 |
PDBsum entry 1i5c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signaling protein, transferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1i5c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.13.3
- histidine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
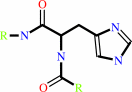 protein L-histidine
protein L-histidine
|
=
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Struct Biol
8:353-360
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Nucleotide binding by the histidine kinase CheA.
|
|
A.M.Bilwes,
C.M.Quezada,
L.R.Croal,
B.R.Crane,
M.I.Simon.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
To probe the structural basis for protein histidine kinase (PHK) catalytic
activity and the prospects for PHK-specific inhibitor design, we report the
crystal structures for the nucleotide binding domain of Thermotoga maritima CheA
with ADP and three ATP analogs (ADPNP, ADPCP and TNP-ATP) bound with either
Mg(2+) or Mn(2+). The conformation of ADPNP bound to CheA and related ATPases
differs from that reported in the ADPNP complex of PHK EnvZ. Interactions of the
active site with the nucleotide gamma-phosphate and its associated Mg(2+) ion
are linked to conformational changes in an ATP-lid that could mediate
recognition of the substrate domain. The inhibitor TNP-ATP binds CheA with its
phosphates in a nonproductive conformation and its adenine and trinitrophenyl
groups in two adjacent binding pockets. The trinitrophenyl interaction may be
exploited for designing CheA-targeted drugs that would not interfere with host
ATPases.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Stereo view of ADPCP -Mg2+ bound to P4. Three ADPCP
phosphates, the Asn 409 carbonyl and two water molecules (W6,
W7) coordinate Mg2+ in octahedral geometry (black bonds).
Peptide nitrogens from Gly 506 and Met 507 in the P-loop
(magenta) hydrogen bond to the nucleotide phosphates. The omit
electron density map (green) is contoured at 2.5  .
Figure produced with Bobscript41 and Raster3d^42. .
Figure produced with Bobscript41 and Raster3d^42.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Stereo views of the interactions between P4 and bound
nucleotides. a, ADPCP -Mg2+ in MolA hydrogen bonds (dashed
lines) to water molecules (blue spheres, W), protein side chains
in the nucleotide pocket (gray) and the main chain of the
ATP-lid (magenta). b, ADP bound in MolA. c, ADP bound in MolB
has a different conformation for the  -phosphate
than in MolA. Figure produced with Molscript43 and Raster3d^42. -phosphate
than in MolA. Figure produced with Molscript43 and Raster3d^42.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Struct Biol
(2001,
8,
353-360)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Toyoshima,
S.Yonekura,
J.Tsueda,
and
S.Iwasawa
(2011).
Trinitrophenyl derivatives bind differently from parent adenine nucleotides to Ca2+-ATPase in the absence of Ca2+.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
1833-1838.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.King-Scott,
P.V.Konarev,
S.Panjikar,
R.Jordanova,
D.I.Svergun,
and
P.A.Tucker
(2011).
Structural characterization of the multidomain regulatory protein Rv1364c from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Structure,
19,
56-69.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Guarnieri,
B.S.Blagg,
and
R.Zhao
(2011).
A high-throughput TNP-ATP displacement assay for screening inhibitors of ATP-binding in bacterial histidine kinases.
|
| |
Assay Drug Dev Technol,
9,
174-183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kahraman,
R.J.Morris,
R.A.Laskowski,
A.D.Favia,
and
J.M.Thornton
(2010).
On the diversity of physicochemical environments experienced by identical ligands in binding pockets of unrelated proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
78,
1120-1136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Bhatnagar,
P.P.Borbat,
A.M.Pollard,
A.M.Bilwes,
J.H.Freed,
and
B.R.Crane
(2010).
Structure of the ternary complex formed by a chemotaxis receptor signaling domain, the CheA histidine kinase, and the coupling protein CheW as determined by pulsed dipolar ESR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
3824-3841.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Stewart
(2010).
Protein histidine kinases: assembly of active sites and their regulation in signaling pathways.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
13,
133-141.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.H.Chen,
C.Schilde,
and
P.Schaap
(2010).
Functional dissection of adenylate cyclase R, an inducer of spore encapsulation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
41724-41731.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Eaton,
and
R.C.Stewart
(2009).
The two active sites of Thermotoga maritima CheA dimers bind ATP with dramatically different affinities.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
6412-6422.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Gao,
and
A.M.Stock
(2009).
Biological insights from structures of two-component proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
63,
133-154.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Yamada,
H.Sugimoto,
M.Kobayashi,
A.Ohno,
H.Nakamura,
and
Y.Shiro
(2009).
