 |
PDBsum entry 1jlh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.9
- glucose-6-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
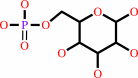 alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
|
=
|
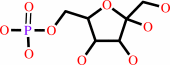 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochim Biophys Acta
1645:117-122
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of human phosphoglucose isomerase and analysis of the initial catalytic steps.
|
|
A.T.Cordeiro,
P.H.Godoi,
C.H.Silva,
R.C.Garratt,
G.Oliva,
O.H.Thiemann.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The second enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI),
catalyses an intracellular aldose-ketose isomerization. Here we describe the
human recombinant PGI structure (hPGI) solved in the absence of active site
ligands. Crystals isomorphous to those previously reported were used to collect
a 94% complete data set to a limiting resolution of 2.1 A. From the comparison
between the free active site hPGI structure and the available human and rabbit
PGI (rPGI) structures, a mechanism for protein initial catalytic steps is
proposed. Binding of the phosphate moiety of the substrate to two distinct
elements of the active site is responsible for driving a series of structural
changes resulting in the polarisation of the active site histidine, priming it
for the initial ring-opening step of catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
B.Schlichting,
M.Felgendreher,
and
P.Schönheit
(2005).
Cupin-type phosphoglucose isomerases (Cupin-PGIs) constitute a novel metal-dependent PGI family representing a convergent line of PGI evolution.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
1621-1631.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.T.Cordeiro,
P.A.Michels,
L.F.Delboni,
and
O.H.Thiemann
(2004).
The crystal structure of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase from Leishmania mexicana reveals novel active site features.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
2765-2772.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.T.Cordeiro,
R.Hardré,
P.A.Michels,
L.Salmon,
L.F.Delboni,
and
O.H.Thiemann
(2004).
Leishmania mexicana mexicana glucose-6-phosphate isomerase: crystallization, molecular-replacement solution and inhibition.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
915-919.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
D.Wendorff,
and
P.Schönheit
(2004).
Bifunctional phosphoglucose/phosphomannose isomerases from the Archaea Aeropyrum pernix and Thermoplasma acidophilum constitute a novel enzyme family within the phosphoglucose isomerase superfamily.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
2262-2272.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

