 |
PDBsum entry 1mar

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase(NADP)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1mar
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
* C-alpha coords only
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.21
- aldose reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
an alditol + NAD+ = an aldose + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
an alditol + NADP+ = an aldose + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
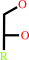 alditol
alditol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
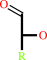 aldose
aldose
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 alditol
alditol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
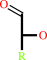 aldose
aldose
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.300
- NADP-retinol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
all-trans-retinol + NADP+ = all-trans-retinal + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
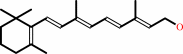 all-trans-retinol
all-trans-retinol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
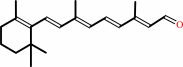 all-trans-retinal
all-trans-retinal
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.372
- D/L-glyceraldehyde reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
glycerol + NADP+ = L-glyceraldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
glycerol + NADP+ = D-glyceraldehyde + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
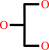 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
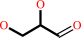 L-glyceraldehyde
L-glyceraldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 glycerol
glycerol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
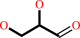 D-glyceraldehyde
D-glyceraldehyde
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.54
- allyl-alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
allyl alcohol + NADP+ = acrolein + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
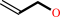 allyl alcohol
allyl alcohol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
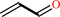 acrolein
acrolein
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
90:9847-9851
(1993)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Refined 1.8 A structure of human aldose reductase complexed with the potent inhibitor zopolrestat.
|
|
D.K.Wilson,
I.Tarle,
J.M.Petrash,
F.A.Quiocho.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
As the action of aldose reductase (EC 1.1.1.21) is believed to be linked to the
pathogenesis of diabetic complications affecting the nervous, renal, and visual
systems, the development of therapeutic agents has attracted intense effort. We
report the refined 1.8 A x-ray structure of the human holoenzyme complexed with
zopolrestat, one of the most potent noncompetitive inhibitors. The zopolrestat
fits snugly in the hydrophobic active site pocket and induces a hinge-flap
motion of two peptide segments that closes the pocket. Excellent complementarity
and affinity are achieved on inhibitor binding by the formation of 110 contacts
(< or = 4 A) with 15 residues (10 hydrophobic), 13 with the NADPH coenzyme
and 9 with four water molecules. The structure is key to understanding the mode
of action of this class of inhibitors and for rational design of better
therapeutics.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Ahmed,
S.Villinger,
and
H.Gohlke
(2010).
Large-scale comparison of protein essential dynamics from molecular dynamics simulations and coarse-grained normal mode analyses.
|
| |
Proteins,
78,
3341-3352.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.A.Barski,
S.M.Tipparaju,
and
A.Bhatnagar
(2008).
The aldo-keto reductase superfamily and its role in drug metabolism and detoxification.
|
| |
Drug Metab Rev,
40,
553-624.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Carbone,
S.Endo,
R.Sumii,
R.P.Chung,
T.Matsunaga,
A.Hara,
and
O.El-Kabbani
(2008).
Structures of dimeric dihydrodiol dehydrogenase apoenzyme and inhibitor complex: probing the subunit interface with site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
176-187.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Rakowitz,
G.Piccolruaz,
C.Pirker,
and
B.Matuszczak
(2007).
Novel aldose reductase inhibitors derived from 6-[[(diphenylmethylene)amino]oxy]hexanoic acid.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
340,
202-208.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.K.Soni,
and
S.G.Kaskhedikar
(2007).
Exploring structural feature of aldose-reductase inhibition by 5-[[2-(omega-carboxyalkoxy)aryl]methylene]-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidine derivatives employing Fujita-Ban and Hansch approach.
|
| |
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo),
55,
72-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Biadene,
I.Hazemann,
A.Cousido,
S.Ginell,
A.Joachimiak,
G.M.Sheldrick,
A.Podjarny,
and
T.R.Schneider
(2007).
The atomic resolution structure of human aldose reductase reveals that rearrangement of a bound ligand allows the opening of the safety-belt loop.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
665-672.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Rakowitz,
A.Gmeiner,
and
B.Matuszczak
(2006).
Discovery of novel aldose reductase inhibitors characterized by an alkoxy-substituted phenylacetic acid core.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
339,
559-563.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Rakowitz,
H.Angerer,
and
B.Matuszczak
(2006).
Synthesis and aldose reductase inhibitory activities of novel O-substituted hydroxyphenylacetic acid derivatives.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
339,
547-558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Brownlee,
E.Carlson,
A.C.Milne,
E.Pape,
and
D.H.Harrison
(2006).
Structural and thermodynamic studies of simple aldose reductase-inhibitor complexes.
|
| |
Bioorg Chem,
34,
424-444.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Singh,
M.A.White,
K.V.Ramana,
J.M.Petrash,
S.J.Watowich,
A.Bhatnagar,
and
S.K.Srivastava
(2006).
Structure of a glutathione conjugate bound to the active site of aldose reductase.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
101-110.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Rakowitz,
B.Hennig,
M.Nagano,
S.Steger,
L.Costantino,
and
B.Matuszczak
(2005).
