 |
PDBsum entry 1j3b

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.49
- phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
oxaloacetate + ATP = phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
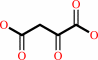 oxaloacetate
oxaloacetate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
=
|
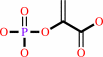 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
61:1500-1507
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of ATP-dependent phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from Thermus thermophilus HB8 showing the structural basis of induced fit and thermostability.
|
|
M.Sugahara,
N.Ohshima,
Y.Ukita,
M.Sugahara,
N.Kunishima.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In order to understand the induced fit and the thermostabilization mechanisms of
ATP-dependent phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, the crystal structure of the
enzyme from the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus HB8 (TtPEPCK) was
determined and compared with those of orthologues of known structure from two
mesophilic organisms. The protomer structures in these orthologues, which
exhibit open/closed interdomain conformations, are similar. Isomorphous crystals
of unliganded and ATP-bound TtPEPCK were obtained. The asymmetric units of both
crystal forms contain two protomers A and B with closed and open conformations,
respectively. ATP was only observed in the interdomain cleft of the closed
protomer, suggesting that the induced fit of TtPEPCK agrees with the so-called
;conformational selection' mechanism where ligand binding is not essential for
domain closure although its binding leads to the stabilization of the closed
state. A bound calcium observed in the N-terminal domain of TtPEPCK probably
contributes to the thermal stability. A combination of hydrophobic effects, ion
pairs and entropic effects might also contribute to the thermostability of
TtPEPCK.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1 Ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of TtPEPCK. The
asymmetric unit of the ATP-liganded form comprising the A chain
with closed conformation (blue and light blue) and the B chain
with open conformation (red and pink) is shown. The N- and
C-terminal domains are distinguished by dark and light colours,
respectively. Bound calcium ions are depicted as green spheres.
ATP, phosphate ions and glycerol molecules are depicted as stick
models.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4 Stereo representation of the calcium-binding site.
Bound calcium and water are depicted as green and red spheres,
respectively.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2005,
61,
1500-1507)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Pérez,
and
E.Cardemil
(2010).
Saccharomyces cerevisiae phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase: the relevance of Glu299 and Leu460 for nucleotide binding.
|
| |
Protein J,
29,
299-305.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

