 |
PDBsum entry 1j0c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Acc deaminase mutated to catalytic residue
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: accd, acc deaminase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Williopsis saturnus. Organism_taxid: 4906. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.224
|
R-free:
|
0.299
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Ose,A.Fujino,M.Yao,M.Honma,I.Tanaka
|
Key ref:

|
 |
T.Ose
et al.
(2003).
Reaction intermediate structures of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase: insight into PLP-dependent cyclopropane ring-opening reaction.
J Biol Chem,
278,
41069-41076.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Nov-02
|
Release date:
|
12-May-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q7M523
(1A1D_CYBSA) -
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Cyberlindnera saturnus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
341 a.a.
341 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.99.7
- 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
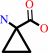 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate
1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
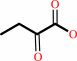 2-oxobutanoate
2-oxobutanoate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
278:41069-41076
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Reaction intermediate structures of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase: insight into PLP-dependent cyclopropane ring-opening reaction.
|
|
T.Ose,
A.Fujino,
M.Yao,
N.Watanabe,
M.Honma,
I.Tanaka.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes have been evolved to catalyze
diverse substrates and to cause the reaction to vary.
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase catalyzes the cyclopropane
ring-opening reaction followed by deamination specifically. Since it was
discovered in 1978, the enzyme has been widely investigated from the mechanistic
and physiological viewpoints because the substrate is a precursor of the plant
hormone ethylene and the enzymatic reaction includes a cyclopropane
ring-opening. We have previously reported the crystal structure of the native
enzyme. Here we report the crystal structures of the two reaction intermediates
created by the mutagenesis complexed with the substrate. The substrate was
validated in the active site of two forms: 1). covalent-bonded external aldimine
with the coenzyme in the K51T form and 2). the non-covalent interaction around
the coenzyme in the Y295F form. The orientations of the substrate in both
structures were quite different form each other. In concert with other
site-specific mutation experiments, this experiment revealed the ingenious and
unique strategies that are used to achieve the specific activity. The substrate
incorporated into the active site is reactivated by a two-phenol charge relay
system to lead to the formation of a Schiff base with the coenzyme. The
catalytic Lys51 residue may play a novel role to abstract the methylene proton
from the substrate in cooperation with other factors, the carboxylate group of
the substrate and the electron-adjusting apparatuses of the coenzyme.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 5.
FIG. 5. A view around active site of which is concerned
with incorporated ACC. The charge relay system from two tyrosine
residues and the modeling position of Lys51 are shown.
|
 |
Figure 7.
FIG. 7. The putative total mechanism catalyzed by yACCD.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2003,
278,
41069-41076)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Todorovic,
and
B.R.Glick
(2008).
The interconversion of ACC deaminase and D: -cysteine desulfhydrase by directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Planta,
229,
193-205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Arshad,
M.Saleem,
and
S.Hussain
(2007).
Perspectives of bacterial ACC deaminase in phytoremediation.
|
| |
Trends Biotechnol,
25,
356-362.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.R.Glick
(2005).
Modulation of plant ethylene levels by the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
251,
1-7.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

