 |
PDBsum entry 1v9t

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/isomerase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1v9t
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
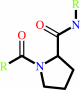 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
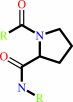 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Eur J Biochem
271:3794-3803
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Escherichia coli cyclophilin B binds a highly distorted form of trans-prolyl peptide isomer.
|
|
M.Konno,
Y.Sano,
K.Okudaira,
Y.Kawaguchi,
Y.Yamagishi-Ohmori,
S.Fushinobu,
H.Matsuzawa.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cyclophilins facilitate the peptidyl-prolyl isomerization of a trans-isomer to a
cis-isomer in the refolding process of unfolded proteins to recover the natural
folding state with cis-proline conformation. To date, only short peptides with a
cis-form proline have been observed in complexes of human and Escherichia coli
proteins of cyclophilin A, which is present in cytoplasm. The crystal structures
analyzed in this study show two complexes in which peptides having a trans-form
proline, i.e. succinyl-Ala-trans-Pro-Ala-p-nitroanilide and
acetyl-Ala-Ala-trans-Pro-Ala-amidomethylcoumarin, are bound on a K163T mutant of
Escherichia coli cyclophilin B, the preprotein of which has a signal sequence.
Comparison with cis-form peptides bound to cyclophilin A reveals that in any
case the proline ring is inserted into the hydrophobic pocket and a hydrogen
bond between CO of Pro and Neta2 of Arg is formed to fix the peptide. On the
other hand, in the cis-isomer, the formation of two hydrogen bonds of NH and CO
of Ala preceding Pro with the protein fixes the peptide, whereas in the
trans-isomer formation of a hydrogen bond between CO preceding Ala-Pro and His47
Nepsilon2 via a mediating water molecule allows the large distortion in the
orientation of Ala of Ala-Pro. Although loss of double bond character of the
amide bond of Ala-Pro is essential to the isomerization pathway occurring by
rotating around its bond, these peptides have forms impossible to undergo proton
transfer from the guanidyl group of Arg to the prolyl N atom, which induces loss
of double bond character.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. The ribbon model of the  -barrel
structure of E. coli CyPB consisting of the upper and the lower -barrel
structure of E. coli CyPB consisting of the upper and the lower
 -sheets
enclosed by two helices. The colors of ribbon are shown
corresponding to those of Fig. 1. The loop colored in green is
the region expected to affect the selection of the substrate.
Thr163 is located outside of -sheets
enclosed by two helices. The colors of ribbon are shown
corresponding to those of Fig. 1. The loop colored in green is
the region expected to affect the selection of the substrate.
Thr163 is located outside of  8 strand. The
Suc-Ala-trans-Pro-Ala-pNA is also shown by ball-and-sticks
model. Figures 2,3,4,5,6 and 7 were prepared using the programs
MOLSCRIPT[35] and RASTER3D[36]. 8 strand. The
Suc-Ala-trans-Pro-Ala-pNA is also shown by ball-and-sticks
model. Figures 2,3,4,5,6 and 7 were prepared using the programs
MOLSCRIPT[35] and RASTER3D[36].
|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. A stereo view of Suc-Ala-trans-Pro-Ala-pNA (green)
and Ac-Ala-Ala-trans-Pro-Ala-AMC (yellow) bound to superimposed
E. coli CyPB molecules. The hydrogen bonds are shown in broken
lines. The CyPB molecules shown in Figs 4, 6 and 7 were rotated
by 45° around the horizontal axis from those shown in Figs 2
and 3.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the Federation of European Biochemical Societies:
Eur J Biochem
(2004,
271,
3794-3803)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
The tripeptide Suc-Ala-Pro-Ala-pNA and the tetrapeptide Ac-Ala-Ala-Pro-Ala-AMC have the distorted trans-form, allowing them to bury deeply into the cleft of CyPB molecules. The Ala-Pro-Ala segments of the tripeptide and tetrapeptide occupy the exactly same positions. The phi and psi angles of the Ala residue of Ala-Pro are rarely observed for residues of linear short peptides containing no glycine.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.K.Jin,
S.S.Krishna,
R.Schwarzenbacher,
D.McMullan,
P.Abdubek,
S.Agarwalla,
E.Ambing,
H.Axelrod,
J.M.Canaves,
H.J.Chiu,
A.M.Deacon,
M.DiDonato,
M.A.Elsliger,
J.Feuerhelm,
A.Godzik,
C.Grittini,
S.K.Grzechnik,
J.Hale,
E.Hampton,
J.Haugen,
M.Hornsby,
L.Jaroszewski,
H.E.Klock,
M.W.Knuth,
E.Koesema,
A.Kreusch,
P.Kuhn,
S.A.Lesley,
M.D.Miller,
K.Moy,
E.Nigoghossian,
L.Okach,
S.Oommachen,
J.Paulsen,
K.Quijano,
R.Reyes,
C.Rife,
R.C.Stevens,
G.Spraggon,
H.van den Bedem,
J.Velasquez,
A.White,
G.Wolf,
G.W.Han,
Q.Xu,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2006).
Crystal structure of TM1367 from Thermotoga maritima at 1.90 A resolution reveals an atypical member of the cyclophilin (peptidylprolyl isomerase) fold.
|
| |
Proteins,
63,
1112-1118.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Mogensen,
and
D.E.Otzen
(2005).
Interactions between folding factors and bacterial outer membrane proteins.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
57,
326-346.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