Structure of PAS-linked histidine kinase and the response regulator complex.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
1333-1344.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Noriega,
R.Schmidt,
M.J.Gray,
L.L.Chen,
and
V.Stewart
(2008).
Autophosphorylation and dephosphorylation by soluble forms of the nitrate-responsive sensors NarX and NarQ from Escherichia coli K-12.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
3869-3876.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kovári,
O.Barabás,
B.Varga,
A.Békési,
F.Tölgyesi,
J.Fidy,
J.Nagy,
and
B.G.Vértessy
(2008).
Methylene substitution at the alpha-beta bridging position within the phosphate chain of dUDP profoundly perturbs ligand accommodation into the dUTPase active site.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
308-319.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Frederick,
E.A.Rogers,
and
R.T.Marconi
(2008).
Analysis of a growth-phase-regulated two-component regulatory system in the periodontal pathogen Treponema denticola.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
6162-6169.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Mukherjee,
M.Sharma,
H.Urlaub,
G.P.Bourenkov,
R.Jahn,
T.C.Südhof,
and
M.C.Wahl
(2008).
CASK Functions as a Mg2+-independent neurexin kinase.
|
| |
Cell,
133,
328-339.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.A.Plesniak,
K.Botsch,
M.Leibrand,
M.Kelly,
D.Sem,
J.A.Adams,
and
P.Jennings
(2008).
Transferred NOE and saturation transfer difference NMR studies of novobiocin binding to EnvZ suggest binding mode similar to DNA gyrase.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
71,
28-35.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Sachdeva,
A.Narayan,
R.Misra,
V.Brahmachari,
and
Y.Singh
(2008).
Loss of kinase activity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis multidomain protein Rv1364c.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
6295-6308.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Perez,
and
A.M.Stock
(2007).
Characterization of the Thermotoga maritima chemotaxis methylation system that lacks pentapeptide-dependent methyltransferase CheR:MCP tethering.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
63,
363-378.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Miller,
S.C.Kohout,
K.A.Gilman,
and
J.J.Falke
(2006).
CheA Kinase of bacterial chemotaxis: chemical mapping of four essential docking sites.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
8699-8711.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.S.Blagg,
and
T.D.Kerr
(2006).
Hsp90 inhibitors: small molecules that transform the Hsp90 protein folding machinery into a catalyst for protein degradation.
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
26,
310-338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Avila,
B.A.Kornilayev,
and
B.S.Blagg
(2006).
Development and optimization of a useful assay for determining Hsp90's inherent ATPase activity.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
14,
1134-1142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Soulat,
J.M.Jault,
B.Duclos,
C.Geourjon,
A.J.Cozzone,
and
C.Grangeasse
(2006).
Staphylococcus aureus operates protein-tyrosine phosphorylation through a specific mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
14048-14056.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.B.Gagnon,
R.England,
and
E.Delpire
(2006).
Characterization of SPAK and OSR1, regulatory kinases of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
26,
689-698.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Baker,
P.M.Wolanin,
and
J.B.Stock
(2006).
Signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis.
|
| |
Bioessays,
28,
9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Weis
(2006).
Inch by inch, row by row.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
13,
382-384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Conners,
E.F.Mongodin,
M.R.Johnson,
C.I.Montero,
K.E.Nelson,
and
R.M.Kelly
(2006).
Microbial biochemistry, physiology, and biotechnology of hyperthermophilic Thermotoga species.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
30,
872-905.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Qin,
J.Zhang,
B.Xu,
L.Chen,
Y.Wu,
X.Yang,
X.Shen,
S.Molin,
A.Danchin,
H.Jiang,
and
D.Qu
(2006).
Structure-based discovery of inhibitors of the YycG histidine kinase: new chemical leads to combat Staphylococcus epidermidis infections.
|
| |
BMC Microbiol,
6,
96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Marina,
C.D.Waldburger,
and
W.A.Hendrickson
(2005).
Structure of the entire cytoplasmic portion of a sensor histidine-kinase protein.
|
| |
EMBO J,
24,
4247-4259.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Quezada,
D.J.Hamel,
C.Gradinaru,
A.M.Bilwes,
F.W.Dahlquist,
B.R.Crane,
and
M.I.Simon
(2005).
Structural and chemical requirements for histidine phosphorylation by the chemotaxis kinase CheA.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
30581-30585.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Gadelle,
C.Bocs,
M.Graille,
and
P.Forterre
(2005).
Inhibition of archaeal growth and DNA topoisomerase VI activities by the Hsp90 inhibitor radicicol.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
33,
2310-2317.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Brautigam,
Y.Chelliah,
and
J.Deisenhofer
(2004).
