 |
PDBsum entry 2b7s

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2b7s
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
R381k mutant of flavocytochrome c3
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fumarate reductase flavoprotein subunit. Chain: a. Synonym: flavocytochrome c3, flavocytochromE C, fcc3. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Shewanella frigidimarina. Organism_taxid: 56812. Gene: fcc. Expressed in: shewanella frigidimarina. Expression_system_taxid: 56812.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.12Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.147
|
R-free:
|
0.197
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.L.Pankhurst,C.G.Mowat,E.L.Rothery,C.S.Miles,M.D.Walkinshaw, G.A.Reid,S.K.Chapman
|
Key ref:

|
 |
K.L.Pankhurst
et al.
(2006).
A proton delivery pathway in the soluble fumarate reductase from Shewanella frigidimarina.
J Biol Chem,
281,
20589-20597.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Oct-05
|
Release date:
|
23-May-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0C278
(FCCA_SHEFR) -
Fumarate reductase (cytochrome) from Shewanella frigidimarina
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
571 a.a.
568 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.3.2.4
- fumarate reductase (cytochrome).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 Fe(III)-[cytochrome c] + succinate = fumarate + 2 Fe(II)-[cytochrome c] + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2
×
Fe(III)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
succinate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
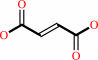 fumarate
fumarate
|
+
|
2
×
Fe(II)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:20589-20597
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A proton delivery pathway in the soluble fumarate reductase from Shewanella frigidimarina.
|
|
K.L.Pankhurst,
C.G.Mowat,
E.L.Rothery,
J.M.Hudson,
A.K.Jones,
C.S.Miles,
M.D.Walkinshaw,
F.A.Armstrong,
G.A.Reid,
S.K.Chapman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The mechanism for fumarate reduction by the soluble fumarate reductase from
Shewanella frigidimarina involves hydride transfer from FAD and proton transfer
from the active-site acid, Arg-402. It has been proposed that Arg-402 forms part
of a proton transfer pathway that also involves Glu-378 and Arg-381 but,
unusually, does not involve any bound water molecules. To gain further insight
into the importance of this proton pathway we have perturbed it by substituting
Arg-381 by lysine and methionine and Glu-378 by aspartate. Although all the
mutant enzymes retain measurable activities, there are orders-of-magnitude
decreases in their k(cat) values compared with the wild-type enzyme. Solvent
kinetic isotope effects show that proton transfer is rate-limiting in the
wild-type and mutant enzymes. Proton inventories indicate that the proton
pathway involves multiple exchangeable groups. Fast scan protein-film
voltammetric studies on wild-type and R381K enzymes show that the proton
transfer pathway delivers one proton per catalytic cycle and is not required for
transporting the other proton, which transfers as a hydride from the reduced,
protonated FAD. The crystal structures of E378D and R381M mutant enzymes have
been determined to 1.7 and 2.1 A resolution, respectively. They allow an
examination of the structural changes that disturb proton transport. Taken
together, the results indicate that Arg-381, Glu-378, and Arg-402 form a proton
pathway that is completely conserved throughout the fumarate reductase/succinate
dehydrogenase family of enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
FIGURE 6. Stereoview overlay of the wild-type
(gray/atom-type colors), E378D (green), and R381K (purple)
flavocytochromes c[3]. This figure was generated using BOBSCRIPT
(39) and RASTER 3D (40).
|
 |
Figure 7.
FIGURE 7. The reaction mechanism for fumarate reduction by
flavocytochrome c[3] showing the pathways taken by each of the
two protons required to complete the catalytic cycle. This is an
abbreviated version of the mechanism previously reported (12).
One proton is transferred directly (from solvent or at least by
a pathway not involving Arg-381, Glu-378, or Arg-402) to the FAD
in a reaction coupled to its two-electron reduction. The
substrate is twisted out of plane and polarized by interactions
with positively charged residues. This facilitates hydride
transfer from flavin N5 to the fumarate C2. Arg-402 acts as the
active site acid donating a proton to fumarate C3. Arg-402 is
reprotonated via the proton pathway involving Glu-378 and
Arg-381.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
20589-20597)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
T.M.Tomasiak,
E.Maklashina,
G.Cecchini,
and
T.M.Iverson
(2008).
A threonine on the active site loop controls transition state formation in Escherichia coli respiratory complex II.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
15460-15468.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