Synthesis of novel benzoic acid derivatives with benzothiazolyl subunit and evaluation as aldose reductase inhibitors.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
338,
411-418.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Rakowitz,
P.Muigg,
N.Schröder,
and
B.Matuszczak
(2005).
On the synthesis of bioisosters of o-benzothiazolyloxybenzoic acids and evaluation as aldose reductase inhibitors.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
338,
419-426.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.I.Howard,
R.Sanishvili,
R.E.Cachau,
A.Mitschler,
B.Chevrier,
P.Barth,
V.Lamour,
M.Van Zandt,
E.Sibley,
C.Bon,
D.Moras,
T.R.Schneider,
A.Joachimiak,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
Ultrahigh resolution drug design I: details of interactions in human aldose reductase-inhibitor complex at 0.66 A.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
792-804.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Ruiz,
I.Hazemann,
A.Mitschler,
A.Joachimiak,
T.Schneider,
M.Karplus,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
The crystallographic structure of the aldose reductase-IDD552 complex shows direct proton donation from tyrosine 48.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1347-1354.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
C.Darmanin,
T.R.Schneider,
I.Hazemann,
F.Ruiz,
M.Oka,
A.Joachimiak,
C.Schulze-Briese,
T.Tomizaki,
A.Mitschler,
and
A.Podjarny
(2004).
Ultrahigh resolution drug design. II. Atomic resolution structures of human aldose reductase holoenzyme complexed with Fidarestat and Minalrestat: implications for the binding of cyclic imide inhibitors.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
805-813.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Kraemer,
I.Hazemann,
A.D.Podjarny,
and
G.Klebe
(2004).
Virtual screening for inhibitors of human aldose reductase.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
814-823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Obmolova,
A.Teplyakov,
P.P.Khil,
A.J.Howard,
R.D.Camerini-Otero,
and
G.L.Gilliland
(2003).
Crystal structure of the Escherichia coli Tas protein, an NADP(H)-dependent aldo-keto reductase.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
323-325.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Teodoro,
G.N.Phillips,
and
L.E.Kavraki
(2003).
Understanding protein flexibility through dimensionality reduction.
|
| |
J Comput Biol,
10,
617-634.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
P.Ramsland,
C.Darmanin,
R.P.Chung,
and
A.Podjarny
(2003).
Structure of human aldose reductase holoenzyme in complex with statil: an approach to structure-based inhibitor design of the enzyme.
|
| |
Proteins,
50,
230-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Teague
(2003).
Implications of protein flexibility for drug discovery.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
2,
527-541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Mura,
M.Cappiello,
P.G.Vilardo,
I.Cecconi,
M.Dal Monte,
and
A.Del Corso
(2003).
Signalling potential and protein modifying ability of physiological thiols.
|
| |
Biofactors,
17,
279-285.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kinoshita,
H.Miyake,
T.Fujii,
S.Takakura,
and
T.Goto
(2002).
The structure of human recombinant aldose reductase complexed with the potent inhibitor zenarestat.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
622-626.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Anderson,
R.H.O'Neil,
T.S.Surti,
and
R.M.Stroud
(2001).
Approaches to solving the rigid receptor problem by identifying a minimal set of flexible residues during ligand docking.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
8,
445-457.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Nidetzky,
P.Mayr,
W.Neuhauser,
and
M.Puchberger
(2001).
Structural and functional properties of aldose xylose reductase from the D-xylose-metabolizing yeast Candida tenuis.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
130,
583-595.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Hur,
and
D.K.Wilson
(2000).
Crystallization and aldo-keto reductase activity of Gcy1p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
763-765.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Rastelli,
L.Antolini,
S.Benvenuti,
and
L.Costantino
(2000).
Structural bases for the inhibition of aldose reductase by phenolic compounds.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
8,
1151-1158.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Bohren,
and
C.E.Grimshaw
(2000).
The sorbinil trap: a predicted dead-end complex confirms the mechanism of aldose reductase inhibition.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
9967-9974.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sugiyama,
Z.Chen,
Y.S.Lee,
and
P.F.Kador
(2000).
Isolation of a non-covalent aldose reductase-nucleotide-inhibitor complex.
|
| |
Biochem Pharmacol,
59,
329-336.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.V.Ramana,
B.L.Dixit,
S.Srivastava,
G.K.Balendiran,
S.K.Srivastava,
and
A.Bhatnagar
(2000).
Selective recognition of glutathiolated aldehydes by aldose reductase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
12172-12180.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.El-Kabbani,
H.Rogniaux,
P.Barth,
R.P.Chung,
E.V.Fletcher,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
and
A.Podjarny
(2000).
Aldose and aldehyde reductases: correlation of molecular modeling and mass spectrometric studies on the binding of inhibitors to the active site.
|
| |
Proteins,
41,
407-414.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Ye,
D.Hyndman,
X.Li,
T.G.Flynn,
and
Z.Jia
(2000).