Tetramerization and ATP binding by a protein comprising the A, B, and C domains of rat synapsin I.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
11948-11956.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Toyoshima,
and
T.Mizutani
(2004).
Crystal structure of the calcium pump with a bound ATP analogue.
|
| |
Nature,
430,
529-535.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Yuan,
and
C.Kent
(2004).
Identification of critical residues of choline kinase A2 from Caenorhabditis elegans.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
17801-17809.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Nakamura,
H.Kumita,
K.Imai,
T.Iizuka,
and
Y.Shiro
(2004).
ADP reduces the oxygen-binding affinity of a sensory histidine kinase, FixL: the possibility of an enhanced reciprocating kinase reaction.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
2742-2746.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Borkovich,
L.A.Alex,
O.Yarden,
M.Freitag,
G.E.Turner,
N.D.Read,
S.Seiler,
D.Bell-Pedersen,
J.Paietta,
N.Plesofsky,
M.Plamann,
M.Goodrich-Tanrikulu,
U.Schulte,
G.Mannhaupt,
F.E.Nargang,
A.Radford,
C.Selitrennikoff,
J.E.Galagan,
J.C.Dunlap,
J.J.Loros,
D.Catcheside,
H.Inoue,
R.Aramayo,
M.Polymenis,
E.U.Selker,
M.S.Sachs,
G.A.Marzluf,
I.Paulsen,
R.Davis,
D.J.Ebbole,
A.Zelter,
E.R.Kalkman,
R.O'Rourke,
F.Bowring,
J.Yeadon,
C.Ishii,
K.Suzuki,
W.Sakai,
and
R.Pratt
(2004).
Lessons from the genome sequence of Neurospora crassa: tracing the path from genomic blueprint to multicellular organism.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
68,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.D.Corbett,
and
J.M.Berger
(2004).
Structure, molecular mechanisms, and evolutionary relationships in DNA topoisomerases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
33,
95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Fernandez-Fuentes,
A.Hermoso,
J.Espadaler,
E.Querol,
F.X.Aviles,
and
B.Oliva
(2004).
Classification of common functional loops of kinase super-families.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
539-555.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Wynn,
M.Kato,
M.Machius,
J.L.Chuang,
J.Li,
D.R.Tomchick,
and
D.T.Chuang
(2004).
Molecular mechanism for regulation of the human mitochondrial branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
2185-2196.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Shaver,
and
P.D.Sniegowski
(2003).
Spontaneously arising mutL mutators in evolving Escherichia coli populations are the result of changes in repeat length.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
185,
6076-6082.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Classen,
S.Olland,
and
J.M.Berger
(2003).
Structure of the topoisomerase II ATPase region and its mechanism of inhibition by the chemotherapeutic agent ICRF-187.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
10629-10634.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hiratsuka
(2003).
Fluorescent and colored trinitrophenylated analogs of ATP and GTP.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
3479-3485.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Campbell,
S.Masuda,
J.L.Sun,
O.Muzzin,
C.A.Olson,
S.Wang,
and
S.A.Darst
(2002).
Crystal structure of the Bacillus stearothermophilus anti-sigma factor SpoIIAB with the sporulation sigma factor sigmaF.
|
| |
Cell,
108,
795-807.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Stephenson,
and
J.A.Hoch
(2002).
Virulence- and antibiotic resistance-associated two-component signal transduction systems of Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria as targets for antimicrobial therapy.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
93,
293-305.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.N.Levit,
T.W.Grebe,
and
J.B.Stock
(2002).
Organization of the receptor-kinase signaling array that regulates Escherichia coli chemotaxis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
36748-36754.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.M.Wolanin,
P.A.Thomason,
and
J.B.Stock
(2002).
Histidine protein kinases: key signal transducers outside the animal kingdom.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
3,
REVIEWS3013.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhu,
and
M.Inouye
(2002).
The role of the G2 box, a conserved motif in the histidine kinase superfamily, in modulating the function of EnvZ.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
45,
653-663.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Guarné,
M.S.Junop,
and
W.Yang
(2001).
Structure and function of the N-terminal 40 kDa fragment of human PMS2: a monomeric GHL ATPase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
20,
5521-5531.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.N.Steussy,
K.M.Popov,
M.M.Bowker-Kinley,
R.B.Sloan,
R.A.Harris,
and
J.A.Hamilton
(2001).
Structure of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Novel folding pattern for a serine protein kinase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
37443-37450.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Machius,
J.L.Chuang,
R.M.Wynn,
D.R.Tomchick,
and
D.T.Chuang
(2001).
Structure of rat BCKD kinase: nucleotide-induced domain communication in a mitochondrial protein kinase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
11218-11223.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

