 |
PDBsum entry 1mff

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Cytokine
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor y95f mutant
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Chain: a, b, c. Synonym: phenylpyruvate tautomerase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. House mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Gene: mif. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Trimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.231
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.B.Taylor,S.L.Stamps,S.C.Wang,M.L.Hackert,C.P.Whitman
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.L.Stamps
et al.
(2000).
Mechanism of the phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor: properties of the P1G, P1A, Y95F, and N97A mutants.
Biochemistry,
39,
9671-9678.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Oct-98
|
Release date:
|
12-Jul-99
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P34884
(MIF_MOUSE) -
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
115 a.a.
114 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.2.1
- phenylpyruvate tautomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-phenylpyruvate = enol-phenylpyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-phenylpyruvate
|
=
|
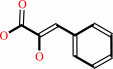 enol-phenylpyruvate
enol-phenylpyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.12
- L-dopachrome isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-dopachrome = 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
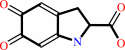 L-dopachrome
L-dopachrome
|
=
|
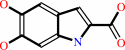 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
39:9671-9678
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism of the phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity of macrophage migration inhibitory factor: properties of the P1G, P1A, Y95F, and N97A mutants.
|
|
S.L.Stamps,
A.B.Taylor,
S.C.Wang,
M.L.Hackert,
C.P.Whitman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Phenylpyruvate tautomerase (PPT) has been studied periodically since its
activity was first described over forty years ago. In the last two years, the
mechanism of PPT has been investigated more extensively because of the discovery
that PPT is the same protein as the immunoregulatory cytokine known as
macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). The mechanism of PPT is likely to
involve general base-general acid catalysis. While several lines of evidence
implicate Pro-1 as the general base, the identity of the general acid remains
unknown. Crystal structures of MIF with the competitive inhibitor
(E)-2-fluoro-p-hydroxycinnamate bound in the active site and that of the protein
complexed with the enol form of a substrate, (p-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate, suggest
that Tyr-95 is the only candidate in the vicinity that can function as a general
acid catalyst. Although Tyr-95 is nearby the bound inhibitor and substrate, it
is not within hydrogen bonding distance of either ligand. In this study, Tyr-95
was mutated to phenylalanine, and the kinetic and structural properties of the
Y95F mutant were determined. This alteration produces a fully active enzyme,
which shows no significant structural changes in the active site. The results
indicate that Tyr-95 does not function as the general acid catalyst in the
reaction catalyzed by wild-type PPT. The mechanism of PPT was studied further by
constructing and characterizing the kinetic properties of two mutants of Pro-1
(P1G and P1A) and one mutant of Asn-97 (N97A). The mutation of Asn-97, a residue
implicated in the binding of the phenolic hydroxy group of the keto and enol
isomers of (p-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate and of (E)-2-fluoro-p-hydroxycinnamate
affects only the binding affinity of the inhibitor. However, the mutations of
Pro-1 have a profound effect on the values of k(cat) and k(cat)/K(m) and clearly
show that Pro-1 is a critical residue in the reaction. The results are discussed
in terms of a mechanism in which Pro-1 functions as both the general acid and
the general base catalyst.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Z.Cournia,
L.Leng,
S.Gandavadi,
X.Du,
R.Bucala,
and
W.L.Jorgensen
(2009).
Discovery of human macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-CD74 antagonists via virtual screening.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
416-424.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Poelarends,
W.H.Johnson,
H.Serrano,
and
C.P.Whitman
(2007).
Phenylpyruvate tautomerase activity of trans-3-chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase: evidence for an enol intermediate in the dehalogenase reaction?
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
9596-9604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Soares,
R.D.Lins,
T.P.Straatsma,
and
J.M.Briggs
(2002).
Internal dynamics and ionization states of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor: comparison between wild-type and mutant forms.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
65,
313-323.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

