 |
PDBsum entry 1tcc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase(carboxylic esterase)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1tcc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.3
- triacylglycerol lipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a triacylglycerol + H2O = a diacylglycerol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
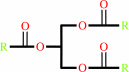 triacylglycerol
triacylglycerol
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
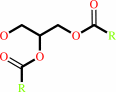 diacylglycerol
diacylglycerol
|
+
|
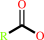 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
2:293-308
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The sequence, crystal structure determination and refinement of two crystal forms of lipase B from Candida antarctica.
|
|
J.Uppenberg,
M.T.Hansen,
S.Patkar,
T.A.Jones.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Lipases constitute a family of enzymes that hydrolyze triglycerides.
They occur in many organisms and display a wide variety of substrate
specificities. In recent years, much progress has been made towards explaining
the mechanism of these enzymes and their ability to hydrolyze their substrates
at an oil-water interface. RESULTS: We have determined the DNA and amino acid
sequences for lipase B from the yeast Candida antarctica. The primary sequence
has no significant homology to any other known lipase and deviates from the
consensus sequence around the active site serine that is found in other lipases.
We have determined the crystal structure of this enzyme using multiple
isomorphous replacement methods for two crystal forms. Models for the
orthorhombic and monoclinic crystal forms of the enzyme have been refined to
1.55 A and 2.1 A resolution, respectively. Lipase B is an alpha/beta type
protein that has many features in common with previously determined lipase
structures and other related enzymes. In the monoclinic crystal form, lipid-like
molecules, most likely beta-octyl glucoside, can be seen close to the active
site. The behaviour of these lipid molecules in the crystal structure has been
studied at different pH values. CONCLUSION: The structure of Candida antarctica
lipase B shows that the enzyme has a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad in its active
site. The structure appears to be in an 'open' conformation with a rather
restricted entrance to the active site. We believe that this accounts for the
substrate specificity and high degree of stereospecificity of this lipase.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Stereo drawing of the Cα trace of CALB. The
structure is coloured red at the amino terminus, then orange,
light green, dark green, pale blue, and finally dark blue at the
carboxyl terminus. Figure 2. Stereo drawing of the Cα trace
of CALB. The structure is coloured red at the amino terminus,
then orange, light green, dark green, pale blue, and finally
dark blue at the carboxyl terminus.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. A stereo picture of the RML-phosphonate inhibitor
complex and an alignment with CALB in this region. All residues
believed to make up the oxyanion hole have a similar
conformation in the two enzymes. Hypothetical hydrogen bonds
from the inhibitor to CALB are indicated by dashed lines. RML is
shown in black, CALB in the colour scheme used for Figure 5.
Figure 7. A stereo picture of the RML-phosphonate inhibitor
complex and an alignment with CALB in this region. All residues
believed to make up the oxyanion hole have a similar
conformation in the two enzymes. Hypothetical hydrogen bonds
from the inhibitor to CALB are indicated by dashed lines. RML is
shown in black, CALB in the colour scheme used for [3]Figure 5.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1994,
2,
293-308)
copyright 1994.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Popescu,
H.Keul,
and
M.Moeller
(2011).
Poly(meth)acrylates obtained by cascade reaction.
|
| |
Macromol Rapid Commun,
32,
559-572.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Loegering,
C.Mueller,
J.P.Voss,
C.Wagenfuehrer,
D.Zahn,
H.P.Bertelsen,
U.Scheffler,
and
R.Luttmann
(2011).
An integrated scale-down plant for optimal recombinant enzyme production by Pichia pastoris.
|
| |
Biotechnol J,
6,
428-436.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Klähn,
G.S.Lim,
A.Seduraman,
and
P.Wu
(2011).
On the different roles of anions and cations in the solvation of enzymes in ionic liquids.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
13,
1649-1662.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Liu,
P.Trodler,
S.Eiben,
K.Koschorreck,
M.Müller,
J.Pleiss,
S.C.Maurer,
C.Branneby,
R.D.Schmid,
and
B.Hauer
(2010).
Rational design of Pseudozyma antarctica lipase B yielding a general esterification catalyst.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
789-795.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Budisa,
W.Wenger,
and
B.Wiltschi
(2010).
Residue-specific global fluorination of Candida antarctica lipase B in Pichia pastoris.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
6,
1630-1639.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kobayashi
(2010).
Lipase-catalyzed polyester synthesis--a green polymer chemistry.
|
| |
Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,
86,
338-365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.García-Urdiales,
N.Ríos-Lombardía,
J.Mangas-Sánchez,
V.Gotor-Fernández,
and
V.Gotor
(2009).
