
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of lysine 5,6-aminomutase in complex with plp, cobalamin, and 5'-deoxyadenosine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
D-lysine 5,6-aminomutase alpha subunit. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. D-lysine 5,6-aminomutase beta subunit. Chain: b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Clostridium sticklandii. Organism_taxid: 1511. Gene: kamde. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.199
|
R-free:
|
0.262
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.Berkovitch,E.Behshad,K.H.Tang,E.A.Enns,P.A.Frey,C.L.Drennan
|
Key ref:

|
 |
F.Berkovitch
et al.
(2004).
A locking mechanism preventing radical damage in the absence of substrate, as revealed by the x-ray structure of lysine 5,6-aminomutase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
15870-15875.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Oct-04
|
Release date:
|
09-Nov-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.5.4.3.3
- lysine 5,6-aminomutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
(3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoate = (3S,5S)-3,5-diaminohexanoate
|
|
2.
|
D-lysine = (2R,5S)-2,5-diaminohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
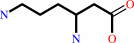 (3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoate
(3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoate
|
=
|
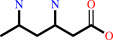 (3S,5S)-3,5-diaminohexanoate
(3S,5S)-3,5-diaminohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
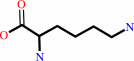 D-lysine
D-lysine
|
=
|
(2R,5S)-2,5-diaminohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Cob(II)alamin; Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cob(II)alamin
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
B12)
matches with 85.71% similarity
|
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
101:15870-15875
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A locking mechanism preventing radical damage in the absence of substrate, as revealed by the x-ray structure of lysine 5,6-aminomutase.
|
|
F.Berkovitch,
E.Behshad,
K.H.Tang,
E.A.Enns,
P.A.Frey,
C.L.Drennan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Lysine 5,6-aminomutase is an adenosylcobalamin and
pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme that catalyzes a 1,2 rearrangement of
the terminal amino group of dl-lysine and of l-beta-lysine. We have solved the
x-ray structure of a substrate-free form of lysine-5,6-aminomutase from
Clostridium sticklandii. In this structure, a Rossmann domain covalently binds
pyridoxal-5'-phosphate by means of lysine 144 and positions it into the putative
active site of a neighboring triosephosphate isomerase barrel domain, while
simultaneously positioning the other cofactor, adenosylcobalamin, approximately
25 A from the active site. In this mode of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate binding, the
cofactor acts as an anchor, tethering the separate polypeptide chain of the
Rossmann domain to the triosephosphate isomerase barrel domain. Upon substrate
binding and transaldimination of the lysine-144 linkage, the Rossmann domain
would be free to rotate and bring adenosylcobalamin, pyridoxal-5'-phosphate, and
substrate into proximity. Thus, the structure embodies a locking mechanism to
keep the adenosylcobalamin out of the active site and prevent radical generation
in the absence of substrate.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Aminomutases in the bacterial lysine fermentation
pathway. (A) 5,6-LAM and 2,3-LAM catalyze similar reactions and
act on similar substrates. Both enzymes require PLP, but 5,6-LAM
is AdoCbl-dependent, whereas 2,3-LAM is an AdoMet-dependent
iron-sulfur enzyme. The natural substrates of 5,6-LAM include
DL-lysine and  -L-lysine. 2,3-LAM acts
on L-lysine and does not accept D-lysine as a substrate. (B)
Proposed mechanism of 5,6-LAM, modified from ref. 38. The boxed
step represents the state of the enzyme observed in this study.
The unboxed steps are proposed to occur while 5,6-LAM is in the
hypothetical top-on conformation (see the Introduction). -L-lysine. 2,3-LAM acts
on L-lysine and does not accept D-lysine as a substrate. (B)
Proposed mechanism of 5,6-LAM, modified from ref. 38. The boxed
step represents the state of the enzyme observed in this study.
The unboxed steps are proposed to occur while 5,6-LAM is in the
hypothetical top-on conformation (see the Introduction).
|
 |
Figure 5.
Fig. 5. Edge-on vs. top-on enzyme conformations. (A)
Structure of the substrate-free form of 5,6-LAM with the
Rossmann domain in an edge-on conformation above the TIM barrel.
Protein domains and cofactors are colored as in Fig. 2 A. Arrows
represent the axes of the TIM barrel and Rossmann domains. (B)
Structure of substrate-bound MCM (Protein Data Bank ID code 1REQ
[PDB]
) with the Rossmann domain sitting directly on top of the TIM
barrel (top-on). The substrate fragment, desulfo-coenzyme A
(dark blue), threads through the TIM barrel domain, effecting
the closure of the TIM barrel to the more compact structure
shown. The Ado moiety of AdoCbl was not observed. We propose
that the substrate-bound 5,6-LAM adopts a subunit arrangement
like that of substrate-bound MCM, with the Rossmann domain and
AdoCbl docked directly onto the center of the TIM barrel (see
Results).
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Arockiasamy,
A.Aggarwal,
C.G.Savva,
A.Holzenburg,
and
J.C.Sacchettini
(2011).
Crystal structure of calcium dodecin (Rv0379), from Mycobacterium tuberculosis with a unique calcium-binding site.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
20,
827-833.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Lewis,
P.S.Coelho,
and
F.H.Arnold
(2011).
Enzymatic functionalization of carbon-hydrogen bonds.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
40,
2003-2021.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.N.Marsh,
D.P.Patterson,
and
L.Li
(2010).
Adenosyl radical: reagent and catalyst in enzyme reactions.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
604-621.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Tang,
S.O.Mansoorabadi,
G.H.Reed,
and
P.A.Frey
(2009).
Radical triplets and suicide inhibition in reactions of 4-thia-D- and 4-thia-L-lysine with lysine 5,6-aminomutase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
8151-8160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Thorgersen,
and
D.M.Downs
(2009).
Oxidative stress and disruption of labile iron generate specific auxotrophic requirements in Salmonella enterica.
|
| |
Microbiology,
155,
295-304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Percudani,
and
A.Peracchi
(2009).
The B6 database: a tool for the description and classification of vitamin B6-dependent enzymatic activities and of the corresponding protein families.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
10,
273.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Chatterjee,
Y.Li,
Y.Zhang,
T.L.Grove,
M.Lee,
C.Krebs,
S.J.Booker,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Reconstitution of ThiC in thiamine pyrimidine biosynthesis expands the radical SAM superfamily.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
4,
758-765.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Toraya,
N.Tamura,
T.Watanabe,
M.Yamanishi,
N.Hieda,
and
K.Mori
(2008).
Mechanism-based inactivation of coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase by 3-unsaturated 1,2-diols and thioglycerol.
|
| |
J Biochem,
144,
437-446.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Ruzicka,
and
P.A.Frey
(2007).
Glutamate 2,3-aminomutase: a new member of the radical SAM superfamily of enzymes.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1774,
286-296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Fukuoka,
Y.Nakanishi,
R.B.Hannak,
B.Kräutler,
and
T.Toraya
(2005).
Homoadenosylcobalamins as probes for exploring the active sites of coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase and ethanolamine ammonia-lyase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
4787-4796.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

