 |
PDBsum entry 1nht

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.4.4
- adenylosuccinate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
AMP and GMP Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
IMP + L-aspartate + GTP = N6-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)-AMP + GDP + phosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
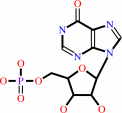 IMP
IMP
|
+
|
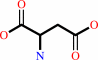 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
+
|
GTP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.67% similarity
|
=
|
N(6)-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl)-AMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
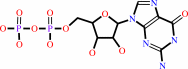 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
272:15200-15205
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Entrapment of 6-thiophosphoryl-IMP in the active site of crystalline adenylosuccinate synthetase from Escherichia coli.
|
|
B.W.Poland,
C.Bruns,
H.J.Fromm,
R.B.Honzatko.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Crystal structures of adenylosuccinate synthetase from Escherichia coli
complexed with Mg2+, 6-thiophosphoryl-IMP, GDP, and hadacidin at 298 and 100 K
have been refined to R-factors of 0.171 and 0.206 against data to 2.8 and 2.5 A
resolution, respectively. Interactions of GDP, Mg2+ and hadacidin are similar to
those observed for the same ligands in the complex of IMP, GDP, NO3-, Mg2+ and
hadacidin (Poland, B. W., Fromm, H. J. & Honzatko, R. B. (1996). J. Mol.
Biol. 264, 1013-1027). Although crystals were grown from solutions containing
6-mercapto-IMP and GTP, the electron density at the active site is consistent
with 6-thiophosphoryl-IMP and GDP. Asp-13 and Gln-224 probably work in concert
to stabilize the 6-thioanion of 6-mercapto-IMP, which in turn is the nucleophile
in the displacement of GDP from the gamma-phosphate of GTP. Once formed,
6-thiophosphoryl-IMP is stable in the active site of the enzyme under the
conditions of the structural investigation. The direct observation of
6-thiophosphoryl-IMP in the active site is consistent with the putative
generation of 6-phosphoryl-IMP along the reaction pathway of the synthetase.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Stereo view of bound ligands in relation to a trace
of  -carbons of
adenylosuccinate synthetase. -carbons of
adenylosuccinate synthetase.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Fig. 6. Proposed mechanism for the phosphotransfer reaction
governed by the synthetase, involving 6-mercapto-IMP as a
substrate. L-Aspartate is not shown here but is putatively
coordinated to Mg2+ as shown in Fig. 7.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(1997,
272,
15200-15205)
copyright 1997.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Choe,
B.W.Poland,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(1999).
Mechanistic implications from crystalline complexes of wild-type and mutant adenylosuccinate synthetases from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
6953-6961.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Lee,
A.Gorrell,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.F.Colman
(1999).
Implication of arginine-131 and arginine-303 in the substrate site of adenylosuccinate synthetase of Escherichia coli by affinity labeling with 6-(4-bromo-2,3-dioxobutyl)thioadenosine 5'-monophosphate.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
5754-5763.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
S.G.Miran,
J.C.Phillips,
A.J.Howard,
F.M.Raushel,
and
H.M.Holden
(1998).
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: caught in the act of glutamine hydrolysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
8825-8831.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

