 |
PDBsum entry 1trh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase(carboxylic esterase)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1trh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.3
- triacylglycerol lipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a triacylglycerol + H2O = a diacylglycerol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
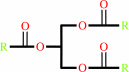 triacylglycerol
triacylglycerol
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
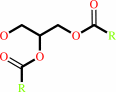 diacylglycerol
diacylglycerol
|
+
|
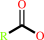 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
3:82-91
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Two conformational states of Candida rugosa lipase.
|
|
P.Grochulski,
Y.Li,
J.D.Schrag,
M.Cygler.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of Candida rugosa lipase in a new crystal form has been determined
and refined at 2.1 A resolution. The lipase molecule was found in an inactive
conformation, with the active site shielded from the solvent by a part of the
polypeptide chain-the flap. Comparison of this structure with the previously
determined "open" form of this lipase, in which the active site is accessible to
the solvent and presumably the substrate, shows that the transition between
these 2 states requires only movement of the flap. The backbone NH groups
forming the putative oxyanion hole do not change position during this
rearrangement, indicating that this feature is preformed in the inactive state.
The 2 lipase conformations probably correspond to states at opposite ends of the
pathway of interfacial activation. Quantitative analysis indicates a large
increase of the hydrophobic surface in the vicinity of the active site. The flap
undergoes a flexible rearrangement during which some of its secondary structure
refolds. The interactions of the flap with the rest of the protein change from
mostly hydrophobic in the inactive form to largely hydrophilic in the "open"
conformation. Although the flap movement cannot be described as a rigid body
motion, it has very definite hinge points at Glu 66 and at Pro 92. The
rearrangement is accompanied by a cis-trans isomerization of this proline, which
likely increases the energy required for the transition between the 2 states,
and may play a role in the stabilization of the active conformation at the
water/lipid interface. Carbohydrate attached at Asn 351 also provides
stabilization for the open conformation of the flap.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Bakolitsa,
A.Kumar,
D.McMullan,
S.S.Krishna,
M.D.Miller,
D.Carlton,
R.Najmanovich,
P.Abdubek,
T.Astakhova,
H.J.Chiu,
T.Clayton,
M.C.Deller,
L.Duan,
Y.Elias,
J.Feuerhelm,
J.C.Grant,
S.K.Grzechnik,
G.W.Han,
L.Jaroszewski,
K.K.Jin,
H.E.Klock,
M.W.Knuth,
P.Kozbial,
D.Marciano,
A.T.Morse,
E.Nigoghossian,
L.Okach,
S.Oommachen,
J.Paulsen,
R.Reyes,
C.L.Rife,
C.V.Trout,
H.van den Bedem,
D.Weekes,
A.White,
Q.Xu,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.M.Deacon,
A.Godzik,
S.A.Lesley,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2010).
The structure of the first representative of Pfam family PF06475 reveals a new fold with possible involvement in glycolipid metabolism.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
66,
1211-1217.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Widmann,
P.B.Juhl,
and
J.Pleiss
(2010).
Structural classification by the Lipase Engineering Database: a case study of Candida antarctica lipase A.
|
| |
BMC Genomics,
11,
123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Trodler,
R.D.Schmid,
and
J.Pleiss
(2009).
Modeling of solvent-dependent conformational transitions in Burkholderia cepacia lipase.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
38.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.G.Williams,
and
S.C.Lovell
(2009).
The effect of sequence evolution on protein structural divergence.
|
| |
Mol Biol Evol,
26,
1055-1065.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Verma,
W.Azmi,
and
S.S.Kanwar
(2008).
Microbial lipases: at the interface of aqueous and non-aqueous media. A review.
|
| |
Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung,
55,
265-294.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kasrayan,
M.Bocola,
A.G.Sandström,
G.Lavén,
and
J.E.Bäckvall
(2007).
Prediction of the Candida antarctica lipase A protein structure by comparative modeling and site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
1409-1415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.P.Fabrichny,
P.Leone,
G.Sulzenbacher,
D.Comoletti,
M.T.Miller,
P.Taylor,
Y.Bourne,
and
P.Marchot
(2007).
Structural analysis of the synaptic protein neuroligin and its beta-neurexin complex: determinants for folding and cell adhesion.
|
| |
Neuron,
56,
979-991.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Sarkar,
C.Reichman,
T.Saleh,
R.B.Birge,
and
C.G.Kalodimos
(2007).
Proline cis-trans isomerization controls autoinhibition of a signaling protein.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
25,
413-426.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.H.Andreotti
(2006).
Opening the pore hinges on proline.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
2,
13-14.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Zorn,
H.Bouws,
M.Takenberg,
M.Nimtz,
R.Getzlaff,
D.E.Breithaupt,
and
R.G.Berger
(2005).
An extracellular carboxylesterase from the basidiomycete Pleurotus sapidus hydrolyses xanthophyll esters.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
386,
435-440.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Tejo,
A.B.Salleh,
and
J.Pleiss
(2004).
Structure and dynamics of Candida rugosa lipase: the role of organic solvent.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
10,
358-366.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.C.Akoh,
G.C.Lee,
and
J.F.Shaw
(2004).
Protein engineering and applications of Candida rugosa lipase isoforms.
|
| |
Lipids,
39,
513-526.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Santiveri,
J.M.Pérez-Cañadillas,
M.K.Vadivelu,
M.D.Allen,
T.J.Rutherford,
N.A.Watkins,
and
M.Bycroft
(2004).
NMR structure of the alpha-hemoglobin stabilizing protein: insights into conformational heterogeneity and binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
34963-34970.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Secundo,
G.Carrea,
C.Tarabiono,
S.Brocca,
and
M.Lotti
(2004).
