 |
PDBsum entry 1std

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase (carbon-oxygen)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1std
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.94
- scytalone dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
scytalone = 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
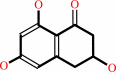 scytalone
scytalone
|
=
|
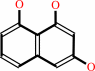 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene
1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
2:937-944
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of scytalone dehydratase--a disease determinant of the rice pathogen, Magnaporthe grisea.
|
|
T.Lundqvist,
J.Rice,
C.N.Hodge,
G.S.Basarab,
J.Pierce,
Y.Lindqvist.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Rice blast is caused by the pathogenic fungus,-Magnaporthe grisea.
Non-pathogenic mutants have been identified that lack enzymes in the
biosynthetic pathway of dihydroxynapthalene-derived melanin. These enzymes are
therefore prime targets for fungicides designed to control rice blast disease.
One of the enzymes identified by genetic analysis as a disease determinant is
scytalone dehydratase. RESULTS: The three-dimensional structure of scytalone
dehydratase in complex with a competitive inhibitor has been determined at 2.9 A
resolution. A novel fold, a cone-shaped alpha + beta barrel, is adopted by the
monomer in this trimeric protein, burying the hydrophobic active site in its
interior. The interactions of the inhibitor with the protein side chains have
been identified. The similarity of the inhibitor to the substrate and the side
chains involved in binding afford some insights into possible catalytic
mechanisms. CONCLUSIONS: These results provide a first look into the structure
and catalytic residues of a non-metal dehydratase, a large class of hitherto
structurally uncharacterized enzymes. It is envisaged that a detailed structural
description of scytalone dehydratase will assist in the design of new inhibitors
for controlling rice blast disease.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. (a) Reactions catalyzed by scytalone dehydratase.
Conversion of scytalone (1) to 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene (2);
conversion of vermelone (3) to 1,8-dihydroxynapthalene (4);
conversion of an artificial substrate (5) to an α
,β-unsaturated ketone (6). (b) Structure of salicylamide
inhibitors; (R)-(+)-N-[1-
(4-bromophenyl)ethyl]-5-fluorosalicylamide
(7),N-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)-5-fluorosalicylamide (8) and
(R)-(+)-N-[1-(4-iodophenyl)ethyl]-5-fluorosalicylamide (9).
Figure 1. (a) Reactions catalyzed by scytalone dehydratase.
Conversion of scytalone (1) to 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene (2);
conversion of vermelone (3) to 1,8-dihydroxynapthalene (4);
conversion of an artificial substrate (5) to an α
,β-unsaturated ketone (6). (b) Structure of salicylamide
inhibitors; (R)-(+)-N-[1-
(4-bromophenyl)ethyl]-5-fluorosalicylamide
(7),N-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)-5-fluorosalicylamide (8) and
(R)-(+)-N-[1-(4-iodophenyl)ethyl]-5-fluorosalicylamide (9).
|
 |
Figure 10.
Figure 10. Reaction mechanism based on a model where the
substrate has been positioned in the active site so as to
overlap with the analogous parts of the inhibitor. Figure 10.
Reaction mechanism based on a model where the substrate has been
positioned in the active site so as to overlap with the
analogous parts of the inhibitor.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1994,
2,
937-944)
copyright 1994.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Li,
K.E.Roege,
and
W.L.Kelly
(2009).
Analysis of the indanomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces antibioticus NRRL 8167.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
1064-1072.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Zhang,
F.Gao,
H.Peng,
H.Cheng,
Y.Liu,
J.Tang,
J.Thompson,
G.Wei,
J.Zhang,
Y.Du,
J.Yan,
and
G.F.Gao
(2009).
Crystal structures of Streptococcus suis mannonate dehydratase (ManD) and its complex with substrate: genetic and biochemical evidence for a catalytic mechanism.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
5832-5837.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Engh,
M.Nowrousian,
and
U.Kück
(2007).
Regulation of melanin biosynthesis via the dihydroxynaphthalene pathway is dependent on sexual development in the ascomycete Sordaria macrospora.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
275,
62-70.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Handa,
S.Kishishita,
S.Morita,
R.Akasaka,
Z.Jin,
J.Chrzas,
L.Chen,
Z.J.Liu,
B.C.Wang,
S.Sugano,
A.Tanaka,
T.Terada,
M.Shirouzu,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2007).
Structure of the human Tim44 C-terminal domain in complex with pentaethylene glycol: ligand-bound form.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
1225-1234.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Gallimore,
C.B.Stark,
A.Bhatt,
B.M.Harvey,
Y.Demydchuk,
V.Bolanos-Garcia,
D.J.Fowler,
J.Staunton,
P.F.Leadlay,
and
J.B.Spencer
(2006).
Evidence for the role of the monB genes in polyether ring formation during monensin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
13,
453-460.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Sultana,
P.Kallio,
A.Jansson,
J.S.Wang,
J.Niemi,
P.Mäntsälä,
and
G.Schneider
(2004).
Structure of the polyketide cyclase SnoaL reveals a novel mechanism for enzymatic aldol condensation.
|
| |
EMBO J,
23,
1911-1921.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Yamada,
T.Motoyama,
M.Nakasako,
S.Kagabu,
T.Kudo,
and
I.Yamaguchi
(2004).
