 |
PDBsum entry 1s8h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase, toxin
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1s8h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
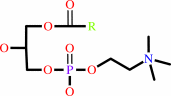 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
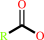 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
280:7326-7335
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A molecular mechanism for Lys49-phospholipase A2 activity based on ligand-induced conformational change.
|
|
A.L.Ambrosio,
M.C.Nonato,
H.S.de Araújo,
R.Arni,
R.J.Ward,
C.L.Ownby,
D.H.de Souza,
R.C.Garratt.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Agkistrodon contortrix laticinctus myotoxin is a Lys(49)-phospholipase A(2) (EC
3.1.1.4) isolated from the venom of the serpent A. contortrix laticinctus
(broad-banded copperhead). We present here three monomeric crystal structures of
the myotoxin, obtained under different crystallization conditions. The three
forms present notable structural differences and reveal that the presence of a
ligand in the active site (naturally presumed to be a fatty acid) induces the
exposure of a hydrophobic surface (the hydrophobic knuckle) toward the C
terminus. The knuckle in A. contortrix laticinctus myotoxin involves the side
chains of Phe(121) and Phe(124) and is a consequence of the formation of a
canonical structure for the main chain within the region of residues 118-125.
Comparison with other Lys(49)-phospholipase A(2) myotoxins shows that although
the knuckle is a generic structural motif common to all members of the family,
it is not readily recognizable by simple sequence analyses. An activation
mechanism is proposed that relates fatty acid retention at the active site to
conformational changes within the C-terminal region, a part of the molecule that
has long been associated with Ca(2+)-independent membrane damaging activity and
myotoxicity. This provides, for the first time, a direct structural connection
between the phospholipase "active site" and the C-terminal
"myotoxic site," justifying the otherwise enigmatic conservation of
the residues of the former in supposedly catalytically inactive molecules.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
FIG. 4. Stereo view ribbon representation of the C terminus
and calcium binding loops of the 18 available structures.
Thirteen of the 18 available structures of Lys49-PLA[2] present
the canonical conformation. Red, form I of ACL myotoxin (PDB
code 1S8G [PDB]
), chains A and B of piratoxin-II (PDB code 1QLL [PDB]
), chains A and B of myotoxin-II (PDB code 1CLP [PDB]
), chain A of structure 1, and chains A and B of structure 2, a
monomer of structure 3 (with stearic acid bound), where a slight
difference in the conformation of residues Tyr120 and Leu121 is
observed, and monomer of structure 4 (complexed with a PEG
fragment) of BthTX-I, acutohemolysin (PDB code 1MC2 [PDB]
), and chains A and B for NumMT-I, both in complex with stearic
acid. The Lys122 (C-  shown as balls)
interacts with the Cys29-Gly30 peptide bond at the Ca^2+ binding
loop. Moreover, seven of these present a fatty acid molecule
inside the hydrophobic channel. The remaining five structures
where the Lys122 points toward the solvent region and the C
terminus show a high degree of variability: in white, form II of
ACL myotoxin (PDB code 1S8H [PDB]
) and A. piscivorus piscivorus (PDB code 1PPA [PDB]
); in yellow, chain B of structure I from BthTX-I; in green,
form III of ACL myotoxin (PDB code 1S8I [PDB]
), and in blue, GodMT-II (1GOD). shown as balls)
interacts with the Cys29-Gly30 peptide bond at the Ca^2+ binding
loop. Moreover, seven of these present a fatty acid molecule
inside the hydrophobic channel. The remaining five structures
where the Lys122 points toward the solvent region and the C
terminus show a high degree of variability: in white, form II of
ACL myotoxin (PDB code 1S8H [PDB]
) and A. piscivorus piscivorus (PDB code 1PPA [PDB]
); in yellow, chain B of structure I from BthTX-I; in green,
form III of ACL myotoxin (PDB code 1S8I [PDB]
), and in blue, GodMT-II (1GOD).
|
 |
Figure 6.
FIG. 6. The hydrophobic knuckle. a, presence of a large
non-polar surface exposed to the solvent (potential surface map,
calculated by GRASP (89)), formed by hydrophobic residues
surrounding Lys122, and constituting the hydrophobic knuckle. In
all cases, Lys122 interacts with the Cys29-Gly30 peptide bond,
and a ligand is bound to the hydrophobic channel. Positive
charges surround the base of the knuckle. b, the knuckle can
also be observed in ligand-free structures that present the
canonical conformation for the C-terminal region, where Lys122
interacts with Cys29-Gly30 peptide bond. c, structures where
Lys122 is exposed to the solvent, the hydrophobic knuckle is not
observed.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2005,
280,
7326-7335)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Cintra-Francischinelli,
P.Caccin,
A.Chiavegato,
P.Pizzo,
G.Carmignoto,
Y.Angulo,
B.Lomonte,
J.M.Gutiérrez,
and
C.Montecucco
(2010).
Bothrops snake myotoxins induce a large efflux of ATP and potassium with spreading of cell damage and pain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
14140-14145.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Aragão,
P.Randazzo-Moura,
S.Rostelato-Ferreira,
L.Rodrigues-Simioni,
and
R.J.Ward
(2009).
Shared structural determinants for the calcium-independent liposome membrane permeabilization and sarcolemma depolarization in Bothropstoxin-I, a LYS49-PLA(2) from the venom of Bothrops jararacussu.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
41,
2588-2593.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.H.Kao,
K.C.Chen,
S.R.Lin,
and
L.S.Chang
(2008).
The structural and functional contribution of N-terminal region and His-47 on Taiwan cobra phospholipase A2.
|
| |
J Pept Sci,
14,
342-348.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhou,
T.C.Tan,
S.Valiyaveettil,
M.L.Go,
R.M.Kini,
A.Velazquez-Campoy,
and
J.Sivaraman
(2008).
Structural characterization of myotoxic ecarpholin S from Echis carinatus venom.
|
| |
Biophys J,
95,
3366-3380.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Murakami,
U.Kuch,
D.Mebs,
and
R.K.Arni
(2007).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a novel Arg49 phospholipase A2 homologue from Zhaoermia mangshanensis venom.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
605-607.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Marchi-Salvador,
C.A.Fernandes,
S.F.Amui,
A.M.Soares,
and
M.R.Fontes
(2006).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a myotoxic Lys49-PLA2 from Bothrops jararacussu venom complexed with p-bromophenacyl bromide.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
600-603.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Rouault,
L.D.Rash,
P.Escoubas,
E.Boilard,
J.Bollinger,
B.Lomonte,
T.Maurin,
C.Guillaume,
S.Canaan,
C.Deregnaucourt,
J.Schrével,
A.Doglio,
J.M.Gutiérrez,
M.Lazdunski,
M.H.Gelb,
and
G.Lambeau
(2006).
Neurotoxicity and other pharmacological activities of the snake venom phospholipase A2 OS2: the N-terminal region is more important than enzymatic activity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
5800-5816.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Murakami,
C.C.Melo,
Y.Angulo,
B.Lomonte,
and
R.K.Arni
(2006).
Structure of myotoxin II, a catalytically inactive Lys49 phospholipase A2 homologue from Atropoides nummifer venom.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
423-426.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Nagem,
A.L.Ambrosio,
A.L.Rojas,
M.V.Navarro,
A.M.Golubev,
R.C.Garratt,
and
I.Polikarpov
(2005).
Getting the most out of X-ray home sources.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1022-1030.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