Influence of the nucleophile on the Candida antarctica lipase B-catalysed resolution of a chiral acyl donor.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
1830-1838.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Skjøt,
L.De Maria,
R.Chatterjee,
A.Svendsen,
S.A.Patkar,
P.R.Ostergaard,
and
J.Brask
(2009).
Understanding the plasticity of the alpha/beta hydrolase fold: lid swapping on the Candida antarctica lipase B results in chimeras with interesting biocatalytic properties.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
520-527.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Narayanan,
and
C.P.Chou
(2009).
Alleviation of proteolytic sensitivity to enhance recombinant lipase production in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
75,
5424-5427.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Branco,
M.Graber,
V.Denis,
and
J.Pleiss
(2009).
Molecular mechanism of the hydration of Candida antarctica lipase B in the gas phase: Water adsorption isotherms and molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
2913-2919.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Xu,
L.Zhang,
X.Wang,
D.Wei,
and
T.Li
(2009).
Structure-based substrate screening for an enzyme.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
10,
257.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Qian,
J.R.Horton,
X.Cheng,
and
S.Lutz
(2009).
Structural redesign of lipase B from Candida antarctica by circular permutation and incremental truncation.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
393,
191-201.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.I.Brígida,
A.D.Pinheiro,
A.L.Ferreira,
and
L.R.Gonçalves
(2008).
Immobilization of Candida antarctica lipase B by adsorption to green coconut fiber.
|
| |
Appl Biochem Biotechnol,
146,
173-187.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Nyhlén,
B.Martín-Matute,
A.G.Sandström,
M.Bocola,
and
J.E.Bäckvall
(2008).
Influence of delta-functional groups on the enantiorecognition of secondary alcohols by Candida antarctica lipase B.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
9,
1968-1974.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Mandrich,
V.Menchise,
V.Alterio,
G.De Simone,
C.Pedone,
M.Rossi,
and
G.Manco
(2008).
Functional and structural features of the oxyanion hole in a thermophilic esterase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
1721-1731.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Trodler,
J.Nieveler,
M.Rusnak,
R.D.Schmid,
and
J.Pleiss
(2008).
Rational design of a new one-step purification strategy for Candida antarctica lipase B by ion-exchange chromatography.
|
| |
J Chromatogr A,
1179,
161-167.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Trodler,
and
J.Pleiss
(2008).
Modeling structure and flexibility of Candida antarctica lipase B in organic solvents.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
8,
9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Jung,
and
S.Park
(2008).
Improving the expression yield of Candida antarctica lipase B in Escherichia coli by mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biotechnol Lett,
30,
717-722.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kasrayan,
M.Bocola,
A.G.Sandström,
G.Lavén,
and
J.E.Bäckvall
(2007).
Prediction of the Candida antarctica lipase A protein structure by comparative modeling and site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
1409-1415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Thongekkaew,
and
C.Boonchird
(2007).
Molecular cloning and functional expression of a novel extracellular lipase from the thermotolerant yeast Candida thermophila.
|
| |
FEMS Yeast Res,
7,
232-243.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kato,
J.Fuchimoto,
T.Tanino,
A.Kondo,
H.Fukuda,
and
M.Ueda
(2007).
Preparation of a whole-cell biocatalyst of mutated Candida antarctica lipase B (mCALB) by a yeast molecular display system and its practical properties.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
75,
549-555.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Tamalampudi,
M.M.Talukder,
S.Hama,
T.Tanino,
Y.Suzuki,
A.Kondo,
and
H.Fukuda
(2007).
Development of recombinant Aspergillus oryzae whole-cell biocatalyst expressing lipase-encoding gene from Candida antarctica.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
75,
387-395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Tanino,
T.Ohno,
T.Aoki,
H.Fukuda,
and
A.Kondo
(2007).
Development of yeast cells displaying Candida antarctica lipase B and their application to ester synthesis reaction.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
75,
1319-1325.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Léonard,
L.Fransson,
S.Lamare,
K.Hult,
and
M.Graber
(2007).
A water molecule in the stereospecificity pocket of Candida antarctica lipase B enhances enantioselectivity towards pentan-2-ol.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
662-667.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Qian,
C.J.Fields,
and
S.Lutz
(2007).
Investigating the structural and functional consequences of circular permutation on lipase B from Candida antarctica.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
1989-1996.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Qian,
C.J.Fields,
Y.Yu,
and
S.Lutz
(2007).
Recent progress in engineering alpha/beta hydrolase-fold family members.
|
| |
Biotechnol J,
2,
192-200.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Liu,
R.D.Schmid,
and
M.Rusnak
(2006).
Functional expression of Candida antarctica lipase B in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm--a screening system for a frequently used biocatalyst.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
72,
1024-1032.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Schneider,
G.Neuberger,
M.Wildpaner,
S.Tian,
I.Berezovsky,
and
F.Eisenhaber
(2006).
