 |
PDBsum entry 2h3e

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of wild-type e. Coli aspartate transcarbamoylase in the presence of n-phosphonacetyl-l-isoasparagine at 2.3a resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase catalytic chain. Chain: a, c. Synonym: aspartate transcarbamylase, atcase. Engineered: yes. Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory chain. Chain: b, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: pyrb. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: pyri.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dodecamer (from PDB file)
Dodecamer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.206
|
R-free:
|
0.250
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Eldo,J.P.Cardia,E.M.O'Day,J.Xia,H.Tsuruta,E.R.Kantrowitz
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Eldo
et al.
(2006).
N-phosphonacetyl-L-isoasparagine a potent and specific inhibitor of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
J Med Chem,
49,
5932-5938.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-May-06
|
Release date:
|
17-Oct-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
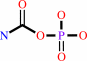 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
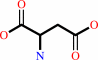 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
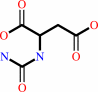 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
49:5932-5938
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
N-phosphonacetyl-L-isoasparagine a potent and specific inhibitor of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
|
J.Eldo,
J.P.Cardia,
E.M.O'Day,
J.Xia,
H.Tsuruta,
E.R.Kantrowitz.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The synthesis of a new inhibitor, N-phosphonacetyl-L-isoasparagine (PALI), of
Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) is reported, as well as
structural studies of the enzyme.PALI complex. PALI was synthesized in 7 steps
from beta-benzyl L-aspartate. The KD of PALI was 2 microM. Kinetics and
small-angle X-ray scattering experiments showed that PALI can induce the
cooperative transition of ATCase from the T to the R state. The X-ray structure
of the enzyme.PALI complex showed 22 hydrogen-bonding interactions between the
enzyme and PALI. The kinetic characterization and crystal structure of the
ATCase.PALI complex also provides detailed information regarding the importance
of the alpha-carboxylate for the binding of the substrate aspartate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Cardia,
J.Eldo,
J.Xia,
E.M.O'Day,
H.Tsuruta,
K.R.Gryncel,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2008).
Use of L-asparagine and N-phosphonacetyl-L-asparagine to investigate the linkage of catalysis and homotropic cooperativity in E. coli aspartate transcarbomoylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
1088-1096.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Eldo,
S.Heng,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Design, synthesis, and bioactivity of novel inhibitors of E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
17,
2086-2090.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

