 |
PDBsum entry 1yjs

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
K226q mutant of serine hydroxymethyltransferase from b. Stearothermophilus, complex with glycine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Chain: a. Fragment: serine methylase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Organism_taxid: 1422. Gene: shmt. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.203
|
R-free:
|
0.227
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Bhavani,V.Trivedi,V.R.Jala,H.S.Subramanya,P.Kaul,K.Purnima, V.Prakash,R.N.Appaji,H.S.Savithri
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Bhavani
et al.
(2005).
Role of Lys-226 in the catalytic mechanism of Bacillus stearothermophilus serine hydroxymethyltransferase--crystal structure and kinetic studies.
Biochemistry,
44,
6929-6937.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Jan-05
|
Release date:
|
31-May-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q7SIB6
(Q7SIB6_GEOSE) -
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
419 a.a.
405 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.2.1
- glycine hydroxymethyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + glycine + H2O = (6S)- 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + L-serine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
glycine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
(6S)- 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
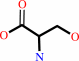 L-serine
L-serine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
44:6929-6937
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Role of Lys-226 in the catalytic mechanism of Bacillus stearothermophilus serine hydroxymethyltransferase--crystal structure and kinetic studies.
|
|
S.Bhavani,
V.Trivedi,
V.R.Jala,
H.S.Subramanya,
P.Kaul,
V.Prakash,
N.Appaji Rao,
H.S.Savithri.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT), a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)-dependent
enzyme catalyzes the reversible conversion of l-Ser and
tetrahydropteroylglutamate (H(4)PteGlu) to Gly and 5,10-methylene
tetrahydropteroylglutamate (CH(2)-H(4)PteGlu). Biochemical and structural
studies on this enzyme have implicated several residues in the catalytic
mechanism, one of them being the active site lysine, which anchors PLP. It has
been proposed that this residue is crucial for product expulsion. However, in
other PLP-dependent enzymes, the corresponding residue has been implicated in
the proton abstraction step of catalysis. In the present investigation, Lys-226
of Bacillus stearothermophilus SHMT (bsSHMT) was mutated to Met and Gln to
evaluate the role of this residue in catalysis. The mutant enzymes contained 1
mol of PLP per mol of subunit suggesting that Schiff base formation with lysine
is not essential for PLP binding. The 3D structure of the mutant enzymes
revealed that PLP was bound at the active site in an orientation different from
that of the wild-type enzyme. In the presence of substrate, the PLP ring was in
an orientation superimposable with that of the external aldimine complex of
wild-type enzyme. However, the mutant enzymes were inactive, and the kinetic
analysis of the different steps of catalysis revealed that there was a drastic
reduction in the rate of formation of the quinonoid intermediate. Analysis of
these results along with the crystal structures suggested that K-226 is
responsible for flipping of PLP from one orientation to another which is crucial
for H(4)PteGlu-dependent Calpha-Cbeta bond cleavage of l-Ser.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.K.Pang,
J.H.Hunter,
R.Gujjar,
R.Podutoori,
J.Bowman,
D.G.Mudeppa,
and
P.K.Rathod
(2009).
Catalytic and ligand-binding characteristics of Plasmodium falciparum serine hydroxymethyltransferase.
|
| |
Mol Biochem Parasitol,
168,
74-83.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sopitthummakhun,
S.Maenpuen,
Y.Yuthavong,
U.Leartsakulpanich,
and
P.Chaiyen
(2009).
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase from Plasmodium vivax is different in substrate specificity from its homologues.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
4023-4036.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Mukherjee,
S.A.Sievers,
M.T.Brown,
and
P.J.Johnson
(2006).
Identification and biochemical characterization of serine hydroxymethyl transferase in the hydrogenosome of Trichomonas vaginalis.
|
| |
Eukaryot Cell,
5,
2072-2078.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

