
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.5.1.58
- protein farnesyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-cysteinyl-[protein] + (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate = S-(2E,6E)- farnesyl-L-cysteinyl-[protein] + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-cysteinyl-[protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
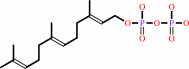 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
=
|
S-(2E,6E)- farnesyl-L-cysteinyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+); Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.5.1.59
- protein geranylgeranyltransferase type I.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
geranylgeranyl diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-[protein] = S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein] + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
geranylgeranyl diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 82.76% similarity
|
+
|
L-cysteinyl-[protein]
|
=
|
S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
45:2388-2409
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
3-Aminopyrrolidinone farnesyltransferase inhibitors: design of macrocyclic compounds with improved pharmacokinetics and excellent cell potency.
|
|
I.M.Bell,
S.N.Gallicchio,
M.Abrams,
L.S.Beese,
D.C.Beshore,
H.Bhimnathwala,
M.J.Bogusky,
C.A.Buser,
J.C.Culberson,
J.Davide,
M.Ellis-Hutchings,
C.Fernandes,
J.B.Gibbs,
S.L.Graham,
K.A.Hamilton,
G.D.Hartman,
D.C.Heimbrook,
C.F.Homnick,
H.E.Huber,
J.R.Huff,
K.Kassahun,
K.S.Koblan,
N.E.Kohl,
R.B.Lobell,
J.J.Lynch,
R.Robinson,
A.D.Rodrigues,
J.S.Taylor,
E.S.Walsh,
T.M.Williams,
C.B.Zartman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A series of macrocyclic 3-aminopyrrolidinone farnesyltransferase inhibitors
(FTIs) has been synthesized. Compared with previously described linear
3-aminopyrrolidinone FTIs such as compound 1, macrocycles such as 49 combined
improved pharmacokinetic properties with a reduced potential for side effects.
In dogs, oral bioavailability was good to excellent, and increases in plasma
half-life were due to attenuated clearance. It was observed that in vivo
clearance correlated with the flexibility of the molecules and this concept
proved useful in the design of FTIs that exhibited low clearance, such as FTI
78. X-ray crystal structures of compounds 49 and 66 complexed with
farnesyltransferase (FTase)-farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) were determined, and they
provide details of the key interactions in such ternary complexes. Optimization
of this 3-aminopyrrolidinone series of compounds led to significant increases in
potency, providing 83 and 85, the most potent inhibitors of FTase in cells
described to date.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Hast,
S.Fletcher,
C.G.Cummings,
E.E.Pusateri,
M.A.Blaskovich,
K.Rivas,
M.H.Gelb,
W.C.Van Voorhis,
S.M.Sebti,
A.D.Hamilton,
and
L.S.Beese
(2009).
Structural basis for binding and selectivity of antimalarial and anticancer ethylenediamine inhibitors to protein farnesyltransferase.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
16,
181-192.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.M.Driggers,
S.P.Hale,
J.Lee,
and
N.K.Terrett
(2008).
The exploration of macrocycles for drug discovery--an underexploited structural class.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
7,
608-624.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Aishima,
D.S.Russel,
L.J.Guibas,
P.D.Adams,
and
A.T.Brunger
(2005).
Automated crystallographic ligand building using the medial axis transform of an electron-density isosurface.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1354-1363.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Lackner,
R.M.Kindt,
P.M.Carroll,
K.Brown,
M.R.Cancilla,
C.Chen,
H.de Silva,
Y.Franke,
B.Guan,
T.Heuer,
T.Hung,
K.Keegan,
J.M.Lee,
V.Manne,
C.O'Brien,
D.Parry,
J.J.Perez-Villar,
R.K.Reddy,
H.Xiao,
H.Zhan,
M.Cockett,
G.Plowman,
K.Fitzgerald,
M.Costa,
and
P.Ross-Macdonald
(2005).
Chemical genetics identifies Rab geranylgeranyl transferase as an apoptotic target of farnesyl transferase inhibitors.
|
| |
Cancer Cell,
7,
325-336.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.G.Lombardino,
and
J.A.Lowe
(2004).
The role of the medicinal chemist in drug discovery--then and now.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
3,
853-862.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ekins
(2004).
Predicting undesirable drug interactions with promiscuous proteins in silico.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
9,
276-285.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Long,
P.J.Casey,
and
L.S.Beese
(2002).
Reaction path of protein farnesyltransferase at atomic resolution.
|
| |
Nature,
419,
645-650.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

