, D, E:
E.C.6.2.1.5
- succinate--CoA ligase (ADP-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
succinate + ATP + CoA = succinyl-CoA + ADP + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
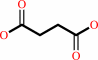 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 40.00% similarity
|
=
|
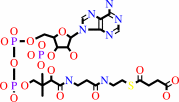 succinyl-CoA
succinyl-CoA
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
63:876-884
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Participation of Cys123alpha of Escherichia coli succinyl-CoA synthetase in catalysis.
|
|
E.Hidber,
E.R.Brownie,
K.Hayakawa,
M.E.Fraser.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Succinyl-CoA synthetase has a highly conserved cysteine residue, Cys123alpha in
the Escherichia coli enzyme, that is located near the CoA-binding site and the
active-site histidine residue. To test whether the succinyl moiety of
succinyl-CoA is transferred to the thiol of Cys123alpha as part of the catalytic
mechanism, this residue was mutated to alanine, serine, threonine and valine.
Each mutant protein was catalytically active, although less active than the wild
type. This proved that the specific formation of a thioester bond with
Cys123alpha is not part of the catalytic mechanism. To understand why the
mutations affected catalysis, the crystal structures of the four mutant proteins
were determined. The alanine mutant showed no structural changes yet had reduced
activity, suggesting that the size of the cysteine is important for optimal
activity. These results explain why this cysteine residue is conserved in the
sequences of succinyl-CoA synthetases from different sources.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4 Stereoview showing part of the C123  V
mutant, including the phosphohistidine loop. For comparison, the
model of the C123 V
mutant, including the phosphohistidine loop. For comparison, the
model of the C123  T
mutant protein from the tetragonal crystal form is superposed.
Shading is according to atom type, as in Fig. 1-, but the C
atoms for the C123 T
mutant protein from the tetragonal crystal form is superposed.
Shading is according to atom type, as in Fig. 1-, but the C
atoms for the C123  T
mutant are cyan. Dotted lines show hydrogen-bonding interactions
present in the C123 T
mutant are cyan. Dotted lines show hydrogen-bonding interactions
present in the C123  T
mutant but not in the C123 T
mutant but not in the C123  V
mutant. V
mutant.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5 Stereoviews of the structures near residue 123 of the
 -subunit
showing the effects of disorder of the phosphohistidine loop.
The structures are shown as ball-and-stick drawings shaded
according to atom type as in Fig. 1-. Dashed lines show
hydrogen-bonding interactions. (a) -subunit
showing the effects of disorder of the phosphohistidine loop.
The structures are shown as ball-and-stick drawings shaded
according to atom type as in Fig. 1-. Dashed lines show
hydrogen-bonding interactions. (a)  -Subunit
of T. thermophilus SCS (PDB code 1oi7 ). (b) Wild-type E. coli
SCS (Fraser et al., 2002[Fraser, M. E., Joyce, M. A., Ryan, D.
G. & Wolodko, W. T. (2002). Biochemistry, 41, 537-546.]). (c)
C123 -Subunit
of T. thermophilus SCS (PDB code 1oi7 ). (b) Wild-type E. coli
SCS (Fraser et al., 2002[Fraser, M. E., Joyce, M. A., Ryan, D.
G. & Wolodko, W. T. (2002). Biochemistry, 41, 537-546.]). (c)
C123  V
mutant protein. V
mutant protein.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2007,
63,
876-884)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

