 |
PDBsum entry 1k5h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1k5h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase. Chain: a, b, c. Synonym: dxp reductoisomerase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 83333. Strain: k12. Cellular_location: chromosomal DNA. Gene: dxr. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.232
|
R-free:
|
0.284
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.Reuter,S.Sanderbrand,H.Jomaa,J.Wiesner,I.Steinbrecher,E.Beck, M.Hintz,G.Klebe,M.T.Stubbs
|
Key ref:

|
 |
K.Reuter
et al.
(2002).
Crystal structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase, a crucial enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis.
J Biol Chem,
277,
5378-5384.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Oct-01
|
Release date:
|
27-Feb-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P45568
(DXR_ECOLI) -
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
398 a.a.
398 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.267
- 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate + NADP+ = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
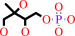 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
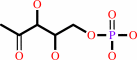 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+) or cobalt cation or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
277:5378-5384
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase, a crucial enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis.
|
|
K.Reuter,
S.Sanderbrand,
H.Jomaa,
J.Wiesner,
I.Steinbrecher,
E.Beck,
M.Hintz,
G.Klebe,
M.T.Stubbs.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We have solved the 2.5-A crystal structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate
reductoisomerase, an enzyme involved in the mevalonate-independent
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. The
structure reveals that the enzyme is present as a homodimer. Each monomer
displays a V-like shape and is composed of an amino-terminal dinucleotide
binding domain, a connective domain, and a carboxyl-terminal four-helix bundle
domain. The connective domain is responsible for dimerization and harbors most
of the active site. The strictly conserved acidic residues Asp(150), Glu(152),
Glu(231), and Glu(234) are clustered at the putative active site and are
probably involved in the binding of divalent cations mandatory for enzyme
activity. The connective and four-helix bundle domains show significant mobility
upon superposition of the dinucleotide binding domains of the three
conformational states present in the asymmetric unit of the crystal. A still
more pronounced flexibility is observed for a loop spanning residues 186 to 216,
which adopts two completely different conformations within the three protein
conformers. A possible involvement of this loop in an induced fit during
substrate binding is discussed.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate via the
MEP pathway. Enzymes are represented by the names of their gene
products. Dxs, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase, Dxr,
1-deoxy- D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase, IspD,
CDP-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate synthetase, IspE,
CDP-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate kinase, IspF,
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Stereo view of the three crystallographically
independent molecules of the asymmetric unit. The orientation of
the proteins as well as the color code for the domains are
identical to those in Fig. 2A. Superposition of the dinucleotide
binding domains shows that corresponding C  atoms of
the connective domains and the four-helix bundles differ
significantly. The flexible loop (residues 186-216) of molecule
A is colored in ochre, those of molecules B and C are colored in
magenta. The yellow NADPH cofactor modeled into the structure is
shown in stick representation. atoms of
the connective domains and the four-helix bundles differ
significantly. The flexible loop (residues 186-216) of molecule
A is colored in ochre, those of molecules B and C are colored in
magenta. The yellow NADPH cofactor modeled into the structure is
shown in stick representation.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2002,
277,
5378-5384)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.E.Englert,
C.Richter,
J.Wiesner,
M.Hintz,
H.Jomaa,
and
H.Schwalbe
(2011).
NMR Studies of DOXP Reductoisomerase and its Inhibitor Complex.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
468-476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Eoh,
P.J.Brennan,
and
D.C.Crick
(2009).
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis MEP (2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate) pathway as a new drug target.
|
| |
Tuberculosis (Edinb),
89,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Williams,
and
J.Andrew McCammon
(2009).
Conformational Dynamics of the Flexible Catalytic Loop in Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-Phosphate Reductoisomerase.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
73,
26-38.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Giessmann,
P.Heidler,
T.Haemers,
S.Van Calenbergh,
A.Reichenberg,
H.Jomaa,
C.Weidemeyer,
S.Sanderbrand,
J.Wiesner,
and
A.Link
(2008).
Towards new antimalarial drugs: synthesis of non-hydrolyzable phosphate mimics as feed for a predictive QSAR study on 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase inhibitors.
|
| |
Chem Biodivers,
5,
643-656.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lauw,
V.Illarionova,
A.Bacher,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.Eisenreich
(2008).
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: studies on the mechanism of 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate synthase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
4060-4073.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
M.A.Avery,
and
C.R.McCurdy
(2007).
Toward Mycobacterium tuberculosis DXR inhibitor design: homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
21,
511-522.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Ortmann,
J.Wiesner,
K.Silber,
G.Klebe,
H.Jomaa,
and
M.Schlitzer
(2007).
Novel deoxyxylulosephosphate-reductoisomerase inhibitors: fosmidomycin derivatives with spacious acyl residues.
|
| |
Arch Pharm (Weinheim),
340,
483-490.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Yajima,
K.Hara,
D.Iino,
Y.Sasaki,
T.Kuzuyama,
K.Ohsawa,
and
H.Seto
(2007).
Structure of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in a quaternary complex with a magnesium ion, NADPH and the antimalarial drug fosmidomycin.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
466-470.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Henriksson,
C.Björkelid,
S.L.Mowbray,
and
T.Unge
(2006).
The 1.9 A resolution structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, a potential drug target.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
807-813.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Cornish,
J.R.Roth,
and
C.D.Poulter
(2006).
Lethal mutations in the isoprenoid pathway of Salmonella enterica.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
1444-1450.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wiesner,
and
F.Seeber
(2005).
The plastid-derived organelle of protozoan human parasites as a target of established and emerging drugs.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
9,
23-44.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kemp,
M.S.Alphey,
C.S.Bond,
M.A.Ferguson,
S.Hecht,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2005).
The identification of isoprenoids that bind in the intersubunit cavity of Escherichia coli 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase by complementary biophysical methods.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
45-52.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Mercklé,
A.de Andrés-Gómez,
B.Dick,
R.J.Cox,
and
C.R.Godfrey
(2005).
A fragment-based approach to understanding inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
6,
1866-1874.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Sgraja,
L.E.Kemp,
N.Ramsden,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2005).
A double mutation of Escherichia coli2C-methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase disrupts six hydrogen bonds with, yet fails to prevent binding of, an isoprenoid diphosphate.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
625-629.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Brandt,
M.A.Dessoy,
M.Fulhorst,
W.Gao,
M.H.Zenk,
and
L.A.Wessjohann
(2004).
A proposed mechanism for the reductive ring opening of the cyclodiphosphate MEcPP, a crucial transformation in the new DXP/MEP pathway to isoprenoids based on modeling studies and feeding experiments.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
5,
311-323.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Miallau,
M.S.Alphey,
L.E.Kemp,
G.A.Leonard,
S.M.McSweeney,
S.Hecht,
A.Bacher,
W.Eisenreich,
F.Rohdich,
and
W.N.Hunter
(2003).
Biosynthesis of isoprenoids: crystal structure of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
9173-9178.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.S.Rangarajan,
J.Sivaraman,
A.Matte,
and
M.Cygler
(2002).
Crystal structure of D-ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RpiA) from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Proteins,
48,
737-740.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Hoeffler,
D.Tritsch,
C.Grosdemange-Billiard,
and
M.Rohmer
(2002).
Isoprenoid biosynthesis via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway. Mechanistic investigations of the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
4446-4457.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

