 |
PDBsum entry 1pjs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/oxidoreductase/lyase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1pjs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/oxidoreductase/lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The co-crystal structure of cysg, the multifunctional methyltransferase/dehydrogenase/ferrochelatase for siroheme synthesis, in complex with it NAD cofactor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Siroheme synthase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: cysg. Engineered: yes. Other_details: residues 1-212 (cysgb) are a dehydrogenase/ferrochelatase, residues 213-457 (cysga) are a bismethyltransferase
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Salmonella typhimurium. Organism_taxid: 602. Gene: cysg or stm3477. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.239
|
R-free:
|
0.281
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.E.Stroupe,H.K.Leech,D.S.Daniels,M.J.Warren,E.D.Getzoff
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.E.Stroupe
et al.
(2003).
CysG structure reveals tetrapyrrole-binding features and novel regulation of siroheme biosynthesis.
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
1064-1073.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
03-Jun-03
|
Release date:
|
02-Dec-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P25924
(CYSG_SALTY) -
Siroheme synthase from Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
457 a.a.
443 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.3.1.76
- precorrin-2 dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Corrin and Siroheme Biosynthesis (part 2)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
precorrin-2 + NAD+ = sirohydrochlorin + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
precorrin-2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
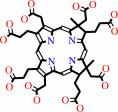 sirohydrochlorin
sirohydrochlorin
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.107
- uroporphyrinogen-III C-methyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
uroporphyrinogen III + 2 S-adenosyl-L-methionine = precorrin-2 + 2 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
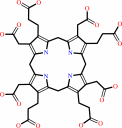 uroporphyrinogen III
uroporphyrinogen III
|
+
|
 2
×
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
2
×
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
|
=
|
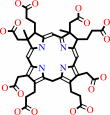 precorrin-2
precorrin-2
|
+
|
 2
×
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
2
×
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.99.1.4
- sirohydrochlorin ferrochelatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
siroheme + 2 H+ = sirohydrochlorin + Fe2+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
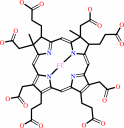 siroheme
siroheme
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
=
|
 sirohydrochlorin
sirohydrochlorin
|
+
|
2
×
Fe(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Struct Biol
10:1064-1073
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
CysG structure reveals tetrapyrrole-binding features and novel regulation of siroheme biosynthesis.
|
|
M.E.Stroupe,
H.K.Leech,
D.S.Daniels,
M.J.Warren,
E.D.Getzoff.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Sulfur metabolism depends on the iron-containing porphinoid siroheme. In
Salmonella enterica, the S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM)-dependent
bismethyltransferase, dehydrogenase and ferrochelatase, CysG, synthesizes
siroheme from uroporphyrinogen III (uro'gen III). The reactions mediated by CysG
encompass two branchpoint intermediates in tetrapyrrole biosynthesis, diverting
flux first from protoporphyrin IX biosynthesis and then from cobalamin (vitamin
B(12)) biosynthesis. We determined the first structure of this multifunctional
siroheme synthase by X-ray crystallography. CysG is a homodimeric gene fusion
product containing two structurally independent modules: a bismethyltransferase
and a dual-function dehydrogenase-chelatase. The methyltransferase active site
is a deep groove with a hydrophobic patch surrounded by hydrogen bond donors.
This asymmetric arrangement of amino acids may be important in directing
substrate binding. Notably, our structure shows that CysG is a phosphoprotein.
From mutational analysis of the post-translationally modified serine, we suggest
a conserved role for phosphorylation in inhibiting dehydrogenase activity and
modulating metabolic flux between siroheme and cobalamin pathways.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Siroheme biosynthesis and its relationship to
cobalamin (vitamin B[12]) and protoporphyrin IX-derived
macrocycles (heme and chlorophyll).
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. A stereo view of the methyltransferase active site
from the native CysG structure, which sits deep within a cleft
between the domains IA and IIA. (a) SAH (green) remains bound
in the active site during purification and crystallization.
Residues that bind SAH and that form the hydrophobic platform in
the center of the active site are purple. Atoms are colored as
in Figure 3. (b) The methyltransferase active site is an
asymmetric slot with charged residues (blue) circling a
hydrophobic patch (purple). (c) A model of uro'gen III in the
CysGA active site. Uro'gen III is dark gray. This
tetrapyrrole-binding model demonstrates the relationship among
residues we know to be important for the methyltransferase
reaction in the context of bound substrate. Same view as in b.
The reactive pyrrole group is marked with an asterisk.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Struct Biol
(2003,
10,
1064-1073)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Pränting,
and
D.I.Andersson
(2010).
