 |
PDBsum entry 1ofd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ofd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.7.1
- glutamate synthase (ferredoxin).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
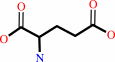
2 oxidized [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin] + 2 L-glutamate = L-glutamine + 2 reduced [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin] + 2-oxoglutarate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2
×
oxidized [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin]
|
+
|
 2
×
L-glutamate
2
×
L-glutamate
|
=
|
L-glutamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
2
×
reduced [2Fe-2S]-[ferredoxin]
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; FMN; Iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
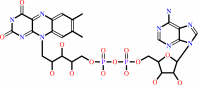 FAD
FAD
|
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
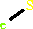 Iron-sulfur
Iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
330:113-128
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The active conformation of glutamate synthase and its binding to ferredoxin.
|
|
R.H.van den Heuvel,
D.I.Svergun,
M.V.Petoukhov,
A.Coda,
B.Curti,
S.Ravasio,
M.A.Vanoni,
A.Mattevi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glutamate synthases (GltS) are crucial enzymes in ammonia assimilation in plants
and bacteria, where they catalyze the formation of two molecules of L-glutamate
from L-glutamine and 2-oxoglutarate. The plant-type ferredoxin-dependent GltS
and the functionally homologous alpha subunit of the bacterial NADPH-dependent
GltS are complex four-domain monomeric enzymes of 140-165 kDa belonging to the
NH(2)-terminal nucleophile family of amidotransferases. The enzymes function
through the channeling of ammonia from the N-terminal amidotransferase domain to
the FMN-binding domain. Here, we report the X-ray structure of the Synechocystis
ferredoxin-dependent GltS with the substrate 2-oxoglutarate and the covalent
inhibitor 5-oxo-L-norleucine bound in their physically distinct active sites
solved using a new crystal form. The covalent Cys1-5-oxo-L-norleucine adduct
mimics the glutamyl-thioester intermediate formed during L-glutamine hydrolysis.
Moreover, we determined a high resolution structure of the GltS:2-oxoglutarate
complex. These structures represent the enzyme in the active conformation. By
comparing these structures with that of GltS alpha subunit and of related
enzymes we propose a mechanism for enzyme self-regulation and ammonia channeling
between the active sites. X-ray small-angle scattering experiments were
performed on solutions containing GltS and its physiological electron donor
ferredoxin (Fd). Using the structure of GltS and the newly determined crystal
structure of Synechocystis Fd, the scattering experiments clearly showed that
GltS forms an equimolar (1:1) complex with Fd. A fundamental consequence of this
result is that two Fd molecules bind consecutively to Fd-GltS to yield the
reduced FMN cofactor during catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the reaction
catalyzed by GltS. The ammonia produced in the amidotransferase
domain is added onto 2-OG in the FMN-binding domain.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. (A) Presentation of the Fd-GltS active site in
the FMN-binding domain with bound 2-OG and a model of bound
2-iminoglutarate. 2-OG and 2-iminoglutarate are depicted as
ball-and-stick in green and red, respectively. Hydrogen bonds
between Lys972 and Gln978 and the carbonyl oxygen atom of 2-OG
are indicated by broken green lines. Potential hydrogen bonds
between Fd-GltS and 2-iminoglutarate are indicated by broken red
lines. (B) Schematic representation of the role of Lys972 and
Glu903 for the dual functionality of the active site in the
FMN-binding domain. Lys972 fixes 2-OG in the proper conformation
for ammonia addition and polarizes the carbonyl oxygen atom.
Upon ammonia addition and water release, Glu903 anchors
2-iminoglutarate in the proper conformation for reduction by FMN.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2003,
330,
113-128)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Yamaoka,
Y.Ozawa,
Y.Ueno,
T.Endo,
Y.Morimoto,
A.Urushiyama,
D.Ohmori,
and
T.Imai
(2011).
