 |
PDBsum entry 1ugc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
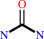 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
35:16429-16434
(1996)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
X-ray crystallographic studies of alanine-65 variants of carbonic anhydrase II reveal the structural basis of compromised proton transfer in catalysis.
|
|
L.R.Scolnick,
D.W.Christianson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The three-dimensional structures of A65F, A65L, A65H, A65T, A65S, and A65G human
carbonic anhydrase II (CAII) variants have been solved by X-ray crystallographic
methods to probe the importance of residue 65 and the structural implications of
its evolutionary drift in the greater family of carbonic anhydrase isozymes.
Structure-activity relationships in this series of CAII variants are correlated
with those established for other carbonic anhydrase isozymes. We conclude that a
bulky side chain at position 65 hinders the formation of an effective solvent
bridge between zinc-bound water and H64 and thereby hinders solvent-mediated
proton transfer between these two groups [Jackman, J. E., Merz, K. M., Jr.,
& Fierke, C. A. (1996) Biochemistry 35, 16421-16428]. Despite the
introduction of a polar hydroxyl group at this position, smaller side chains
such as serine or threonine substituted for A65 do not perturb the formation of
a solvent bridge between H64 and zinc-bound solvent. Thus, the evolution of
residue 65 size is one factor affecting the trajectory of catalytic proton
transfer.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Krishnamurthy,
G.K.Kaufman,
A.R.Urbach,
I.Gitlin,
K.L.Gudiksen,
D.B.Weibel,
and
G.M.Whitesides
(2008).
Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
108,
946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Shimahara,
T.Yoshida,
Y.Shibata,
M.Shimizu,
Y.Kyogoku,
F.Sakiyama,
T.Nakazawa,
S.Tate,
S.Y.Ohki,
T.Kato,
H.Moriyama,
K.Kishida,
Y.Tano,
T.Ohkubo,
and
Y.Kobayashi
(2007).
Tautomerism of histidine 64 associated with proton transfer in catalysis of carbonic anhydrase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
9646-9656.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Marino,
K.Hayakawa,
K.Hatada,
M.Benfatto,
A.Rizzello,
M.Maffia,
and
L.Bubacco
(2007).
Structural features that govern enzymatic activity in carbonic anhydrase from a low-temperature adapted fish, Chionodraco hamatus.
|
| |
Biophys J,
93,
2781-2790.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Yan,
L.Zhang,
R.I.Cukier,
and
Y.Bu
(2007).
Exploration on regulating factors for proton transfer along hydrogen-bonded water chains.
|
| |
Chemphyschem,
8,
944-954.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Okrasa,
and
R.J.Kazlauskas
(2006).
Manganese-substituted carbonic anhydrase as a new peroxidase.
|
| |
Chemistry,
12,
1587-1596.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Huang,
B.Sjöblom,
A.E.Sauer-Eriksson,
and
B.H.Jonsson
(2002).
Organization of an efficient carbonic anhydrase: implications for the mechanism based on structure-function studies of a T199P/C206S mutant.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
7628-7635.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.P.Ryder,
A.K.Oyelere,
J.L.Padilla,
D.Klostermeier,
D.P.Millar,
and
S.A.Strobel
(2001).
Investigation of adenosine base ionization in the hairpin ribozyme by nucleotide analog interference mapping.
|
| |
RNA,
7,
1454-1463.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Elleby,
B.Sjöblom,
and
S.Lindskog
(1999).
Changing the efficiency and specificity of the esterase activity of human carbonic anhydrase II by site-specific mutagenesis.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
262,
516-521.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Christianson,
and
J.D.Cox
(1999).
Catalysis by metal-activated hydroxide in zinc and manganese metalloenzymes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
68,
33-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Tu,
M.Qian,
J.N.Earnhardt,
P.J.Laipis,
and
D.N.Silverman
(1998).
Properties of intramolecular proton transfer in carbonic anhydrase III.
|
| |
Biophys J,
74,
3182-3189.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Earnhardt,
M.Qian,
C.Tu,
P.J.Laipis,
and
D.N.Silverman
(1998).
Intramolecular proton transfer from multiple sites in catalysis by murine carbonic anhydrase V.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
7649-7655.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Jackman,
K.M.Merz,
and
C.A.Fierke
(1996).
Disruption of the active site solvent network in carbonic anhydrase II decreases the efficiency of proton transfer.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
16421-16428.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

