 |
PDBsum entry 1krs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1krs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.6
- lysine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Lys) + L-lysine + ATP = L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
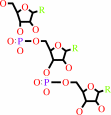 tRNA(Lys)
tRNA(Lys)
|
+
|
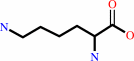 L-lysine
L-lysine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
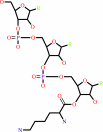 L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys)
L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
253:100-113
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Solution structure of the anticodon-binding domain of Escherichia coli lysyl-tRNA synthetase and studies of its interaction with tRNA(Lys).
|
|
S.Commans,
P.Plateau,
S.Blanquet,
F.Dardel.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A protein domain corresponding to residues 31 to 149 of the E. coli Lysyl-tRNA
synthetase species corresponding to the lysS gene was expressed and
15N-labelled. 1H and 15N NMR resonance assignments for this domain were obtained
by two-dimensional and three-dimensional homonuclear and heteronuclear
spectroscopy. Using distance geometry and simulated annealing, a
three-dimensional structure could be calculated using 701 NOE and 86 dihedral
angle restraints. It is composed of a five-stranded antiparallel beta-barrel
capped by three alpha-helices at its ends. This structure closely resembles that
of the N-terminal domain of the other E. coli lysyl-tRNA synthetase species
expressed from the lysU gene and is highly homologous to the fold observed for
the corresponding region of aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. It is shown that the
isolated N-terminal fragment of lysyl-tRNA synthetase can interact with
tRNA(Lys) as well as with poly (U), which mimics the anticodon sequence. Amino
acid residues involved in these interactions were identified and, in the case of
poly-U, a number of specific protein-RNA contacts were characterized. Specific
recognition of tRNA(Lys) involves a cluster of four structurally well-defined
aromatic residues, anchored on the beta-strands, and basic residues located on
the surrounding loops. This organization is reminiscent of other RNA binding
proteins, such as the U1A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. LysN structure contains a five-stranded
b-barrel. One face of the b-barrel features a cluster of
aromatic residues the side-chains of which are reasonably
well-defined in the solution structure. Shown are the
backbones of the 16 best conformers (red) and the
minimized mean structure (yellow), together with the
side-chains (in blue and white) of Phe85, Tyr98, His139 and
Phe129, from top to bottom. The side-chain of Gln96,
which is correctly defined, is also indicated.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Superposition of the
1
H-
15
N HSQC spectrum of LysN (black) with that of a tRNA
Lys
/LysN mixture of (0.25/1
stoichiometry; red), at 298 K, in 40 mM potassium phosphate (pH 7.0). Only peaks which show a significant broadening
and/or shift are labelled.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1995,
253,
100-113)
copyright 1995.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Hughes,
and
A.D.Ellington
(2010).
Rational design of an orthogonal tryptophanyl nonsense suppressor tRNA.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
38,
6813-6830.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Aliprandi,
C.Sizun,
J.Perez,
F.Mareuil,
S.Caputo,
J.L.Leroy,
B.Odaert,
S.Laalami,
M.Uzan,
and
F.Bontems
(2008).
S1 ribosomal protein functions in translation initiation and ribonuclease RegB activation are mediated by similar RNA-protein interactions: an NMR and SAXS analysis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
13289-13301.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.I.Choi,
K.S.Han,
C.W.Kim,
K.S.Ryu,
B.H.Kim,
K.H.Kim,
S.I.Kim,
T.H.Kang,
H.C.Shin,
K.H.Lim,
H.K.Kim,
J.M.Hyun,
and
B.L.Seong
(2008).
Protein solubility and folding enhancement by interaction with RNA.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
3,
e2677.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Watson,
W.M.Matousek,
E.L.Irimies,
and
A.T.Alexandrescu
(2007).
Partially folded states of staphylococcal nuclease highlight the conserved structural hierarchy of OB-fold proteins.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
9484-9494.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Levengood,
H.Roy,
R.Ishitani,
D.Söll,
O.Nureki,
and
M.Ibba
(2007).
Anticodon recognition and discrimination by the alpha-helix cage domain of class I lysyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
11033-11038.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Herring,
A.Ambrogelly,
C.R.Polycarpo,
and
D.Söll
(2007).
Recognition of pyrrolysine tRNA by the Desulfitobacterium hafniense pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
35,
1270-1278.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Brevet,
J.Chen,
S.Commans,
C.Lazennec,
S.Blanquet,
and
P.Plateau
(2003).
Anticodon recognition in evolution: switching tRNA specificity of an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase by site-directed peptide transplantation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
30927-30935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.L.Theobald,
R.M.Mitton-Fry,
and
D.S.Wuttke
(2003).
Nucleic acid recognition by OB-fold proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
32,
115-133.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Francin,
and
M.Mirande
(2003).
Functional dissection of the eukaryotic-specific tRNA-interacting factor of lysyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
1472-1479.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Mayer,
and
U.L.RajBhandary
(2002).
Conformational change of Escherichia coli initiator methionyl-tRNA(fMet) upon binding to methionyl-tRNA formyl transferase.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
30,
2844-2850.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Oussenko,
R.Sanchez,
and
D.H.Bechhofer
(2002).
Bacillus subtilis YhaM, a member of a new family of 3'-to-5' exonucleases in gram-positive bacteria.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
184,
6250-6259.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Swairjo,
A.J.Morales,
C.C.Wang,
A.R.Ortiz,
and
P.Schimmel
(2000).
Crystal structure of trbp111: a structure-specific tRNA-binding protein.
|
| |
EMBO J,
19,
6287-6298.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ibba,
and
D.Soll
(2000).
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
69,
617-650.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Gite,
Y.Li,
V.Ramesh,
and
U.L.RajBhandary
(2000).
Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase: role of amino acids conserved in the linker region and in the C-terminal domain on the specific recognition of the initiator tRNA.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
2218-2226.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Fraser,
S.J.Norris,
G.M.Weinstock,
O.White,
G.G.Sutton,
R.Dodson,
M.Gwinn,
E.K.Hickey,
R.Clayton,
K.A.Ketchum,
E.Sodergren,
J.M.Hardham,
M.P.McLeod,
S.Salzberg,
J.Peterson,
H.Khalak,
D.Richardson,
J.K.Howell,
M.Chidambaram,
T.Utterback,
L.McDonald,
P.Artiach,
C.Bowman,
M.D.Cotton,
C.Fujii,
S.Garland,
B.Hatch,
K.Horst,
K.Roberts,
M.Sandusky,
J.Weidman,
H.O.Smith,
and
J.C.Venter
(1998).
Complete genome sequence of Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete.
|
| |
Science,
281,
375-388.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.A.Stark,
and
R.T.Hay
(1998).
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) viral protein R (Vpr) interacts with Lys-tRNA synthetase: implications for priming of HIV-1 reverse transcription.
|
| |
J Virol,
72,
3037-3044.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Schmitt,
Y.Mechulam,
M.Fromant,
P.Plateau,
and
S.Blanquet
(1997).
Crystal structure at 1.2 A resolution and active site mapping of Escherichia coli peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
16,
4760-4769.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Schmitt,
S.Blanquet,
and
Y.Mechulam
(1996).
Structure of crystalline Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA(f)Met formyltransferase: comparison with glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
15,
4749-4758.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Cusack,
A.Yaremchuk,
and
M.Tukalo
(1996).
The crystal structures of T. thermophilus lysyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with E. coli tRNA(Lys) and a T. thermophilus tRNA(Lys) transcript: anticodon recognition and conformational changes upon binding of a lysyl-adenylate analogue.
|
| |
EMBO J,
15,
6321-6334.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

