 |
PDBsum entry 1nns

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.1
- asparaginase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-asparagine + H2O = L-aspartate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
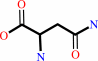 L-asparagine
L-asparagine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-aspartate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
59:416-422
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural comparison of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase in two monoclinic space groups.
|
|
M.Sanches,
J.A.Barbosa,
R.T.de Oliveira,
J.Abrahão Neto,
I.Polikarpov.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The functional L-asparaginase from Escherichia coli is a homotetramer with a
molecular weight of about 142 kDa. The X-ray structure of the enzyme,
crystallized in a new form (space group C2) and refined to 1.95 A resolution, is
compared with that of the previously determined crystal form (space group
P2(1)). The asymmetric unit of the new crystal form contains an L-asparaginase
dimer instead of the tetramer found in the previous crystal form. It is found
that crystal contacts practically do not affect the conformation of the protein.
It is shown that subunit C of the tetrameric form is in a conformation which is
systematically different from that of all other subunits in both crystal forms.
Major conformational differences are confined to the lid loop (residues 14-27).
In addition, the stability of this globular protein is analyzed in terms of the
interactions between hydrophobic parts of the subunits.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2 A schematic representation of the E. coli
L-asparaginase subunit produced using MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis,
1991[Kraulis, P. J. (1991). J. Appl. Cryst. 24, 946-950.]).
Secondary structures marked N belong to the N-terminal domain
and those marked C belong to the C-terminal domain. The
3[10]-helices N  1,
N 1,
N  3,
N 3,
N  6
and N 6
and N  10
are shown in opaque green. 10
are shown in opaque green.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 A graphical representation of the L-asparaginase
tetramer produced using MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis, 1991[Kraulis, P. J.
(1991). J. Appl. Cryst. 24, 946-950.]). Intimate dimers are
formed by subunits drawn in yellow/blue and green/pink.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2003,
59,
416-422)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.Dhavala,
J.Krasotkina,
C.Dubreuil,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2008).
Expression, purification and crystallization of Helicobacter pylori L-asparaginase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
740-742.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Yun,
A.Nourse,
S.W.White,
C.O.Rock,
and
R.J.Heath
(2007).
Crystal structure and allosteric regulation of the cytoplasmic Escherichia coli L-asparaginase I.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
369,
794-811.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Verma,
K.Kumar,
G.Kaur,
and
S.Anand
(2007).
L-asparaginase: a promising chemotherapeutic agent.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biotechnol,
27,
45-62.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Wikman,
J.Krasotkina,
A.Kuchumova,
N.N.Sokolov,
and
A.C.Papageorgiou
(2005).
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
407-409.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

