 |
PDBsum entry 1v47

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.7.4
- sulfate adenylyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
sulfate + ATP + H+ = adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
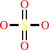 sulfate
sulfate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
43:4111-4118
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of a novel zinc-binding ATP sulfurylase from Thermus thermophilus HB8.
|
|
Y.Taguchi,
M.Sugishima,
K.Fukuyama.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
ATP sulfurylase (ATPS) is a ubiquitous enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the
adenylyl group from ATP to inorganic sulfate, producing adenosine
5'-phosphosulfate (APS) and pyrophosphate. The crystal structure of ATPS from
Thermus thermophilus HB8 (TtATPS, 347 amino acid residues) in complex with APS
was determined at 2.5 A resolution. TtATPS is composed of three domains [domain
I (residues 1-134), domain II (residues 135-290), and domain III (residues
291-347)], like the Riftia pachyptila symbiont ATPS, but lacks a fourth domain
present in ATPSs from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and from the fungus
Penicillium chrysogenum. TtATPS forms a dimer in the crystal, and the manner of
subunit association is different from that observed in dimeric R. pachyptila
symbiont ATPS and in the hexameric S. cerevisiae and P. chrysogenum ATPSs. APS
is located in the active site of TtATPS, which contains several motifs (QXRN,
HXXH, and GRD) conserved in ATPSs. Unexpectedly, TtATPS binds one metal ion per
subunit in domain III. XAFS measurement of the crystal and the Bijvoet
difference Fourier map unambiguously characterized the metal ion as a zinc ion.
The zinc ion is tetrahedrally coordinated by Cys294, Cys297, Cys306, and His310,
and could not be removed from the protein by treatment with EDTA. The zinc ion
binding site is far from the active site. Because all four residues coordinated
to the zinc ion are conserved in the ATPSs from thermophilic bacteria such as
Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Pyrococcus abyssi, and Sulfolobus solfataricus, zinc ion
chelation may contribute to the thermal stability of these ATPSs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
O.Y.Gavel,
A.V.Kladova,
S.A.Bursakov,
J.M.Dias,
S.Texeira,
V.L.Shnyrov,
J.J.Moura,
I.Moura,
M.J.Romão,
and
J.Trincão
(2008).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of adenosine triphosphate sulfurylase (ATPS) from the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ATCC 27774.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
593-595.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Mougous,
D.H.Lee,
S.C.Hubbard,
M.W.Schelle,
D.J.Vocadlo,
J.M.Berger,
and
C.R.Bertozzi
(2006).
Molecular basis for G protein control of the prokaryotic ATP sulfurylase.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
21,
109-122.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

