 |
PDBsum entry 1so5

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.85
- 3-dehydro-L-gulonate-6-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate + H+ = L-xylulose 5-phosphate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate
3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
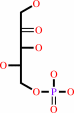 L-xylulose 5-phosphate
L-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 75.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
43:6438-6446
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Evolution of enzymatic activities in the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase suprafamily: crystallographic evidence for a proton relay system in the active site of 3-keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
E.L.Wise,
W.S.Yew,
J.A.Gerlt,
I.Rayment.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
3-Keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase (KGPDC), a member of the orotidine
monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC) suprafamily, catalyzes the Mg(2+)-dependent
decarboxylation of 3-keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate to L-xylulose 5-phosphate.
Structural and biochemical evidence suggests that the KGPDC reaction proceeds
via a Mg(2+)-stabilized 1,2-cis-enediolate intermediate. Protonation of the
enediolate intermediate occurs in a nonstereospecific manner to form L-xylulose
5-phosphate. Although the exact mechanism of proton delivery is not known,
Glu112, His136, and Arg139 have been implicated in this process [Yew, W. S.,
Wise, E., Rayment, I., and Gerlt, J. A. (2004) Biochemistry 43, 6427-6437].
Surprisingly, single amino acid substitutions of these positions do not
substantially reduce catalytic activity but rather alter the stereochemical
course of the reaction. Here, we report the X-ray crystal structures of four
mutants, K64A, H136A, E112Q, and E112Q/H136A, each determined in the presence of
L-threonohydroxamate 4-phosphate, an analogue of the enediolate intermediate, to
1.7, 1.9, 1.8, and 1.9 A resolution, respectively. These structures reveal that
substitutions of Lys64, Glu112, and His136 cause changes in the positions of the
intermediate analogue and two active site water molecules that were previously
identified as possible proton donors. These changes correlate with the observed
alterations in the reaction stereochemistry for these mutants, thereby
supporting a reaction mechanism in which water molecules competitively shuttle
protons from the side chains of His136 and Arg139 to alternate faces of the
cis-enediolate intermediate. These studies further underscore the wide variation
in the reaction mechanisms in the OMPDC suprafamily.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
I.Orita,
A.Kita,
H.Yurimoto,
N.Kato,
Y.Sakai,
and
K.Miki
(2010).
Crystal structure of 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase, a member of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase suprafamily.
|
| |
Proteins,
78,
3488-3492.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yurimoto,
N.Kato,
and
Y.Sakai
(2009).
Genomic organization and biochemistry of the ribulose monophosphate pathway and its application in biotechnology.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
84,
407-416.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Kato,
H.Yurimoto,
and
R.K.Thauer
(2006).
The physiological role of the ribulose monophosphate pathway in bacteria and archaea.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
70,
10-21.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Terao,
K.Miyamoto,
and
H.Ohta
(2006).
Introduction of single mutation changes arylmalonate decarboxylase to racemase.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
3600-3602.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