Application of a sensitive collection heuristic for very large protein families: evolutionary relationship between adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) and classic mammalian lipases.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
7,
164.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Narita,
K.Okano,
T.Tateno,
T.Tanino,
T.Sewaki,
M.H.Sung,
H.Fukuda,
and
A.Kondo
(2006).
Display of active enzymes on the cell surface of Escherichia coli using PgsA anchor protein and their application to bioconversion.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
70,
564-572.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Siddiqui,
and
R.Cavicchioli
(2006).
Cold-adapted enzymes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
75,
403-433.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Schwartz,
and
J.King
(2006).
Frequencies of hydrophobic and hydrophilic runs and alternations in proteins of known structure.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
102-112.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.R.Berendsen,
A.Lapin,
and
M.Reuss
(2006).
Investigations of reaction kinetics for immobilized enzymes--identification of parameters in the presence of diffusion limitation.
|
| |
Biotechnol Prog,
22,
1305-1312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.O.Magnusson,
J.C.Rotticci-Mulder,
A.Santagostino,
and
K.Hult
(2005).
Creating space for large secondary alcohols by rational redesign of Candida antarctica lipase B.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
6,
1051-1056.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Böer,
H.P.Mock,
R.Bode,
G.Gellissen,
and
G.Kunze
(2005).
An extracellular lipase from the dimorphic yeast Arxula adeninivorans: molecular cloning of the ALIP1 gene and characterization of the purified recombinant enzyme.
|
| |
Yeast,
22,
523-535.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Lavandera,
S.Fernández,
J.Magdalena,
M.Ferrero,
R.J.Kazlauskas,
and
V.Gotor
(2005).
An inverse substrate orientation for the regioselective acylation of 3',5'-diaminonucleosides catalyzed by Candida antarctica lipase B?
|
| |
Chembiochem,
6,
1381-1390.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Siddiqui,
and
R.Cavicchioli
(2005).
Improved thermal stability and activity in the cold-adapted lipase B from Candida antarctica following chemical modification with oxidized polysaccharides.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
9,
471-476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Velonia,
O.Flomenbom,
D.Loos,
S.Masuo,
M.Cotlet,
Y.Engelborghs,
J.Hofkens,
A.E.Rowan,
J.Klafter,
R.J.Nolte,
and
F.C.de Schryver
(2005).
Single-enzyme kinetics of CALB-catalyzed hydrolysis.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
560-564.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Barzilai,
S.Kumar,
H.Wolfson,
and
R.Nussinov
(2004).
Potential folding-function interrelationship in proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
635-649.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Janda,
Y.Devedjiev,
D.Cooper,
M.Chruszcz,
U.Derewenda,
A.Gabrys,
W.Minor,
A.Joachimiak,
and
Z.S.Derewenda
(2004).
Harvesting the high-hanging fruit: the structure of the YdeN gene product from Bacillus subtilis at 1.8 angstroms resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1101-1107.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Lovell,
I.W.Davis,
W.B.Arendall,
P.I.de Bakker,
J.M.Word,
M.G.Prisant,
J.S.Richardson,
and
D.C.Richardson
(2003).
Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi,psi and Cbeta deviation.
|
| |
Proteins,
50,
437-450.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Ottosson,
L.Fransson,
and
K.Hult
(2002).
Substrate entropy in enzyme enantioselectivity: an experimental and molecular modeling study of a lipase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1462-1471.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Secundo,
G.Carrea,
C.Soregaroli,
D.Varinelli,
and
R.Morrone
(2001).
Activity of different Candida antarctica lipase B formulations in organic solvents.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
73,
157-163.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.González-Navarro,
M.C.Bañó,
and
C.Abad
(2001).
The closed/open model for lipase activation. Addressing intermediate active forms of fungal enzymes by trapping of conformers in water-restricted environments.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
3174-3183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Pepin,
and
R.Lortie
(2001).
Influence of water activity on the enantioselective esterification of (R,S)-ibuprofen by crosslinked crystals of Candida antarctica lipase B in organic solvent media.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
75,
559-562.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Svendsen
(2000).
Lipase protein engineering.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1543,
223-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zou,
B.M.Hallberg,
T.Bergfors,
F.Oesch,
M.Arand,
S.L.Mowbray,
and
T.A.Jones
(2000).
Structure of Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolase at 1.8 A resolution: implications for the structure and function of the mammalian microsomal class of epoxide hydrolases.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
111-122.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Kleywegt,
and
T.A.Jones
(1999).
Software for handling macromolecular envelopes.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
941-944.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Kleywegt
(1999).
Experimental assessment of differences between related protein crystal structures.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
1878-1884.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Vecchio,
F.Zambianchi,
P.Zacchetti,
F.Secundo,
and
G.Carrea
(1999).