Cyanidioschyzon merolae ferredoxin: A high resolution crystal structure analysis and its thermal stability.
|
| |
FEBS Lett,
585,
1299-1302.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Srivastava,
J.P.Schuermann,
T.A.White,
N.Krishnan,
N.Sanyal,
G.L.Hura,
A.Tan,
M.T.Henzl,
D.F.Becker,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2010).
Crystal structure of the bifunctional proline utilization A flavoenzyme from Bradyrhizobium japonicum.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
2878-2883.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Wisedchaisri,
D.M.Dranow,
T.J.Lie,
J.B.Bonanno,
Y.Patskovsky,
S.A.Ozyurt,
J.M.Sauder,
S.C.Almo,
S.R.Wasserman,
S.K.Burley,
J.A.Leigh,
and
T.Gonen
(2010).
Structural underpinnings of nitrogen regulation by the prototypical nitrogen-responsive transcriptional factor NrpR.
|
| |
Structure,
18,
1512-1521.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Glass,
F.Wolfe-Simon,
and
A.D.Anbar
(2009).
Coevolution of metal availability and nitrogen assimilation in cyanobacteria and algae.
|
| |
Geobiology,
7,
100-123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Vanoni,
and
B.Curti
(2008).
Structure-function studies of glutamate synthases: a class of self-regulated iron-sulfur flavoenzymes essential for nitrogen assimilation.
|
| |
IUBMB Life,
60,
287-300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Dai,
R.Friemann,
D.A.Glauser,
F.Bourquin,
W.Manieri,
P.Schürmann,
and
H.Eklund
(2007).
Structural snapshots along the reaction pathway of ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase.
|
| |
Nature,
448,
92-96.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2007).
Conformational changes in ammonia-channeling glutamine amidotransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
17,
653-664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Geerlof,
J.Brown,
B.Coutard,
M.P.Egloff,
F.J.Enguita,
M.J.Fogg,
R.J.Gilbert,
M.R.Groves,
A.Haouz,
J.E.Nettleship,
P.Nordlund,
R.J.Owens,
M.Ruff,
S.Sainsbury,
D.I.Svergun,
and
M.Wilmanns
(2006).
The impact of protein characterization in structural proteomics.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
1125-1136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Vergauwen,
D.De Vos,
and
J.J.Van Beeumen
(2006).
Characterization of the bifunctional gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase/glutathione synthetase (GshF) of Pasteurella multocida.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
4380-4394.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
M.A.Badet-Denisot,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2006).
Glutamine binding opens the ammonia channel and activates glucosamine-6P synthase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
4404-4412.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Suzuki,
and
D.B.Knaff
(2005).
Glutamate synthase: structural, mechanistic and regulatory properties, and role in the amino acid metabolism.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
83,
191-217.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Vanoni,
L.Dossena,
R.H.van den Heuvel,
and
B.Curti
(2005).
Structure-function studies on the complex iron-sulfur flavoprotein glutamate synthase: the key enzyme of ammonia assimilation.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
83,
219-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.I.Catalina,
R.H.van den Heuvel,
E.van Duijn,
and
A.J.Heck
(2005).
Decharging of globular proteins and protein complexes in electrospray.
|
| |
Chemistry,
11,
960-968.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.I.Muro-Pastor,
J.C.Reyes,
and
F.J.Florencio
(2005).
Ammonium assimilation in cyanobacteria.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
83,
135-150.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Heck,
and
R.H.Van Den Heuvel
(2004).
Investigation of intact protein complexes by mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Mass Spectrom Rev,
23,
368-389.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sugishima,
C.T.Migita,
X.Zhang,
T.Yoshida,
and
K.Fukuyama
(2004).
Crystal structure of heme oxygenase-1 from cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in complex with heme.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
4517-4525.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Coiro,
A.Di Nola,
M.A.Vanoni,
M.Aschi,
A.Coda,
B.Curti,
and
D.Roccatano
(2004).
Molecular dynamics simulation of the interaction between the complex iron-sulfur flavoprotein glutamate synthase and its substrates.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
2979-2991.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