Enzymatic characterization of scytalone dehydratase Val75Met variant found in melanin biosynthesis dehydratase inhibitor (MBI-D) resistant strains of the rice blast fungus.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
68,
615-621.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Arand,
B.M.Hallberg,
J.Zou,
T.Bergfors,
F.Oesch,
M.J.van der Werf,
J.A.de Bont,
T.A.Jones,
and
S.L.Mowbray
(2003).
Structure of Rhodococcus erythropolis limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase reveals a novel active site.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
2583-2592.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fribourg,
and
E.Conti
(2003).
Structural similarity in the absence of sequence homology of the messenger RNA export factors Mtr2 and p15.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
4,
699-703.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Lim,
and
N.C.Strynadka
(2002).
Structural basis for the beta lactam resistance of PBP2a from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
870-876.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Nagata,
K.Mori,
M.Takagi,
A.G.Murzin,
and
J.Damborský
(2001).
Identification of protein fold and catalytic residues of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane dehydrochlorinase LinA.
|
| |
Proteins,
45,
471-477.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Jordan,
Y.J.Zheng,
B.A.Lockett,
and
G.S.Basarab
(2000).
Stereochemistry of the enolization of scytalone by scytalone dehydratase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
2276-2282.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Nixon,
S.M.Firestine,
F.G.Salinas,
and
S.J.Benkovic
(1999).
Rational design of a scytalone dehydratase-like enzyme using a structurally homologous protein scaffold.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
3568-3571.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Cho,
N.C.Ha,
G.Choi,
H.J.Kim,
D.Lee,
K.S.Oh,
K.S.Kim,
W.Lee,
K.Y.Choi,
and
B.H.Oh
(1999).
Crystal structure of delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase from Pseudomonas testosteroni in complex with equilenin settles the correct hydrogen bonding scheme for transition state stabilization.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
32863-32868.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Wawrzak,
T.Sandalova,
J.J.Steffens,
G.S.Basarab,
T.Lundqvist,
Y.Lindqvist,
and
D.B.Jordan
(1999).
High-resolution structures of scytalone dehydratase-inhibitor complexes crystallized at physiological pH.
|
| |
Proteins,
35,
425-439.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Murzin
(1998).
How far divergent evolution goes in proteins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
8,
380-387.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kauppi,
K.Lee,
E.Carredano,
R.E.Parales,
D.T.Gibson,
H.Eklund,
and
S.Ramaswamy
(1998).
Structure of an aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase-naphthalene 1,2-dioxygenase.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
571-586.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nakasako,
T.Motoyama,
Y.Kurahashi,
and
I.Yamaguchi
(1998).
Cryogenic X-ray crystal structure analysis for the complex of scytalone dehydratase of a rice blast fungus and its tight-binding inhibitor, carpropamid: the structural basis of tight-binding inhibition.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
9931-9939.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Motoyama,
K.Imanishi,
and
I.Yamaguchi
(1998).
cDNA cloning, expression, and mutagenesis of scytalone dehydratase needed for pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus, Pyricularia oryzae.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
62,
564-566.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.J.Zheng,
and
T.C.Bruice
(1998).
Role of a critical water in scytalone dehydratase-catalyzed reaction.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
4158-4163.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.W.Kim,
S.S.Cha,
H.S.Cho,
J.S.Kim,
N.C.Ha,
M.J.Cho,
S.Joo,
K.K.Kim,
K.Y.Choi,
and
B.H.Oh
(1997).
High-resolution crystal structures of delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase with and without a reaction intermediate analogue.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
14030-14036.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Andersson,
D.Jordan,
G.Schneider,
B.Valent,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(1996).
Crystallization and preliminary x-ray diffraction study of 1 ,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene reductase from Magnaporthe grisea.
|
| |
Proteins,
24,
525-527.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Andersson,
D.Jordan,
G.Schneider,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(1996).
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene reductase from Magnaporthe grisea with NADPH and an active-site inhibitor.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
1161-1170.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Murzin
(1996).
Structural classification of proteins: new superfamilies.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
6,
386-394.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Leesong,
B.S.Henderson,
J.R.Gillig,
J.M.Schwab,
and
J.L.Smith
(1996).
Structure of a dehydratase-isomerase from the bacterial pathway for biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids: two catalytic activities in one active site.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
253-264.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Howard,
and
B.Valent
(1996).
Breaking and entering: host penetration by the fungal rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe grisea.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
50,
491-512.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Köster,
G.Stier,
R.Ficner,
M.Hölzer,
H.C.Curtius,
D.Suck,
and
S.Ghisla
(1996).
Location of the active site and proposed catalytic mechanism of pterin-4a-carbinolamine dehydratase.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
241,
858-864.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kubo,
Y.Takano,
N.Endo,
N.Yasuda,
S.Tajima,
and
I.Furusawa
(1996).
Cloning and structural analysis of the melanin biosynthesis gene SCD1 encoding scytalone dehydratase in Colletotrichum lagenarium.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
62,
4340-4344.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Johnen,
D.Kowlessur,
B.A.Citron,
and
S.Kaufman
(1995).
Characterization of the wild-type form of 4a-carbinolamine dehydratase and two naturally occurring mutants associated with hyperphenylalaninemia.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
12384-12388.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

