 |
PDBsum entry 2bce

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Cholesterol esterase from bos taurus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cholesterol esterase. Chain: a. Synonym: bile salt activated lipase, bile salt stimulated lipase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Cattle. Organism_taxid: 9913. Organ: pancreas. Expressed in: homo sapiens. Expression_system_taxid: 9606. Expression_system_cell_line: human embryonic kidney cells (hek)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.211
|
R-free:
|
0.250
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.C.-H.Chen,L.J.W.Miercke,J.Krucinski,J.R.Starr,G.Saenz,X.Wang, C.A.Spilburg,L.G.Lange,J.L.Ellsworth,R.M.Stroud
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.C.Chen
et al.
(1998).
Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 A: novel structural features involved in lipase activation.
Biochemistry,
37,
5107-5117.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Jan-98
|
Release date:
|
02-Feb-99
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P30122
(CEL_BOVIN) -
Bile salt-activated lipase (Fragment) from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
597 a.a.
532 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 9 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.13
- sterol esterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a sterol ester + H2O = a sterol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
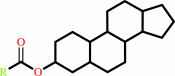 sterol ester
sterol ester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
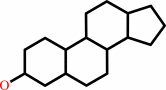 sterol
sterol
|
+
|
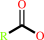 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.3
- triacylglycerol lipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a triacylglycerol + H2O = a diacylglycerol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
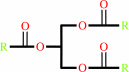 triacylglycerol
triacylglycerol
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
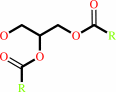 diacylglycerol
diacylglycerol
|
+
|
 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.6
- acetylesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acetyl ester + H2O = an aliphatic alcohol + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
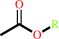 acetyl ester
acetyl ester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 aliphatic alcohol
aliphatic alcohol
|
+
|
 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
37:5107-5117
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 A: novel structural features involved in lipase activation.
|
|
J.C.Chen,
L.J.Miercke,
J.Krucinski,
J.R.Starr,
G.Saenz,
X.Wang,
C.A.Spilburg,
L.G.Lange,
J.L.Ellsworth,
R.M.Stroud.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of pancreatic cholesterol esterase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes a
wide variety of dietary lipids, mediates the absorption of cholesterol esters,
and is dependent on bile salts for optimal activity, is determined to 1.6 A
resolution. A full-length construct, mutated to eliminate two N-linked
glycosylation sites (N187Q/N361Q), was expressed in HEK 293 cells. Enzymatic
activity assays show that the purified, recombinant, mutant enzyme has activity
identical to that of the native, glycosylated enzyme purified from bovine
pancreas. The mutant enzyme is monomeric and exhibits improved homogeneity which
aided in the growth of well-diffracting crystals. Crystals of the mutant enzyme
grew in space group C2, with the following cell dimensions: a = 100.42 A, b =
54.25 A, c = 106.34 A, and beta = 104.12 degrees, with a monomer in the
asymmetric unit. The high-resolution crystal structure of bovine pancreatic
cholesterol esterase (Rcryst = 21.1%; Rfree = 25.0% to 1.6 A resolution) shows
an alpha-beta hydrolase fold with an unusual active site environment around the
catalytic triad. The hydrophobic C terminus of the protein is lodged in the
active site, diverting the oxyanion hole away from the productive binding site
and the catalytic Ser194. The amphipathic, helical lid found in other
triglyceride lipases is truncated in the structure of cholesterol esterase and
therefore is not a salient feature of activation of this lipase. These two
structural features, along with the bile salt-dependent activity of the enzyme,
implicate a new mode of lipase activation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Lin,
S.J.Yeh,
I.R.Chen,
and
G.Lin
(2011).
Stereoselective inhibition of cholesterol esterase by enantiomers of exo- and endo-2-norbornyl-N-n-butylcarbamates.
|
| |
Protein J,
30,
220-227.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.G.Williams,
and
S.C.Lovell
(2009).
The effect of sequence evolution on protein structural divergence.
|
| |
Mol Biol Evol,
26,
1055-1065.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Maeda,
T.Mizuno,
M.Bunya,
S.Sugihara,
D.Nakayama,
S.Tsunasawa,
Y.Hirota,
and
A.Sugihara
(2008).
Characterization of novel cholesterol esterase from Trichoderma sp. AS59 with high ability to synthesize steryl esters.
|
| |
J Biosci Bioeng,
105,
341-349.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Arya,
M.Datta,
and
B.D.Malhotra
(2008).
Recent advances in cholesterol biosensor.
|
| |
Biosens Bioelectron,
23,
1083-1100.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Chiou,
M.C.Lin,
M.T.Hwang,
H.G.Chang,
and
G.Lin
(2008).
Benzene-di-N-substituted carbamates as conformationally constrained substrate analogs of cholesterol esterase.
|
| |
Protein J,
27,
276-282.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
S.Y.Chiou,
B.C.Hwu,
and
C.W.Hsieh
(2006).
