 |
PDBsum entry 1jlt

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain B:
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
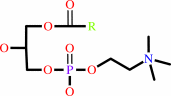 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
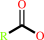 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
57:1552-1559
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of the neurotoxic complex vipoxin at 1.4 A resolution.
|
|
S.Banumathi,
K.R.Rajashankar,
C.Nötzel,
B.Aleksiev,
T.P.Singh,
N.Genov,
C.Betzel.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Vipoxin is a neurotoxic postsynaptic heterodimeric complex from the venom of
Vipera ammodytes meridionalis, the most toxic snake in Europe. It consists of a
basic and highly toxic phospholipase A(2) and an acidic non-toxic protein
inhibitor. The two polypeptide chains have the same chain length and share 62%
amino-acid identity. Vipoxin is a unique example of evolution of the catalytic
and toxic phospholipase A(2) functions into inhibitory and non-toxic functions.
The crystal structure of the complex has been determined by the
molecular-replacement method and refined to 1.4 A resolution to an R factor of
18.2%. The complex formation decreases the accessible surface area of the two
subunits by approximately 1480 A(2), which results in a reduction of toxicity
and catalytic activity. The catalytic and substrate-binding sites of the vipoxin
phospholipase A(2) are identical or similar to those of other group I/II
enzymes. Two 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol molecules are present in the hydrophobic
channel close to the active site. The two subunits lack calcium ions. The
negatively charged Asp49 of the phospholipase A(2), which participates in the
Ca(2+)-binding sites of other snake-venom phospholipase A(2)s, is neutralized by
the side chain of Lys69 from the inhibitor. Attempts have been made to identify
the toxicity region and to explain the reduced catalytic activity and toxicity
of the phospholipase A(2) subunit.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Ribbon representation of the PLA[2]. The disulfide
bridges and active-site residues are shown as ball-and-stick
models. Secondary-structure regions and the Ca^2+-binding region
as well as regions of pharmacological functions are labelled.
Additionally, conserved and invariant residues found in
approximately 200 sequences of PLA[2]s (Danse et al.,
1997[Danse, J. M., Gasparini, S. & Menez, A. (1997). Venom
Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Structure, Function and Mechanism,
edited by R. M. Kini, pp. 29-72. Chichester: John Wiley &
Sons.]) are labelled at their C^  position. position.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2 Stereo figure showing the electron density in the
active-site region with superimposed amino acids, solvent water
and one MPD molecule. All hydrogen bonds and interactions are
indicated with their distances.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2001,
57,
1552-1559)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.Doley,
and
R.M.Kini
(2009).
Protein complexes in snake venom.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
66,
2851-2871.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Ferquel,
L.de Haro,
V.Jan,
I.Guillemin,
S.Jourdain,
A.Teynié,
J.d'Alayer,
and
V.Choumet
(2007).
Reappraisal of Vipera aspis Venom Neurotoxicity.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
2,
e1194.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Jabeen,
N.Singh,
R.K.Singh,
J.Jasti,
S.Sharma,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Crystal structure of a heterodimer of phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera at 2.3 A resolution reveals the presence of a new PLA2-like protein with a novel cys 32-Cys 49 disulphide bridge with a bound sugar at the substrate-binding site.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
329-337.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Gao,
V.G.Starkov,
V.I.Tsetlin,
Y.N.Utkin,
Z.J.Lin,
and
R.C.Bi
(2005).
Isolation and preliminary crystallographic studies of two new phospholipases A2 from Vipera nikolskii venom.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
189-192.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Guillemin,
C.Bouchier,
T.Garrigues,
A.Wisner,
and
V.Choumet
(2003).
Sequences and structural organization of phospholipase A2 genes from Vipera aspis aspis, V. aspis zinnikeri and Vipera berus berus venom. Identification of the origin of a new viper population based on ammodytin I1 heterogeneity.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
2697-2706.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

