 |
PDBsum entry 1kcc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.1.15
- endo-polygalacturonase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n+m + H2O = (1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n + (1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)m
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n+m
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
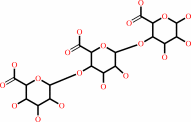 (1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n
|
+
|
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)m
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:6651-6659
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Active-site architecture of endopolygalacturonase I from Stereum purpureum revealed by crystal structures in native and ligand-bound forms at atomic resolution.
|
|
T.Shimizu,
T.Nakatsu,
K.Miyairi,
T.Okuno,
H.Kato.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Crystal structures of endopolygalacturonase from Stereum purpureum were solved
in native and two galacturonic acid complex states at atomic resolution.
Endopolygalacturonase catalyzes the hydrolysis of alpha-1,4-glycosidic linkage
of polygalacturonate in pectin. The native structure was determined by the
multiple wavelength anomalous dispersion method and was refined anisotropically
with SHELXL-97, with an R factor of 11.4% and an R(free) factor of 14.0% at 0.96
A resolution. The enzyme folds into a right-handed parallel beta-helix with 10
complete turns. The crystal structures of its binary complex with one
D-galacturonate and its ternary complex with two D-galacturonates were also
determined to identify the substrate binding site at 1.0 and 1.15 A resolutions,
respectively. In the binary complex, one beta-D-galactopyranuronate was found in
the +1 subsite, thus proving the strong affinity of the +1 subsite expected from
the bond cleavage frequency on oligogalacturonates. In the ternary complex, an
additional beta-D-galactofuranuronate was found in the -1 subsite. In both
subsites, the recognition of the galacturonate carboxy group is important in
galacturonate binding. In the +1 subsite, the carboxy group interacts with three
basic residues, His195, Arg226, and Lys228, which were conserved in all
endopolygalacturonases. In the -1 subsite, the unique nonprolyl cis-peptide bond
is believed to be involved in binding the carboxy group of the substrate. The
active site architecture of the complexes provides insight into the mechanism of
inverting glycosyl hydrolases and also sheds light on the basis of the
differences between the family 28 and the other inverting glycosyl hydrolases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Hidaka,
S.Fushinobu,
Y.Honda,
T.Wakagi,
H.Shoun,
and
M.Kitaoka
(2010).
Structural explanation for the acquisition of glycosynthase activity.
|
| |
J Biochem,
147,
237-244.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ogawa,
T.Shimizu,
T.Kimura,
K.Utoh,
T.Okuno,
and
K.Miyairi
(2010).
The pro-form of Stereum purpureum endopolygalacturonase I is inactivated by a pro-sequence in the C-terminal region.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
74,
558-562.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.da Silveira,
D.E.Pires,
R.C.Minardi,
C.Ribeiro,
C.J.Veloso,
J.C.Lopes,
W.Meira,
G.Neshich,
C.H.Ramos,
R.Habesch,
and
M.M.Santoro
(2009).
Protein cutoff scanning: A comparative analysis of cutoff dependent and cutoff free methods for prospecting contacts in proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
74,
727-743.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.T.Philominathan,
O.Matsushita,
R.Gensure,
and
J.Sakon
(2009).
Ca2+-induced linker transformation leads to a compact and rigid collagen-binding domain of Clostridium histolyticum collagenase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
3589-3601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Abbott,
and
A.B.Boraston
(2008).
Structural biology of pectin degradation by Enterobacteriaceae.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
72,
301.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.B.Vordtriede,
and
M.D.Yoder
(2008).
Crystallization, X-ray diffraction analysis and preliminary structure determination of the polygalacturonase PehA from Agrobacterium vitis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
645-647.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Fukuyama,
and
T.Okada
(2007).
Structures of cyanide, nitric oxide and hydroxylamine complexes of Arthromyces ramosusperoxidase at 100 K refined to 1.3 A resolution: coordination geometries of the ligands to the haem iron.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
472-477.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.D.Kluskens,
G.J.van Alebeek,
J.Walther,
A.G.Voragen,
W.M.de Vos,
and
J.van der Oost
(2005).
Characterization and mode of action of an exopolygalacturonase from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
5464-5473.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Douthit,
M.Dlakic,
D.E.Ohman,
and
M.J.Franklin
(2005).
Epimerase active domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgG, a protein that contains a right-handed beta-helix.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
4573-4583.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Golan,
D.Shallom,
A.Teplitsky,
G.Zaide,
S.Shulami,
T.Baasov,
V.Stojanoff,
A.Thompson,
Y.Shoham,
and
G.Shoham
(2004).
Crystal structures of Geobacillus stearothermophilus alpha-glucuronidase complexed with its substrate and products: mechanistic implications.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
3014-3024.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Michel,
K.Pojasek,
Y.Li,
T.Sulea,
R.J.Linhardt,
R.Raman,
V.Prabhakar,
R.Sasisekharan,
and
M.Cygler
(2004).
The structure of chondroitin B lyase complexed with glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides unravels a calcium-dependent catalytic machinery.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
32882-32896.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Choi,
B.H.Lee,
C.H.Chae,
and
W.Shin
(2004).
Computer modeling of the rhamnogalacturonase-"hairy" pectin complex.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
22-33.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Larsson,
R.Andersson,
J.Ståhlberg,
L.Kenne,
and
T.A.Jones
(2003).
Dextranase from Penicillium minioluteum: reaction course, crystal structure, and product complex.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
1111-1121.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Takeda,
H.Miyatake,
N.Yokota,
S.Matsuyama,
H.Tokuda,
and
K.Miki
(2003).
A practical phasing procedure using the MAD method without the aid of XAFS measurements: successful solution in the structure determination of the outer-membrane lipoprotein carrier LolA.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1440-1446.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