Activity and enantioselectivity of wildtype and lid mutated Candida rugosa lipase isoform 1 in organic solvents.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
86,
236-240.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Bourne,
H.C.Kolb,
Z.Radić,
K.B.Sharpless,
P.Taylor,
and
P.Marchot
(2004).
Freeze-frame inhibitor captures acetylcholinesterase in a unique conformation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
1449-1454.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Mancheño J,
M.A.Pernas M,
M.L.Rúa M,
and
J.A.Hermoso
(2003).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of two different crystal forms of the lipase 2 isoform from the yeast Candida rugosa.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
499-501.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Brocca,
F.Secundo,
M.Ossola,
L.Alberghina,
G.Carrea,
and
M.Lotti
(2003).
Sequence of the lid affects activity and specificity of Candida rugosa lipase isoenzymes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
2312-2319.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.N.Brazin,
R.J.Mallis,
D.B.Fulton,
and
A.H.Andreotti
(2002).
Regulation of the tyrosine kinase Itk by the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase cyclophilin A.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
1899-1904.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Yapoudjian,
M.G.Ivanova,
A.M.Brzozowski,
S.A.Patkar,
J.Vind,
A.Svendsen,
and
R.Verger
(2002).
Binding of Thermomyces (Humicola) lanuginosa lipase to the mixed micelles of cis-parinaric acid/NaTDC.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
1613-1621.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.González-Navarro,
M.C.Bañó,
and
C.Abad
(2001).
The closed/open model for lipase activation. Addressing intermediate active forms of fungal enzymes by trapping of conformers in water-restricted environments.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
3174-3183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.H.Kahlow,
R.D.Schmid,
and
J.Pleiss
(2001).
A model of the pressure dependence of the enantioselectivity of Candida rugosalipase towards (+/-)-menthol.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
1942-1952.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Brocca,
M.Persson,
E.Wehtje,
P.Adlercreutz,
L.Alberghina,
and
M.Lotti
(2000).
Mutants provide evidence of the importance of glycosydic chains in the activation of lipase 1 from Candida rugosa.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
985-990.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Terzyan,
C.S.Wang,
D.Downs,
B.Hunter,
and
X.C.Zhang
(2000).
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human bile salt activated lipase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
1783-1790.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Cajal,
A.Svendsen,
V.Girona,
S.A.Patkar,
and
M.A.Alsina
(2000).
Interfacial control of lid opening in Thermomyces lanuginosa lipase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
413-423.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Krooshof,
R.Floris,
A.W.Tepper,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1999).
Thermodynamic analysis of halide binding to haloalkane dehalogenase suggests the occurrence of large conformational changes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
355-360.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zuegg,
K.Gruber,
M.Gugganig,
U.G.Wagner,
and
C.Kratky
(1999).
Three-dimensional structures of enzyme-substrate complexes of the hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
1990-2000.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.E.Jaeger,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
M.T.Reetz
(1999).
Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
53,
315-351.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Gonzalez-Navarro,
and
L.Braco
(1998).
Lipase-enhanced activity in flavour ester reactions by trapping enzyme conformers in the presence of interfaces
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
59,
122-127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Chen,
L.J.Miercke,
J.Krucinski,
J.R.Starr,
G.Saenz,
X.Wang,
C.A.Spilburg,
L.G.Lange,
J.L.Ellsworth,
and
R.M.Stroud
(1998).
Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 A: novel structural features involved in lipase activation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
5107-5117.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.B.Ravelli,
M.L.Raves,
Z.Ren,
D.Bourgeois,
M.Roth,
J.Kroon,
I.Silman,
and
J.L.Sussman
(1998).
Static Laue diffraction studies on acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
54,
1359-1366.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Löwendahl,
and
S.Allenmark
(1997).
Analysis of a lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution by chiral normal-phase liquid chromatography.
|
| |
Biomed Chromatogr,
11,
289-295.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Hernáiz,
J.M.Sánchez-Montero,
and
J.V.Sinisterra
(1997).
Influence of the nature of modifier in the enzymatic activity of chemical modified semipurified lipase from Candida rugosa.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
55,
252-260.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Kynclova,
E.Elsner,
A.Köpf,
G.Hawa,
T.Schalkhammer,
and
F.Pittner
(1996).
Novel method for coupling of poly(ethyleneglycol) to carboxylic acid moieties of proteins.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
9,
644-651.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Mingarro,
H.González-Navarro,
and
L.Braco
(1996).
Trapping of different lipase conformers in water-restricted environments.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
9935-9944.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zandonella,
L.Haalck,
F.Spener,
K.Faber,
F.Paltauf,
and
A.Hermetter
(1995).
Inversion of lipase stereospecificity for fluorogenic alkyldiacyl glycerols. Effect of substrate solubilization.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
231,
50-55.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Mingarro,
C.Abad,
and
L.Braco
(1995).
Interfacial activation-based molecular bioimprinting of lipolytic enzymes.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
3308-3312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Stadler,
A.Kovac,
L.Haalck,
F.Spener,
and
F.Paltauf
(1995).
Stereoselectivity of microbial lipases. The substitution at position sn-2 of triacylglycerol analogs influences the stereoselectivity of different microbial lipases.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
227,
335-343.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Norin,
F.Haeffner,
A.Achour,
T.Norin,
and
K.Hult
(1994).
Computer modeling of substrate binding to lipases from Rhizomucor miehei, Humicola lanuginosa, and Candida rugosa.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
1493-1503.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