Crystal structure of CHO reductase, a member of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily.
|
| |
Proteins,
38,
41-48.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Calderone,
B.Chevrier,
M.Van Zandt,
V.Lamour,
E.Howard,
A.Poterszman,
P.Barth,
A.Mitschler,
J.Lu,
D.M.Dvornik,
G.Klebe,
O.Kraemer,
A.R.Moorman,
D.Moras,
and
A.Podjarny
(2000).
The structure of human aldose reductase bound to the inhibitor IDD384.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
536-540.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Rogniaux,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
P.Barth,
J.F.Biellmann,
J.Barbanton,
M.van Zandt,
B.Chevrier,
E.Howard,
A.Mitschler,
N.Potier,
L.Urzhumtseva,
D.Moras,
and
A.Podjarny
(1999).
Binding of aldose reductase inhibitors: correlation of crystallographic and mass spectrometric studies.
|
| |
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom,
10,
635-647.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Costantino,
G.Rastelli,
P.Vianello,
G.Cignarella,
and
D.Barlocco
(1999).
Diabetes complications and their potential prevention: aldose reductase inhibition and other approaches.
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
19,
3.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.J.Oates,
and
B.L.Mylari
(1999).
Aldose reductase inhibitors: therapeutic implications for diabetic complications.
|
| |
Expert Opin Investig Drugs,
8,
2095-2119.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Srivastava,
S.J.Watowich,
J.M.Petrash,
S.K.Srivastava,
and
A.Bhatnagar
(1999).
Structural and kinetic determinants of aldehyde reduction by aldose reductase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
42-54.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Crabbe,
and
D.Goode
(1998).
Aldose reductase: a window to the treatment of diabetic complications?
|
| |
Prog Retin Eye Res,
17,
313-383.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nakasako,
T.Motoyama,
Y.Kurahashi,
and
I.Yamaguchi
(1998).
Cryogenic X-ray crystal structure analysis for the complex of scytalone dehydratase of a rice blast fungus and its tight-binding inhibitor, carpropamid: the structural basis of tight-binding inhibition.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
9931-9939.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Srivastava,
T.M.Harter,
A.Chandra,
A.Bhatnagar,
S.K.Srivastava,
and
J.M.Petrash
(1998).
Kinetic studies of FR-1, a growth factor-inducible aldo-keto reductase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
12909-12917.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.S.Lee,
M.Hodoscek,
B.R.Brooks,
and
P.F.Kador
(1998).
Catalytic mechanism of aldose reductase studied by the combined potentials of quantum mechanics and molecular mechanics.
|
| |
Biophys Chem,
70,
203-216.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Scuric,
S.C.Stain,
W.F.Anderson,
and
J.J.Hwang
(1998).
New member of aldose reductase family proteins overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
|
| |
Hepatology,
27,
943-950.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Urzhumtsev,
F.Tête-Favier,
A.Mitschler,
J.Barbanton,
P.Barth,
L.Urzhumtseva,
J.F.Biellmann,
A.Podjarny,
and
D.Moras
(1997).
A 'specificity' pocket inferred from the crystal structures of the complexes of aldose reductase with the pharmaceutically important inhibitors tolrestat and sorbinil.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
601-612.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bennett,
R.H.Albert,
J.M.Jez,
H.Ma,
T.M.Penning,
and
M.Lewis
(1997).
Steroid recognition and regulation of hormone action: crystal structure of testosterone and NADP+ bound to 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
799-812.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Potier,
P.Barth,
D.Tritsch,
J.F.Biellmann,
and
A.Van Dorsselaer
(1997).
Study of non-covalent enzyme-inhibitor complexes of aldose reductase by electrospray mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
243,
274-282.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.el-Kabbani,
D.A.Carper,
M.H.McGowan,
Y.Devedjiev,
K.J.Rees-Milton,
and
T.G.Flynn
(1997).
Studies on the inhibitor-binding site of porcine aldehyde reductase: crystal structure of the holoenzyme-inhibitor ternary complex.
|
| |
Proteins,
29,
186-192.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bennett,
B.P.Schlegel,
J.M.Jez,
T.M.Penning,
and
M.Lewis
(1996).
Structure of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase complexed with NADP+.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
10702-10711.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.A.Barski,
K.H.Gabbay,
and
K.M.Bohren
(1996).
The C-terminal loop of aldehyde reductase determines the substrate and inhibitor specificity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
14276-14280.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Nakano,
and
J.M.Petrash
(1996).
Kinetic and spectroscopic evidence for active site inhibition of human aldose reductase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
11196-11202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.el-Kabbani,
K.Judge,
S.L.Ginell,
D.A.Myles,
L.J.DeLucas,
and
T.G.Flynn
(1995).
Structure of porcine aldehyde reductase holoenzyme.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
2,
687-692.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Gui,
T.Tanimoto,
Y.Kokai,
and
C.Nishimura
(1995).
Presence of a closely related subgroup in the aldo-ketoreductase family of the mouse.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
227,
448-453.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.J.Demopoulos,
and
E.Rekka
(1995).
Isomeric benzoylpyrroleacetic acids: some structural aspects for aldose reductase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities.
|
| |
J Pharm Sci,
84,
79-82.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