Probing structure-function relationships of serine hydrolases and proteases with carbamate and thiocarbamate inhibitors.
|
| |
Protein J,
25,
33-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Cheruku,
Z.Xu,
R.Dutia,
P.Lobel,
and
J.Storch
(2006).
Mechanism of cholesterol transfer from the Niemann-Pick type C2 protein to model membranes supports a role in lysosomal cholesterol transport.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
31594-31604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
W.C.Liao,
and
Z.H.Ku
(2005).
Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the pre-steady state of Pseudomonas species lipase inhibitions by p-nirophenyl-N-substituted carbamates.
|
| |
Protein J,
24,
201-207.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.P.McGlacken,
and
I.J.Fairlamb
(2005).
2-Pyrone natural products and mimetics: isolation, characterisation and biological activity.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
22,
369-385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.D.Hayward,
R.J.Cain,
E.J.McGhie,
N.Phillips,
M.J.Garner,
and
V.Koronakis
(2005).
Cholesterol binding by the bacterial type III translocon is essential for virulence effector delivery into mammalian cells.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
56,
590-603.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Chiou,
C.Y.Lai,
L.Y.Lin,
and
G.Lin
(2005).
Probing stereoselective inhibition of the acyl binding site of cholesterol esterase with four diastereomers of 2'-N-alpha-methylbenzylcarbamyl-1, 1'-bi-2-naphthol.
|
| |
BMC Biochem,
6,
17.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Aubert-Jousset,
V.Sbarra,
and
D.Lombardo
(2004).
Site-directed mutagenesis of the distal basic cluster of pancreatic bile salt-dependent lipase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
39697-39704.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.F.Mugford,
S.M.Lait,
B.A.Keay,
and
R.J.Kazlauskas
(2004).
Enantiocomplementary enzymatic resolution of the chiral auxiliary: cis,cis-6-(2,2-dimethylpropanamido)spiro[4.4]nonan-1-ol and the molecular basis for the high enantioselectivity of subtilisin Carlsberg.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
5,
980-987.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Friedland,
H.L.Liou,
P.Lobel,
and
A.M.Stock
(2003).
Structure of a cholesterol-binding protein deficient in Niemann-Pick type C2 disease.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
2512-2517.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Balaji,
S.Aruna,
and
N.Srinivasan
(2003).
Tolerance to the substitution of buried apolar residues by charged residues in the homologous protein structures.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
783-791.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Sugihara,
Y.Shimada,
A.Nomura,
T.Terai,
M.Imayasu,
Y.Nagai,
T.Nagao,
Y.Watanabe,
and
Y.Tominaga
(2002).
Purification and characterization of a novel cholesterol esterase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with its application to cleaning lipid-stained contact lenses.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
66,
2347-2355.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Reva,
A.Finkelstein,
and
S.Topiol
(2002).
Threading with chemostructural restrictions method for predicting fold and functionally significant residues: application to dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP-IV).
|
| |
Proteins,
47,
180-193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bencharit,
C.L.Morton,
E.L.Howard-Williams,
M.K.Danks,
P.M.Potter,
and
M.R.Redinbo
(2002).
Structural insights into CPT-11 activation by mammalian carboxylesterases.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
337-342.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lindquist,
L.Bläckberg,
and
O.Hernell
(2002).
Human bile salt-stimulated lipase has a high frequency of size variation due to a hypervariable region in exon 11.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
759-767.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Lu,
S.Lin,
C.C.Chang,
and
T.Y.Chang
(2002).
Mutant acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1 devoid of cysteine residues remains catalytically active.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
711-718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
W.C.Liao,
and
S.Y.Chiou
(2000).
Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the pre-steady-state inhibition of cholesterol esterase by 4-nitrophenyl-N-substituted carbamates.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
8,
2601-2607.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Kingston,
H.M.Baker,
K.M.Loomes,
L.Bläckberg,
O.Hernell,
and
E.N.Baker
(2000).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of native and recombinant human bile-salt dependent lipase: strategies for improvement of diffraction quality.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
478-480.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Terzyan,
C.S.Wang,
D.Downs,
B.Hunter,
and
X.C.Zhang
(2000).
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human bile salt activated lipase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
1783-1790.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
C.T.Shieh,
Y.C.Tsai,
C.I.Hwang,
C.P.Lu,
and
G.H.Chen
(1999).
Structure-reactivity probes for active site shapes of cholesterol esterase by carbamate inhibitors.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1431,
500-511.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Loomes,
H.E.Senior,
P.M.West,
and
A.M.Roberton
(1999).
Functional protective role for mucin glycosylated repetitive domains.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
266,
105-111.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nardini,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1999).
Alpha/beta hydrolase fold enzymes: the family keeps growing.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
9,
732-737.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Heikinheimo,
A.Goldman,
C.Jeffries,
and
D.L.Ollis
(1999).
Of barn owls and bankers: a lush variety of alpha/beta hydrolases.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
R141-R146.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Tsujita,
M.Sumiyoshi,
and
H.Okuda
(1999).
Wax ester-synthesizing activity of lipases.
|
| |
Lipids,
34,
1159-1166.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

