 |
PDBsum entry 1s3b

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1s3b
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of maob in complex with n-methyl-n-propargyl-1(r)- aminoindan
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] b. Chain: a, b. Synonym: monoamine oxidase, mao-b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: maob. Expressed in: pichia pastoris. Expression_system_taxid: 4922.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.65Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.204
|
R-free:
|
0.223
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Binda,F.Hubalek,M.Li,Y.Herzig,J.Sterling,D.E.Edmondson,A.Mattevi
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Binda
et al.
(2004).
Crystal structures of monoamine oxidase B in complex with four inhibitors of the N-propargylaminoindan class.
J Med Chem,
47,
1767-1774.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Jan-04
|
Release date:
|
30-Mar-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P27338
(AOFB_HUMAN) -
Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
520 a.a.
499 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.21
- primary-amine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a primary methyl amine + O2 + H2O = an aldehyde + H2O2 + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
primary methyl amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
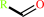 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.4
- monoamine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a secondary aliphatic amine + O2 + H2O = a primary amine + an aldehyde + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
secondary aliphatic amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
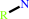 primary amine
primary amine
|
+
|
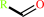 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
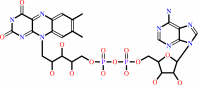 FAD
FAD
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
47:1767-1774
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of monoamine oxidase B in complex with four inhibitors of the N-propargylaminoindan class.
|
|
C.Binda,
F.Hubálek,
M.Li,
Y.Herzig,
J.Sterling,
D.E.Edmondson,
A.Mattevi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO B) is an outer mitochondrial membrane enzyme that
catalyzes the oxidation of arylalkylamine neurotransmitters. The crystal
structures of MAO B in complex with four of the N-propargylaminoindan class of
MAO covalent inhibitors (rasagiline, N-propargyl-1(S)-aminoindan,
6-hydroxy-N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan, and N-methyl-N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan)
have been determined at a resolution of better than 2.1 A. Rasagiline,
6-hydroxy-N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan, and N-methyl-N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan
adopt essentially the same conformation with the extended propargyl chain
covalently bound to the flavin and the indan ring located in the rear of the
substrate cavity. N-Propargyl-1(S)-aminoindan binds with the indan ring in a
flipped conformation with respect to the other inhibitors, which causes a slight
movement of the Tyr326 side chain. Four ordered water molecules are an integral
part of the active site and establish H-bond interactions to the inhibitor
atoms. These structural studies may guide future drug design to improve
selectivity and efficacy by introducing appropriate substituents on the
rasagiline molecular scaffold.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Schwarzer
(2010).
Chemical tools in chromatin research.
|
| |
J Pept Sci,
16,
530-537.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Weinreb,
T.Amit,
O.Bar-Am,
and
M.B.Youdim
(2010).
Rasagiline: a novel anti-Parkinsonian monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor with neuroprotective activity.
|
| |
Prog Neurobiol,
92,
330-344.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Gal,
Z.A.Abassi,
and
M.B.Youdim
(2010).
limited potentiation of blood pressure in response to oral tyramine by the anti-Parkinson brain selective multifunctional monoamine oxidase-AB inhibitor, M30.
|
| |
Neurotox Res,
18,
143-150.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Naoi,
and
W.Maruyama
(2009).
Functional mechanism of neuroprotection by inhibitors of type B monoamine oxidase in Parkinson's disease.
|
| |
Expert Rev Neurother,
9,
1233-1250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.W.van Hellemond,
M.van Dijk,
D.P.Heuts,
D.B.Janssen,
and
M.W.Fraaije
(2008).
Discovery and characterization of a putrescine oxidase from Rhodococcus erythropolis NCIMB 11540.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
78,
455-463.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Forneris,
C.Binda,
E.Battaglioli,
and
A.Mattevi
(2008).
LSD1: oxidative chemistry for multifaceted functions in chromatin regulation.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
33,
181-189.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hruschka,
T.C.Rosen,
S.Yoshida,
K.L.Kirk,
R.Fröhlich,
B.Wibbeling,
and
G.Haufe
(2008).
Fluorinated phenylcyclopropylamines. Part 5: Effects of electron-withdrawing or -donating aryl substituents on the inhibition of monoamine oxidases A and B by 2-aryl-2-fluoro-cyclopropylamines.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
16,
7148-7166.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.White,
W.H.Johnson,
C.P.Whitman,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2008).
Structural basis for the inactivation of Thermus thermophilus proline dehydrogenase by N-propargylglycine.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
5573-5580.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Yelekçi,
O.Karahan,
and
M.Toprakçi
(2007).
Docking of novel reversible monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: efficient prediction of ligand binding sites and estimation of inhibitors thermodynamic properties.
|
| |
J Neural Transm,
114,
725-732.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Akyüz,
S.S.Erdem,
and
D.E.Edmondson
(2007).
The aromatic cage in the active site of monoamine oxidase B: effect on the structural and electronic properties of bound benzylamine and p-nitrobenzylamine.
|
| |
J Neural Transm,
114,
693-698.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.B.Youdim,
D.Edmondson,
and
K.F.Tipton
(2006).
The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
|
| |
Nat Rev Neurosci,
7,
295-309.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Gütschow,
and
M.Meusel
(2006).
[Enzyme inhibitors in Parkinson treatment]
|
| |
Pharm Unserer Zeit,
35,
218-225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Vlok,
S.F.Malan,
N.Castagnoli,
J.J.Bergh,
and
J.P.Petzer
(2006).
Inhibition of monoamine oxidase B by analogues of the adenosine A2A receptor antagonist (E)-8-(3-chlorostyryl)caffeine (CSC).
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
14,
3512-3521.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Binda,
F.Hubálek,
M.Li,
Y.Herzig,
J.Sterling,
D.E.Edmondson,
and
A.Mattevi
(2005).
Binding of rasagiline-related inhibitors to human monoamine oxidases: a kinetic and crystallographic analysis.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
48,
8148-8154.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Hubálek,
C.Binda,
A.Khalil,
M.Li,
A.Mattevi,
N.Castagnoli,
and
D.E.Edmondson
(2005).
Demonstration of isoleucine 199 as a structural determinant for the selective inhibition of human monoamine oxidase B by specific reversible inhibitors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
15761-15766.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Zheng,
S.Gal,
L.M.Weiner,
O.Bar-Am,
A.Warshawsky,
M.Fridkin,
and
M.B.Youdim
(2005).
Novel multifunctional neuroprotective iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs for neurodegenerative diseases: in vitro studies on antioxidant activity, prevention of lipid peroxide formation and monoamine oxidase inhibition.
|
| |
J Neurochem,
95,
68-78.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.De Colibus,
M.Li,
C.Binda,
A.Lustig,
D.E.Edmondson,
and
A.Mattevi
(2005).
Three-dimensional structure of human monoamine oxidase A (MAO A): relation to the structures of rat MAO A and human MAO B.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
12684-12689.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nadella,
M.A.Bianchet,
S.B.Gabelli,
J.Barrila,
and
L.M.Amzel
(2005).
Structure and activity of the axon guidance protein MICAL.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
16830-16835.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Gal,
H.Zheng,
M.Fridkin,
and
M.B.Youdim
(2005).
Novel multifunctional neuroprotective iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. In vivo selective brain monoamine oxidase inhibition and prevention of MPTP-induced striatal dopamine depletion.
|
| |
J Neurochem,
95,
79-88.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Rosen,
S.Yoshida,
K.L.Kirk,
and
G.Haufe
(2004).
Fluorinated phenylcyclopropylamines as inhibitors of monoamine oxidases.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
5,
1033-1043.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

