 |
PDBsum entry 1vbs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/ isomerase substrate
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1vbs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
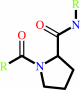 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
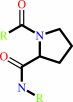 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Febs Lett
432:202-206
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mapping the stereospecificity of peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerases.
|
|
C.Schiene,
U.Reimer,
M.Schutkowski,
G.Fischer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The stereospecificity of peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerases (PPIases) was
studied using tetrapeptide substrate analogs in which one amino acid residue was
replaced by the cognate D-amino acid in various positions of the peptide chain.
Reversed stereocenters around proline markedly increased the rate of the
spontaneous trans to cis isomerization of the prolyl bond whereas cis to trans
isomerizations were less sensitive. PPIases like human cyclophilin18, human
FKBP12, Escherichia coli parvulin10 and the PPIase domain of E. coli trigger
factor exhibited stereoselectivity demanding at the P1 to P2' position of the
substrate chain. The discriminating factor for stereoselectivity was the lack of
formation of the Michaelis complexes of the diastereomeric substrates. However,
D-alanine at the P1 position preserved considerable affinity to the active site,
and largely prevented activation of the catalytic machinery for all PPIases
investigated.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Time course of fluorescence at 416 nm after jumping
from the peptide stock solution in TFE/LiCl into the final
buffer solution using 20 μM Abz-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-NH-Np at 10°C.
A, uncatalyzed (k=7.9×10^3 s^−1); B, 1 nM rhCyp18cy
(k=15.3×10^3 s^−1). Measurements were done in 35 mM
HEPES pH 7.8, λ[ex]=320 nm.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from the Federation of European Biochemical Societies:
Febs Lett
(1998,
432,
202-206)
copyright 1998.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Fischer,
and
S.Wawra
(2006).
Polypeptide binding proteins: what remains to be discovered?
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
61,
1388-1396.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jordens,
V.Janssens,
S.Longin,
I.Stevens,
E.Martens,
G.Bultynck,
Y.Engelborghs,
E.Lescrinier,
E.Waelkens,
J.Goris,
and
C.Van Hoof
(2006).
The protein phosphatase 2A phosphatase activator is a novel peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans-isomerase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
6349-6357.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Schiene-Fischer,
J.Habazettl,
F.X.Schmid,
and
G.Fischer
(2002).
The hsp70 chaperone DnaK is a secondary amide peptide bond cis-trans isomerase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
419-424.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kiessig,
J.Reissmann,
C.Rascher,
G.Küllertz,
A.Fischer,
and
F.Thunecke
(2001).
Application of a green fluorescent fusion protein to study protein-protein interactions by electrophoretic methods.
|
| |
Electrophoresis,
22,
1428-1435.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