Mechanisms and physiological effects of protamine resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2.
|
| |
J Antimicrob Chemother,
65,
876-887.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Zappa,
K.Li,
and
C.E.Bauer
(2010).
The tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathway and its regulation in Rhodobacter capsulatus.
|
| |
Adv Exp Med Biol,
675,
229-250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Thorgersen,
and
D.M.Downs
(2009).
Oxidative stress and disruption of labile iron generate specific auxotrophic requirements in Salmonella enterica.
|
| |
Microbiology,
155,
295-304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Zajicek,
S.Bali,
S.Arnold,
A.A.Brindley,
M.J.Warren,
and
S.J.Ferguson
(2009).
d(1) haem biogenesis - assessing the roles of three nir gene products.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
6399-6411.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Lobo,
A.Brindley,
M.J.Warren,
and
L.M.Saraiva
(2009).
Functional characterization of the early steps of tetrapyrrole biosynthesis and modification in Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough.
|
| |
Biochem J,
420,
317-325.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Storbeck,
J.Walther,
J.Müller,
V.Parmar,
H.M.Schiebel,
D.Kemken,
T.Dülcks,
M.J.Warren,
and
G.Layer
(2009).
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa nirE gene encodes the S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent uroporphyrinogen III methyltransferase required for heme d(1) biosynthesis.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
5973-5982.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.L.Schubert,
R.S.Rose,
H.K.Leech,
A.A.Brindley,
C.P.Hill,
S.E.Rigby,
and
M.J.Warren
(2008).
Structure and function of SirC from Bacillus megaterium: a metal-binding precorrin-2 dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Biochem J,
415,
257-263.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Medlock,
L.Swartz,
T.A.Dailey,
H.A.Dailey,
and
W.N.Lanzilotta
(2007).
Substrate interactions with human ferrochelatase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
1789-1793.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Fan,
Q.Liu,
Q.Hao,
M.Teng,
and
L.Niu
(2007).
Crystal structure of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
3573-3580.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Xiong,
C.E.Bauer,
and
A.Pancholy
(2007).
Insight into the haem d1 biosynthesis pathway in heliobacteria through bioinformatics analysis.
|
| |
Microbiology,
153,
3548-3562.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Matsushita,
N.N.Suzuki,
K.Obara,
Y.Fujioka,
Y.Ohsumi,
and
F.Inagaki
(2007).
Structure of Atg5.Atg16, a complex essential for autophagy.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
6763-6772.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Thorgersen,
and
D.M.Downs
(2007).
Cobalt targets multiple metabolic processes in Salmonella enterica.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
7774-7781.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Frank,
E.Deery,
A.A.Brindley,
H.K.Leech,
A.Lawrence,
P.Heathcote,
H.L.Schubert,
K.Brocklehurst,
S.E.Rigby,
M.J.Warren,
and
R.W.Pickersgill
(2007).
Elucidation of substrate specificity in the cobalamin (vitamin B12) biosynthetic methyltransferases. Structure and function of the C20 methyltransferase (CbiL) from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
23957-23969.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Al-Karadaghi,
R.Franco,
M.Hansson,
J.A.Shelnutt,
G.Isaya,
and
G.C.Ferreira
(2006).
Chelatases: distort to select?
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
31,
135-142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Cai,
T.K.h.Shokhireva,
D.L.Lichtenberger,
and
F.A.Walker
(2006).
NMR and EPR studies of chloroiron(III) tetraphenyl-chlorin and its complexes with imidazoles and pyridines of widely differing basicities.
|
| |
Inorg Chem,
45,
3519-3531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Deva,
E.N.Baker,
C.J.Squire,
and
C.A.Smith
(2006).
Structure of Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl:L-alanine ligase (MurC).
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
1466-1474.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Raux-Deery,
H.K.Leech,
K.A.Nakrieko,
K.J.McLean,
A.W.Munro,
P.Heathcote,
S.E.Rigby,
A.G.Smith,
and
M.J.Warren
(2005).
Identification and characterization of the terminal enzyme of siroheme biosynthesis from Arabidopsis thaliana: a plastid-located sirohydrochlorin ferrochelatase containing a 2FE-2S center.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
4713-4721.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.H.Rehse,
T.Kitao,
and
T.H.Tahirov
(2005).
Structure of a closed-form uroporphyrinogen-III C-methyltransferase from Thermus thermophilus.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
913-919.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Z.Kozbial,
and
A.R.Mushegian
(2005).
Natural history of S-adenosylmethionine-binding proteins.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
5,
19.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

