 |
PDBsum entry 1vq2

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.4.12
- dCMP deaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dCMP + H2O + H+ = dUMP + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
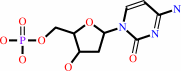 dCMP
dCMP
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
dUMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
43:13715-13723
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Three-dimensional structure of the R115E mutant of T4-bacteriophage 2'-deoxycytidylate deaminase.
|
|
R.Almog,
F.Maley,
G.F.Maley,
R.Maccoll,
P.Van Roey.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
2'-Deoxycytidylate deaminase (dCD) converts deoxycytidine 5'-monophosphate
(dCMP) to deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate and is a major supplier of the substrate
for thymidylate synthase, an important enzyme in DNA synthesis and a major
target for cancer chemotherapy. Wild-type dCD is allosterically regulated by the
end products of its metabolic pathway, deoxycytidine 5'-triphosphate and
deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate, which act as an activator and an inhibitor,
respectively. The first crystal structure of a dCD, in the form of the R115E
mutant of the T4-bacteriophage enzyme complexed with the active site inhibitor
pyrimidin-2-one deoxyribotide, has been determined at 2.2 A resolution. This
mutant of dCD is active, even in the absence of the allosteric regulators. The
molecular topology of dCD is related to that of cytidine deaminase (CDA) but
with modifications for formation of the binding site for the phosphate group of
dCMP. The enzyme has a zinc ion-based mechanism that is similar to that of CDA.
A second zinc ion that is present in bacteriophage dCD, but absent in mammalian
dCD and CDA, is important for the structural integrity of the enzyme and for the
binding of the phosphate group of the substrate or inhibitor. Although the R115E
mutant of dCD is a dimer in solution, it crystallizes as a hexamer, mimicking
the natural state of the wild-type enzyme. Residues 112 and 115, which are known
to be important for the binding of the allosteric regulators, are found in a
pocket that is at the intersubunit interfaces in the hexamer but distant from
the substrate-binding site. The substrate-binding site is composed of residues
from a single protein molecule and is sequestered in a deep groove. This groove
is located at the outer surface of the hexamer but ends at the subunit interface
that also includes residue 115. It is proposed that the absence of subunit
interactions at this interface in the dimeric R115E mutant renders the
substrate-binding site accessible. In contrast, for the wild-type enzyme,
binding of dCTP induces an allosteric effect that affects the subunit
interactions and results in an increase in the accessibility of the binding site.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
M.Morar,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Structural biology of the purine biosynthetic pathway.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
65,
3699-3724.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Johansson,
M.Thymark,
J.H.Bynck,
M.Fanø,
S.Larsen,
and
M.Willemoës
(2007).
Regulation of dCTP deaminase from Escherichia coli by nonallosteric dTTP binding to an inactive form of the enzyme.
|
| |
FEBS J,
274,
4188-4198.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
F.Maley,
G.F.Maley,
G.Duncan,
D.D.Dunigan,
and
J.L.Van Etten
(2007).
Chloroviruses encode a bifunctional dCMP-dCTP deaminase that produces two key intermediates in dTTP formation.
|
| |
J Virol,
81,
7662-7671.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wang,
R.Shinkura,
M.Muramatsu,
H.Nagaoka,
K.Kinoshita,
and
T.Honjo
(2006).
Identification of a specific domain required for dimerization of activation-induced cytidine deaminase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
19115-19123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Chen,
Y.C.Chang,
C.H.Lin,
C.H.Lin,
and
S.H.Liaw
(2006).
Crystal structure of a bifunctional deaminase and reductase from Bacillus subtilis involved in riboflavin biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
7605-7613.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

