 |
PDBsum entry 1kof

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.12
- gluconokinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-gluconate + ATP = 6-phospho-D-gluconate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
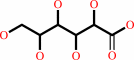 D-gluconate
D-gluconate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
 6-phospho-D-gluconate
6-phospho-D-gluconate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
318:1057-1069
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Conformational changes during the catalytic cycle of gluconate kinase as revealed by X-ray crystallography.
|
|
L.Kraft,
G.A.Sprenger,
Y.Lindqvist.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of gluconate kinase from Escherichia coli has been
determined to 2.0 A resolution by X-ray crystallography. The three-dimensional
structure was solved by multi-wavelength anomalous dispersion, using a crystal
of selenomethionine-substituted enzyme. Gluconate kinase is an alpha/beta
structure consisting of a twisted parallel beta-sheet surrounded by
alpha-helices with overall topology similar to nucleoside monophosphate (NMP)
kinases, such as adenylate kinase. In order to identify residues involved in
substrate binding and catalysis, structures of binary complexes with ATP, the
ATP analogue adenosine 5'-(beta,gamma-methylene) triphosphate and the product,
gluconate-6-phosphate have been determined. Significant conformational changes
are induced upon binding of ATP to the enzyme. The largest changes involve a
hinge-bending motion of the NMP(bind) part and a motion of the LID with adjacent
helices, which opens the cavity to the second substrate, gluconate. Opening of
the active site cleft upon ATP binding is the opposite of what has been observed
in the NMP kinase family so far, which usually close their active site to
prevent fortuitous hydrolysis of ATP. The conformational change positions the
side-chain of Arg120 to stack with the purine ring of ATP and the side-chain of
Arg124 is shifted to interact with the alpha-phosphate in ATP, at the same time
protecting ATP from solvent water. The beta and gamma-phosphate groups of ATP
bind in the predicted P-loop. A conserved lysine side-chain interacts with the
gamma-phosphate group, and might promote phosphoryl transfer.
Gluconate-6-phosphate binds with its phosphate group in a similar position as
the gamma-phosphate of ATP, consistent with inline phosphoryl transfer. The
gluconate binding-pocket in GntK is located in a different position than the
nucleoside binding-site usually found in NMP kinases.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Schematic view of the homodimer of gluconate
kinase. The colouring is by B-factor, from 10 Å2 (blue)
via grey to 50 Å2 (red). Two chloride ions bound in
apo-enzyme mark the binding sites for the phosphate and
carboxyl-group of gluconate-6-phosphate. This and all other
Figures were generated using BOBSCRIPT[46.] and Raster3D [47.]
if not otherwise specified.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Stereo picture of the superimposed C^a-traces of
(a) adenylate kinase (ligated with Ap[5]A, a bisubstrate
analogue) (yellow) and GntK (red) and of (b)
adenosine-5-phosphosulphate kinase (green) and GntK (red),
showing the differences in the NMP[bind] region and the LID.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2002,
318,
1057-1069)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Walia,
K.Gajendar,
and
A.Surolia
(2011).
Identification of critical residues of the mycobacterial dephosphocoenzyme a kinase by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
PLoS One,
6,
e15228.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Walia,
P.Kumar,
and
A.Surolia
(2009).
The role of UPF0157 in the folding of M. tuberculosis dephosphocoenzyme A kinase and the regulation of the latter by CTP.
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e7645.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Araiso,
R.L.Sherrer,
R.Ishitani,
J.M.Ho,
D.Söll,
and
O.Nureki
(2009).
Structure of a tRNA-dependent kinase essential for selenocysteine decoding.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
16215-16220.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Fucile,
S.Falconer,
and
D.Christendat
(2008).
Evolutionary diversification of plant shikimate kinase gene duplicates.
|
| |
PLoS Genet,
4,
e1000292.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Brylinski,
and
J.Skolnick
(2008).
What is the relationship between the global structures of apo and holo proteins?
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
363-377.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Chang,
X.X.Yan,
S.Y.Gu,
J.F.Liu,
and
D.C.Liang
(2008).
Crystal structure of human phosphomevalonate kinase at 1.8 A resolution.
|
| |
Proteins,
73,
254-258.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Sherrer,
P.O'Donoghue,
and
D.Söll
(2008).
Characterization and evolutionary history of an archaeal kinase involved in selenocysteinyl-tRNA formation.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
1247-1259.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Khan,
S.Xiang,
and
L.Tong
(2007).
Crystal structure of human nicotinamide riboside kinase.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1005-1013.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Herdendorf,
and
H.M.Miziorko
(2007).
Functional evaluation of conserved basic residues in human phosphomevalonate kinase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
11780-11788.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Tempel,
W.M.Rabeh,
K.L.Bogan,
P.Belenky,
M.Wojcik,
H.F.Seidle,
L.Nedyalkova,
T.Yang,
A.A.Sauve,
H.W.Park,
and
C.Brenner
(2007).
Nicotinamide riboside kinase structures reveal new pathways to NAD+.
|
| |
PLoS Biol,
5,
e263.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Pereira,
J.S.de Oliveira,
F.Canduri,
M.V.Dias,
M.S.Palma,
L.A.Basso,
D.S.Santos,
and
W.F.de Azevedo
(2004).
Structure of shikimate kinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals the binding of shikimic acid.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
2310-2319.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Fernandez-Fuentes,
A.Hermoso,
J.Espadaler,
E.Querol,
F.X.Aviles,
and
B.Oliva
(2004).
Classification of common functional loops of kinase super-families.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
539-555.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