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy study of dehydrated lipases from candida antarctica B and pseudomonas cepacia
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
64,
545-551.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.E.Jaeger,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
M.T.Reetz
(1999).
Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
53,
315-351.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Longhi,
and
C.Cambillau
(1999).
Structure-activity of cutinase, a small lipolytic enzyme.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
185-196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Haeffner,
T.Norin,
and
K.Hult
(1998).
Molecular modeling of the enantioselectivity in lipase-catalyzed transesterification reactions.
|
| |
Biophys J,
74,
1251-1262.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Horsted,
E.S.Dey,
S.Holmberg,
and
M.C.Kielland-Brandt
(1998).
A novel esterase from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis, a possible function for the yeast TIP1 gene.
|
| |
Yeast,
14,
793-803.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Patkar,
J.Vind,
E.Kelstrup,
M.W.Christensen,
A.Svendsen,
K.Borch,
and
O.Kirk
(1998).
Effect of mutations in Candida antarctica B lipase.
|
| |
Chem Phys Lipids,
93,
95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Anthonsen,
and
B.H.Hoff
(1998).
Resolution of derivatives of 1,2-propanediol with lipase B from Candida antarctica. Effect of substrate structure, medium, water activity and acyl donor on enantiomeric ratio.
|
| |
Chem Phys Lipids,
93,
199-207.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.O.Triantafyllou,
E.Wehtje,
P.Adlercreutz,
and
B.Mattiasson
(1997).
How do additives affect enzyme activity and stability in nonaqueous media?
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
54,
67-76.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.K.Kim,
H.K.Song,
D.H.Shin,
K.Y.Hwang,
and
S.W.Suh
(1997).
The crystal structure of a triacylglycerol lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia reveals a highly open conformation in the absence of a bound inhibitor.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
173-185.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Longhi,
M.Mannesse,
H.M.Verheij,
G.H.De Haas,
M.Egmond,
E.Knoops-Mouthuy,
and
C.Cambillau
(1997).
Crystal structure of cutinase covalently inhibited by a triglyceride analogue.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
6,
275-286.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Wang,
C.S.Wang,
J.Tang,
F.Dyda,
and
X.C.Zhang
(1997).
The crystal structure of bovine bile salt activated lipase: insights into the bile salt activation mechanism.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
1209-1218.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Nicolas,
M.Egmond,
C.T.Verrips,
J.de Vlieg,
S.Longhi,
C.Cambillau,
and
C.Martinez
(1996).
Contribution of cutinase serine 42 side chain to the stabilization of the oxyanion transition state.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
398-410.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Contreras,
M.Karlsson,
T.Osterlund,
H.Laurell,
A.Svensson,
and
C.Holm
(1996).
Hormone-sensitive lipase is structurally related to acetylcholinesterase, bile salt-stimulated lipase, and several fungal lipases. Building of a three-dimensional model for the catalytic domain of hormone-sensitive lipase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
31426-31430.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Simons,
H.Adams,
R.C.Cox,
N.Dekker,
F.Götz,
A.J.Slotboom,
and
H.M.Verheij
(1996).
The lipase from Staphylococcus aureus. Expression in Escherichia coli, large-scale purification and comparison of substrate specificity to Staphylococcus hyicus lipase.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
242,
760-769.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Gulomova,
E.Ziomek,
J.D.Schrag,
K.Davranov,
and
M.Cygler
(1996).
Purification and characterization of a Penicillium sp. lipase which discriminates against diglycerides.
|
| |
Lipids,
31,
379-384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Ghosh,
Z.Wawrzak,
V.Z.Pletnev,
N.Li,
R.Kaiser,
W.Pangborn,
H.Jörnvall,
M.Erman,
and
W.L.Duax
(1995).
Structure of uncomplexed and linoleate-bound Candida cylindracea cholesterol esterase.
|
| |
Structure,
3,
279-288.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Tjoelker,
C.Eberhardt,
J.Unger,
H.L.Trong,
G.A.Zimmerman,
T.M.McIntyre,
D.M.Stafforini,
S.M.Prescott,
and
P.W.Gray
(1995).
Plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase is a secreted phospholipase A2 with a catalytic triad.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
25481-25487.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Rubin
(1994).
Grease pit chemistry exposed.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
1,
568-572.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Björkling,
A.Dahl,
S.Patkar,
and
M.Zundel
(1994).
Inhibition of lipases by phosphonates.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
2,
697-705.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Kazlauskas
(1994).
Elucidating structure-mechanism relationships in lipases: prospects for predicting and engineering catalytic properties.
|
| |
Trends Biotechnol,
12,
464-472.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

