 |
PDBsum entry 1j04

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.44
- alanine--glyoxylate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
glyoxylate + L-alanine = glycine + pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
glyoxylate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 83.33% similarity
|
+
|
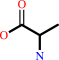 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
=
|
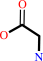 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
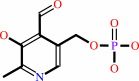 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.51
- serine--pyruvate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-serine + pyruvate = 3-hydroxypyruvate + L-alanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
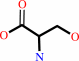 L-serine
L-serine
|
+
|
pyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
=
|
3-hydroxypyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 85.71% similarity
|
+
|
 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
66:233-236
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural implications of a G170R mutation of alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase that is associated with peroxisome-to-mitochondrion mistargeting.
|
|
S.Djordjevic,
X.Zhang,
M.Bartlam,
S.Ye,
Z.Rao,
C.J.Danpure.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In a subset of patients with the hereditary kidney-stone disease primary
hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1), the liver-specific enzyme alanine:glyoxylate
aminotransferase (AGT) is mistargeted from peroxisomes to mitochondria. This is
a consequence of the combined presence of the common P11L polymorphism and a
disease-specific G170R mutation. In this paper, the crystal structure of mutant
human AGT containing the G170R replacement determined at a resolution of 2.6 A
is reported. The crystal structure of AGT consists of an intimate dimer in which
an extended N-terminal segment of 21 amino acids from one subunit wraps as an
elongated irregular coil around the outside of the crystallographic
symmetry-related subunit. In addition to the N-terminal segment, the monomer
structure contains a large domain of 261 amino acids and a small C-terminal
domain of 110 amino acids. Comparison of the mutant AGT structure and that of
wild-type normal AGT shows that the two structures are almost identical, with a
backbone-atom r.m.s. deviation of 0.34 A. However, evidence of significant local
structural changes in the vicinity of the G170R mutation might be linked to the
apparent decrease in protein stability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

