 |
PDBsum entry 1k5q

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.5.1.11
- penicillin amidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Penicillin Biosynthesis and Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a penicillin + H2O = 6-aminopenicillanate + a carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 penicillin
penicillin
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
6-aminopenicillanate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.18% similarity
|
+
|
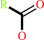 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Protein Eng Des Sel
17:473-480
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and kinetic studies on ligand binding in wild-type and active-site mutants of penicillin acylase.
|
|
W.B.Alkema,
C.M.Hensgens,
H.J.Snijder,
E.Keizer,
B.W.Dijkstra,
D.B.Janssen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Penicillin acylase catalyses the condensation of Calpha-substituted phenylacetic
acids with beta-lactam nucleophiles, producing semi-synthetic beta-lactam
antibiotics. For efficient synthesis a low affinity for phenylacetic acid and a
high affinity for Calpha-substituted phenylacetic acid derivatives is desirable.
We made three active site mutants, alphaF146Y, betaF24A and alphaF146Y/betaF24A,
which all had a 2- to 10-fold higher affinity for Calpha-substituted compounds
than wild-type enzyme. In addition, betaF24A had a 20-fold reduced affinity for
phenylacetic acid. The molecular basis of the improved properties was
investigated by X-ray crystallography. These studies showed that the higher
affinity of alphaF146Y for (R)-alpha-methylphenylacetic acid can be explained by
van der Waals interactions between alphaY146:OH and the Calpha-substituent. The
betaF24A mutation causes an opening of the phenylacetic acid binding site. Only
(R)-alpha-methylphenylacetic acid, but not phenylacetic acid, induces a
conformation with the ligand tightly bound, explaining the weak binding of
phenylacetic acid. A comparison of the betaF24A structure with other open
conformations of penicillin acylase showed that betaF24 has a fixed position,
whereas alphaF146 acts as a flexible lid on the binding site and reorients its
position to achieve optimal substrate binding.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Bernardino,
P.Fernandes,
and
L.P.Fonseca
(2010).
Improved specific productivity in cephalexin synthesis by immobilized PGA in silica magnetic micro-particles.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
107,
753-762.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wang,
Q.Zhang,
H.Huang,
Z.Yuan,
D.Ding,
S.Yang,
and
W.Jiang
(2007).
Increasing synthetic performance of penicillin G acylase from Bacillus megaterium by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
74,
1023-1030.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

