 |
PDBsum entry 1r0c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, G:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
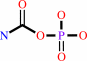 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
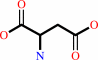 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
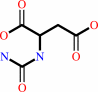 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
43:6422-6426
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Products in the T-state of aspartate transcarbamylase: crystal structure of the phosphate and N-carbamyl-L-aspartate ligated enzyme.
|
|
J.Huang,
W.N.Lipscomb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli ligated to
products (phosphate and N-carbamyl-l-aspartate) has been determined at 2.37 A
resolution (R-factor = 0.23, R(free) = 0.27). Results might indicate a product
release mode, rather than close analogues to the transition state like those
found in our earlier studies of other ligands (N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate,
carbamyl phosphate plus malonate, phosphonoacetamide plus malonate, or citrate
plus phosphate). Ordered product release, first carbamylaspartate (CLA) and then
phosphate, might be facilitated by a 4 A movement of phosphate from the
substrate-analogue position to the product (phosphate) binding position, and by
a somewhat similar release movement of the other product (CLA) relative to its
analogue (citrate). This movement is consistent with earlier studies of binding
of either pyrophosphate or phosphate alone [Honzatko, R. B., and Lipscomb, W. N.
(1982) J. Mol. Biol. 160, 265-286].

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Stieglitz,
J.Xia,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2009).
The first high pH structure of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
74,
318-327.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Shi,
X.Yu,
L.Roth,
H.Morizono,
M.Tuchman,
and
N.M.Allewell
(2006).
Structures of N-acetylornithine transcarbamoylase from Xanthomonas campestris complexed with substrates and substrate analogs imply mechanisms for substrate binding and catalysis.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
532-542.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.De Vos,
P.Hulpiau,
B.Vergauwen,
S.N.Savvides,
and
J.Van Beeumen
(2005).
Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of a cold-adapted aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Moritella profunda.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
279-281.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

