 |
PDBsum entry 1xen

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.88
- peptide deformylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide] + H2O = N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide] + formate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-terminal N-formyl-L-methionyl-[peptide]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
N-terminal L-methionyl- [peptide]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
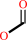 formate
formate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
127:4558-4559
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of E. coli peptide deformylase bound to formate: insight into the preference for Fe2+ over Zn2+ as the active site metal.
|
|
R.Jain,
B.Hao,
R.P.Liu,
M.K.Chan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
E. coli peptide deformylase (PDF) catalyzes the deformylation of nascent
polypeptides generated during protein synthesis. While PDF was originally
thought to be a zinc enzyme, subsequent studies revealed that the active site
metal is iron. In an attempt to understand this unusual metal preference,
high-resolution structures of Fe-, Co-, and Zn-PDF were determined in complex
with its deformylation product, formate. In all three structures, the formate
ion binds the metal and forms hydrogen-bonding interactions with the backbone
nitrogen of Leu91, the amide side chain of Gln50, and the carboxylate side chain
of Glu133. One key difference, however, is how the formate binds the metal. In
Fe-PDF and Co-PDF, formate binds in a bidentate fashion, while in Zn-PDF, it
binds in a monodentate fashion. Importantly, these structural results provide
the first clues into the origins of PDF's metal-dependent activity differences.
On the basis of these structures, we propose that the basis for the higher
activity of Fe-PDF stems from the better ability of iron to bind and activate
the tetrahedral transition state required for cleavage of the N-terminal formyl
group.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Martin,
and
J.A.Imlay
(2011).
The alternative aerobic ribonucleotide reductase of Escherichia coli, NrdEF, is a manganese-dependent enzyme that enables cell replication during periods of iron starvation.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
80,
319-334.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hernick,
S.G.Gattis,
J.E.Penner-Hahn,
and
C.A.Fierke
(2010).
Activation of Escherichia coli UDP-3-O-[(R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl]-N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase by Fe2+ yields a more efficient enzyme with altered ligand affinity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
2246-2255.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Song,
H.Tan,
K.Takemoto,
and
T.Akutsu
(2008).
HSEpred: predict half-sphere exposure from protein sequences.
|
| |
Bioinformatics,
24,
1489-1497.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.T.Nguyen,
J.C.Wu,
J.A.Boylan,
F.C.Gherardini,
and
D.Pei
(2007).
Zinc is the metal cofactor of Borrelia burgdorferi peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
468,
217-225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Namuswe,
and
D.P.Goldberg
(2006).
A combinatorial approach to minimal peptide models of a metalloprotein active site.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
2326-2328.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.V.Karambelkar,
C.Xiao,
Y.Zhang,
A.A.Sarjeant,
and
D.P.Goldberg
(2006).
Geometric preferences in iron(II) and zinc(II) model complexes of peptide deformylase.
|
| |
Inorg Chem,
45,
1409-1411.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fieulaine,
C.Juillan-Binard,
A.Serero,
F.Dardel,
C.Giglione,
T.Meinnel,
and
J.L.Ferrer
(2005).
The crystal structure of mitochondrial (Type 1A) peptide deformylase provides clear guidelines for the design of inhibitors specific for the bacterial forms.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
42315-42324.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

