 |
PDBsum entry 1v1s

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.45
- 2-dehydro-3-deoxygluconokinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate + ATP = 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D- gluconate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-gluconate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
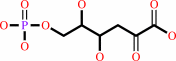 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D- gluconate
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D- gluconate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
340:477-489
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of Thermus thermophilus 2-Keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase: evidence for recognition of an open chain substrate.
|
|
N.Ohshima,
E.Inagaki,
K.Yasuike,
K.Takio,
T.H.Tahirov.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
2-Keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase (KDGK) catalyzes the phosphorylation of
2-keto-3-deoxygluconate (KDG) to 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDGP). The
genome sequence of Thermus thermophilus HB8 contains an open reading frame that
has a 30% identity to Escherichia coli KDGK. The KDGK activity of T.thermophilus
protein (TtKDGK) has been confirmed, and its crystal structure has been
determined by the molecular replacement method and refined with two crystal
forms to 2.3 angstroms and 3.2 angstroms, respectively. The enzyme is a hexamer
organized as a trimer of dimers. Each subunit is composed of two domains, a
larger alpha/beta domain and a smaller beta-sheet domain, similar to that of
ribokinase and adenosine kinase, members of the PfkB family of carbohydrate
kinases. Furthermore, the TtKDGK structure with its KDG and ATP analogue was
determined and refined at 2.1 angstroms. The bound KDG was observed
predominantly as an open chain structure. The positioning of ligands and the
conservation of important catalytic residues suggest that the reaction mechanism
is likely to be similar to that of other members of the PfkB family, including
ribokinase. In particular, the Asp251 is postulated to have a role in
transferring the gamma-phosphate of ATP to the 5'-hydroxyl group of KDG.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. The overall view of (a) TtKDGK and (b) EcRK
dimers. The view is parallel to the pseudo 2-fold axis in (a)
and crystallographic 2-fold axis in (b). Subunits are
represented by ribbons and are colored green and cyan. The bound
ligands are drawn by balls and sticks. The figure was prepared
using Molscript[30.] and Raster3D. [30.]
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. The KDG binding. (a) 2F[o] -F[c] Fourier maps of
bound KDG in the A subunit of TtKDGK. The open chain keto form
of KDG and side-chain of Arg167 colored by atom colors: carbon
atoms in yellow, nitrogen atoms in cyan and oxygen atoms in red.
The modeled a-furanose form of KDG is in cyan. (b) and (c) The
hydrogen bonds between the KDG and (b) A and (c) B subunits of
TtKDGK. (a) Was prepared using TURBO-FRODO and the (b) and (c)
were prepared using Molscript[30.] and Raster3D. [31.]
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2004,
340,
477-489)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Trinh,
A.Asipu,
D.T.Bonthron,
and
S.E.Phillips
(2009).
Structures of alternatively spliced isoforms of human ketohexokinase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
201-211.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Guixé,
and
F.Merino
(2009).
The ADP-dependent sugar kinase family: kinetic and evolutionary aspects.
|
| |
IUBMB Life,
61,
753-761.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Merino,
and
V.Guixé
(2008).
Specificity evolution of the ADP-dependent sugar kinase family: in silico studies of the glucokinase/phosphofructokinase bifunctional enzyme from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
4033-4044.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.I.Mathews,
D.McMullan,
M.D.Miller,
J.M.Canaves,
M.A.Elsliger,
R.Floyd,
S.K.Grzechnik,
L.Jaroszewski,
H.E.Klock,
E.Koesema,
J.S.Kovarik,
A.Kreusch,
P.Kuhn,
T.M.McPhillips,
A.T.Morse,
K.Quijano,
C.L.Rife,
R.Schwarzenbacher,
G.Spraggon,
R.C.Stevens,
H.van den Bedem,
D.Weekes,
G.Wolf,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
A.M.Deacon,
A.Godzik,
S.A.Lesley,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2008).
Crystal structure of 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase (TM0067) from Thermotoga maritima at 2.05 A resolution.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
603-608.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Potter,
M.Kerou,
H.J.Lamble,
S.D.Bull,
D.W.Hough,
M.J.Danson,
and
G.L.Taylor
(2008).
The structure of Sulfolobus solfataricus 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
1283-1287.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Miallau,
W.N.Hunter,
S.M.McSweeney,
and
G.A.Leonard
(2007).
Structures of Staphylococcus aureus D-tagatose-6-phosphate kinase implicate domain motions in specificity and mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
19948-19957.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Reddy,
S.K.Palaninathan,
N.D.Shetty,
J.L.Owen,
M.D.Watson,
and
J.C.Sacchettini
(2007).
High resolution crystal structures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis adenosine kinase: insights into the mechanism and specificity of this novel prokaryotic enzyme.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
27334-27342.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
L.Arnfors,
R.Ladenstein,
and
P.Schönheit
(2007).
The phosphofructokinase-B (MJ0406) from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii represents a nucleoside kinase with a broad substrate specificity.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
11,
105-114.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
M.H.El Kouni,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2007).
Substrate analogs induce an intermediate conformational change in Toxoplasma gondii adenosine kinase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
126-134.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Arnfors,
T.Hansen,
P.Schönheit,
R.Ladenstein,
and
W.Meining
(2006).
Structure of Methanocaldococcus jannaschii nucleoside kinase: an archaeal member of the ribokinase family.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
1085-1097.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
M.H.El Kouni,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2006).
Structure of Toxoplasma gondii adenosine kinase in complex with an ATP analog at 1.1 angstroms resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
140-145.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Arnfors,
T.Hansen,
W.Meining,
P.Schönheit,
and
R.Ladenstein
(2005).
Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of a nucleoside kinase from the hyperthermophile Methanocaldococcus jannaschii.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
591-594.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Wang,
M.C.Long,
S.Ranganathan,
V.Escuyer,
W.B.Parker,
and
R.Li
(2005).
Overexpression, purification and crystallographic analysis of a unique adenosine kinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
553-557.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

