 |
PDBsum entry 2arm

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the complex of phospholipase a2 with a natural compound atropine at 1.2 a resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phospholipase a2 vrv-pl-viiia. Chain: a. Synonym: phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase, dpla2. Ec: 3.1.1.4
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Daboia russellii pulchella. Organism_taxid: 97228
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.23Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.189
|
R-free:
|
0.204
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
N.Singh,A.Pal,T.Jabeen,S.Sharma,M.Perbandt,C.Betzel,T.P.Singh
|
Key ref:

|
 |
N.Singh
et al.
(2006).
Crystal structures of the complexes of a group IIA phospholipase A2 with two natural anti-inflammatory agents, anisic acid, and atropine reveal a similar mode of binding.
Proteins,
64,
89-100.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Aug-05
|
Release date:
|
20-Sep-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P59071
(PA2B8_DABRR) -
Basic phospholipase A2 VRV-PL-VIIIa from Daboia russelii
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
121 a.a.
121 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
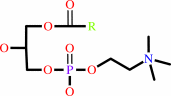 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
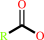 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
64:89-100
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of the complexes of a group IIA phospholipase A2 with two natural anti-inflammatory agents, anisic acid, and atropine reveal a similar mode of binding.
|
|
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
A.Pal,
S.Sharma,
M.Perbandt,
C.Betzel,
T.P.Singh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Secretory low molecular weight phospholipase A(2)s (PLA(2)s) are believed to be
involved in the release of arachidonic acid, a precursor for the biosynthesis of
pro-inflammatory eicosanoids. Therefore, the specific inhibitors of these
enzymes may act as potent anti-inflammatory agents. Similarly, the compounds
with known anti-inflammatory properties should act as specific inhibitors. Two
plant compounds, (a) anisic acid (4-methoxy benzoic acid) and (b) atropine
(8-methyl-8-azabicyclo oct-3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate), have been used in
various inflammatory disorders. Both compounds (a) and (b) have been found to
inhibit PLA(2) activity having binding constants of 4.5 x 10(-5) M and 2.1 x
10(-8) M, respectively. A group IIA PLA(2) was isolated and purified from the
venom of Daboia russelli pulchella (DRP) and its complexes were made with anisic
acid and atropine. The crystal structures of the two complexes (i) and (ii) of
PLA(2) with compounds (a) and (b) have been determined at 1.3 and 1.2 A
resolutions, respectively. The high-quality observed electron densities for the
two compounds allowed the accurate determinations of their atomic positions. The
structures revealed that these compounds bound to the enzyme at the substrate -
binding cleft and their positions were stabilized by networks of hydrogen bonds
and hydrophobic interactions. The most characteristic interactions involving Asp
49 and His 48 were clearly observed in both complexes, although the residues
that formed hydrophobic interactions with these compounds were not identical
because their positions did not exactly superimpose in the large
substrate-binding hydrophobic channel. Owing to a relatively small size, the
structure of anisic acid did not alter upon binding to PLA(2), while that of
atropine changed significantly when compared with its native crystal structure.
The conformation of the protein also did not show notable changes upon the
bindings of these ligands. The mode of binding of anisic acid to the present
group II PLA(2) is almost identical to its binding with bovine pancreatic PLA(2)
of group I. On the other hand, the binding of atropine to PLA(2) is similar to
that of another plant alkaloid aristolochic acid.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. The superimposition of atropine (yellow) from the
present structure on its structure in the uncomplexed states
(blue).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2006,
64,
89-100)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Gardiner,
Z.Andreeva,
D.Barton,
A.Ritchie,
R.Overall,
and
J.Marc
(2008).
The phospholipase A inhibitor, aristolochic acid, disrupts cortical microtubule arrays and root growth in Arabidopsis.
|
| |
Plant Biol (Stuttg),
10,
725-731.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Dos Santos,
F.H.Fagundes,
B.R.Teixeira,
M.H.Toyama,
and
R.Aparicio
(2008).
Purification and Preliminary Crystallographic Analysis of a New Lys49-PLA2 from B. Jararacussu.
|
| |
Int J Mol Sci,
9,
736-750.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

