 |
PDBsum entry 1v2g

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.2
- arylesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a phenyl acetate + H2O = a phenol + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
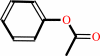 phenyl acetate
phenyl acetate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
phenol
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.00% similarity
|
+
|
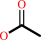 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.5
- lysophospholipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = sn-glycerol 3-phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
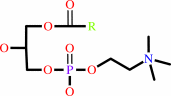 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
sn-glycerol 3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
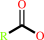 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.2.14
- oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(9Z)-octadecenoyl-[ACP] + H2O = (9Z)-octadecenoate + holo-[ACP] + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
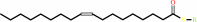 Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]
Oleoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
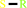 [acyl-carrier-protein]
[acyl-carrier-protein]
|
+
|
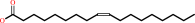 oleate
oleate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.2.2
- palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hexadecanoyl-CoA + H2O = hexadecanoate + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
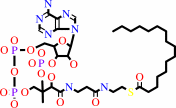 hexadecanoyl-CoA
hexadecanoyl-CoA
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 hexadecanoate
hexadecanoate
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
44:1971-1979
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate specificities of Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/lysophospholipase L1 are governed by its switch loop movement.
|
|
Y.C.Lo,
S.C.Lin,
J.F.Shaw,
Y.C.Liaw.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Escherichia coli thioesterase I/protease I/lysophospholipase L(1) (TAP) is a
multifunctional lysophospholipase and acyl-CoA thioesterase with a
SGNH-hydrolase fold. The relationship between TAP's structure and its versatile
substrate specificity, however, is unclear. Here, we present the crystal
structure of TAP in complex with octanoic acid (TAP-OCA; OCA, a free fatty acid
with eight carbon atoms, C(8)). A structural comparison of native TAP with
TAP-OCA reveals a remarkable conformational change in loop(75)(-)(80), called
"switch loop movement", upon OCA binding to the substrate-binding crevice of
TAP. OCA binding to the substrate-binding crevice results in a continuous
hydrophobic surface, which triggers switch loop movement. The switch loop
movement is acyl chain length dependent, with an effect of stabilizing the
Michaelis complex (MC) of TAP during catalysis, and is essential for TAP's
substrate preference. The finding of a sulfate ion binding site in the TAP
structures, together with previous enzyme kinetic analyses, leads us to
postulate that a putative CoA binding site is essential for efficient catalysis
of thioesters in TAP. We also present the crystal structure of L109P-OCA (TAP's
L109P mutant in complex with OCA), in which Leu109 mutated to Pro109 abolishes
switch loop movement. This result strengthens our hypothesis that the switch
loop movement is induced by hydrophobic interactions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Cantu,
Y.Chen,
and
P.J.Reilly
(2010).
Thioesterases: a new perspective based on their primary and tertiary structures.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
19,
1281-1295.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Leščić Ašler,
N.Ivić,
F.Kovačić,
S.Schell,
J.Knorr,
U.Krauss,
S.Wilhelm,
B.Kojić-Prodić,
and
K.E.Jaeger
(2010).
Probing enzyme promiscuity of SGNH hydrolases.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
2158-2167.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Brzuszkiewicz,
E.Nowak,
Z.Dauter,
M.Dauter,
H.Cieśliński,
A.Długołecka,
and
J.Kur
(2009).
Structure of EstA esterase from psychrotrophic Pseudoalteromonas sp. 643A covalently inhibited by monoethylphosphonate.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
862-865.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

