 |
PDBsum entry 1hpc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transit peptide
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1hpc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transit peptide
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Refined structures at 2 angstroms and 2.2 angstroms of the two forms of the h-protein, a lipoamide-containing protein of the glycine decarboxylase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
H protein of the glycine cleavage system. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pisum sativum. Pea. Organism_taxid: 3888
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Pares,C.Cohen-Addad,L.Sieker,M.Neuburger,R.Douce
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Pares
et al.
(1995).
Refined structures at 2 and 2.2 A resolution of two forms of the H-protein, a lipoamide-containing protein of the glycine decarboxylase complex.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
51,
1041-1051.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Feb-94
|
Release date:
|
08-May-95
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P16048
(GCSH_PEA) -
Glycine cleavage system H protein, mitochondrial from Pisum sativum
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
165 a.a.
131 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.4.2
- glycine dehydrogenase (aminomethyl-transferring).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Glycine Cleavage System
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-[(R)-lipoyl]-L-lysyl-[glycine-cleavage complex H protein] + glycine + H+ = N6-[(R)-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[glycine- cleavage complex H protein] + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-[(R)-lipoyl]-L-lysyl-[glycine-cleavage complex H protein]
|
+
|
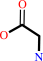 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
N(6)-[(R)-S(8)-aminomethyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[glycine- cleavage complex H protein]
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
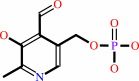 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
51:1041-1051
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Refined structures at 2 and 2.2 A resolution of two forms of the H-protein, a lipoamide-containing protein of the glycine decarboxylase complex.
|
|
S.Pares,
C.Cohen-Addad,
L.C.Sieker,
M.Neuburger,
R.Douce.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
H-protein, a 14 kDa lipoic acid-containing protein is a component of the glycine
decarboxylase complex. This complex which consists of four protein components
(P-, H-, T- and L-protein) catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of glycine.
The mechanistic heart of the complex is provided by the lipoic acid attached to
a lysine residue of the H-protein. It undergoes a cycle of transformations, i.e.
reductive methylamination, methylamine transfer, and electron transfer. We
present details of the crystal structures of the H-protein, in its two forms,
H-Pro(Ox) with oxidized lipoamide and H-Pro(Met) with methylamine-loaded
lipoamide. X-ray diffraction data were collected from crystals of H-Pro(Ox) to 2
and H-Pro(Met) to 2.2 A resolution. The final R-factor value for the H-Pro(Ox)
is 18.5% for data with F > 2sigma. in the range of 8.0-2.0 A resolution. The
refinement confirmed our previous model, refined to 2.6 A, of a beta-fold
sandwich structure with two beta-sheets. The lipoamide arm attached to Lys63,
located in the loop of a hairpin conformation, is clearly visible at the surface
of the protein. The H-Pro(Met) has been crystallized in orthorhombic and
monoclinic forms and the structures were solved by molecular replacement,
starting from the H-Pro(Ox) model. The orthorhombic structure has been refined
with a final R-factor value of 18.5% for data with F > 2sigma in the range of
8.0-2.2 A resolution. The structure of the monoclinic form has been refined with
a final R-factor value of 17.5% for data with F > 2sigma in the range of
15.0-3.0 A. In these two structures which have similar packing, the protein
conformation is identical to the conformation found in the H-Pro(Ox). The main
change lies in the position of the lipoamide group which has moved significantly
when loaded with methylamine. In this case the methylamine-lipoamide group is
tucked into a cleft at the surface of the protein where it is stabilized by
hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts. Thus, it is totally protected and not
free to move in aqueous solvent. In addition, the H-protein presents some
sequence and structural analogies with other lipoate- and biotin-containing
proteins and also with proteins of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar
phosphotransferase system.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Fig. 6. H-PrOMet orthorhombic crystl form. Plot of the average B-factor
values. Same represenaton as in Fig. 3.
|
 |
Figure 9.
Fig. 9. Stereo viw of the structure of the H-protein an location of the
lipoamide arm. (a H-Proox, (b) H-PrOMet.
|
 |
Figure 11.
Fig. 11. Connolly surface of the cavity containing the lipoamide group.
This cavity is essentially identical in H-PrOMet and H-Proox. The
figue was generated with the program MS (Connolly, 1983) and
TURBO-FRODO (Roussel & Cambiau, 1989).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(1995,
51,
1041-1051)
copyright 1995.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Higashiura,
T.Kurakane,
M.Matsuda,
M.Suzuki,
K.Inaka,
M.Sato,
T.Kobayashi,
T.Tanaka,
H.Tanaka,
K.Fujiwara,
and
A.Nakagawa
(2010).
High-resolution X-ray crystal structure of bovine H-protein at 0.88 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
698-708.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.K.Lokanath,
C.Kuroishi,
N.Okazaki,
and
N.Kunishima
(2005).
Crystal structure of a component of glycine cleavage system: T-protein from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3 at 1.5 A resolution.
|
| |
Proteins,
58,
769-773.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Roche,
and
M.J.Field
(2001).
Theoretical study of the conformation of the lipoamide arm in a mutant H protein.
|
| |
Proteins,
45,
237-240.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Faure,
J.Bourguignon,
M.Neuburger,
D.MacHerel,
L.Sieker,
R.Ober,
R.Kahn,
C.Cohen-Addad,
and
R.Douce
(2000).
Interaction between the lipoamide-containing H-protein and the lipoamide dehydrogenase (L-protein) of the glycine decarboxylase multienzyme system 2. Crystal structures of H- and L-proteins.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
267,
2890-2898.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Roche,
K.Hinsen,
and
M.J.Field
(1999).
Theoretical study of the conformation of the H-protein lipoamide arm as a function of its terminal group.
|
| |
Proteins,
36,
228-237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Gueguen,
D.Macherel,
M.Neuburger,
C.S.Pierre,
M.Jaquinod,
P.Gans,
R.Douce,
and
J.Bourguignon
(1999).
Structural and functional characterization of H protein mutants of the glycine decarboxylase complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
26344-26352.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

