 |
PDBsum entry 2ffq

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
GTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 93.94% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
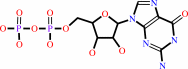 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
62:725-733
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of human neuronal Rab6B in the active and inactive form.
|
|
I.Garcia-Saez,
S.Tcherniuk,
F.Kozielski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Rab small G-protein family plays important roles in eukaryotes as regulators
of vesicle traffic. In Rab proteins, the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP is coupled
with association with and dissociation from membranes. Conformational changes
related to their different nucleotide states determine their effector
specificity. The crystal structure of human neuronal Rab6B was solved in its
'inactive' (with bound MgGDP) and 'active' (MgGTPgammaS-bound) forms to 2.3 and
1.8 A, respectively. Both crystallized in space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with
similar unit-cell parameters, allowing the comparison of both structures without
packing artifacts. Conformational changes between the inactive GDP and active
GTP-like state are observed mainly in the switch I and switch II regions,
confirming their role as a molecular switch. Compared with other Rab proteins,
additional changes are observed in the Rab6 subfamily-specific RabSF3 region
that might contribute to the specificity of Rab6 for its different effector
proteins.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 (a) Assignment of secondary-structural elements of
Rab6B-GTP  S
(grey) and Rab6B-GDP (blue). The areas of high flexibility
(higher B factor) found in the Rab6B-GDP structure are
highlighted in red (a star indicates the area of disorder around
switch I and a circle indicates the area of disorder around
switch II) and green (inside SF3 region). (b) Structural
alignment of Rab6B-GTP S
(grey) and Rab6B-GDP (blue). The areas of high flexibility
(higher B factor) found in the Rab6B-GDP structure are
highlighted in red (a star indicates the area of disorder around
switch I and a circle indicates the area of disorder around
switch II) and green (inside SF3 region). (b) Structural
alignment of Rab6B-GTP  S
and Rab6B-GDP following the same colour code. S
and Rab6B-GDP following the same colour code.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5 Surface representation of Rab6B-GDP (a, c) and
Rab6B-GTP  S
(b, d). The surface corresponding to the switch I and switch II
regions is coloured in red. The neighbouring modified areas are
depicted in green and include helix S
(b, d). The surface corresponding to the switch I and switch II
regions is coloured in red. The neighbouring modified areas are
depicted in green and include helix  3,
the N-terminal area of 3,
the N-terminal area of  5,
which forms the SF3 consensus domain, 5,
which forms the SF3 consensus domain,  1 ( 1 (
 2 in
Rab6B-GDP) and guanine nucleotide-binding G2. (c) and (d) are
views of (a) and (b) from below, respectively. The locations of
the three residues that differ with respect to Rab6A' are
highlighted in yellow; an asterisk indicates that the residue is
buried. 2 in
Rab6B-GDP) and guanine nucleotide-binding G2. (c) and (d) are
views of (a) and (b) from below, respectively. The locations of
the three residues that differ with respect to Rab6A' are
highlighted in yellow; an asterisk indicates that the residue is
buried.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2006,
62,
725-733)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
O.Vielemeyer,
C.Nizak,
A.J.Jimenez,
A.Echard,
B.Goud,
J.Camonis,
J.C.Rain,
and
F.Perez
(2010).
Characterization of single chain antibody targets through yeast two hybrid.
|
| |
BMC Biotechnol,
10,
59.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Tan,
C.Vonrhein,
O.S.Smart,
G.Bricogne,
M.Bollati,
Y.Kusov,
G.Hansen,
J.R.Mesters,
C.L.Schmidt,
and
R.Hilgenfeld
(2009).
The SARS-Unique Domain (SUD) of SARS Coronavirus Contains Two Macrodomains That Bind G-Quadruplexes.
|
| |
PLoS Pathog,
5,
e1000428.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

