 |
PDBsum entry 1hkc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Phosphotransferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1hkc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.1
- hexokinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a D-hexose + ATP = a D-hexose 6-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
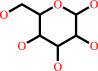 D-hexose
D-hexose
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
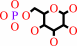 D-hexose 6-phosphate
D-hexose 6-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
282:345-357
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Regulation of hexokinase I: crystal structure of recombinant human brain hexokinase complexed with glucose and phosphate.
|
|
A.E.Aleshin,
C.Zeng,
H.D.Bartunik,
H.J.Fromm,
R.B.Honzatko.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Hexokinase I, the pacemaker of glycolysis in brain tissue and red blood cells,
is comprised of two similar domains fused into a single polypeptide chain. The
C-terminal half of hexokinase I is catalytically active, whereas the N-terminal
half is necessary for the relief of product inhibition by phosphate. A
crystalline complex of recombinant human hexokinase I with glucose and phosphate
(2.8 A resolution) reveals a single binding site for phosphate and glucose at
the N-terminal half of the enzyme. Glucose and phosphate stabilize the
N-terminal half in a closed conformation. Unexpectedly, glucose binds weakly to
the C-terminal half of the enzyme and does not by itself stabilize a closed
conformation. Evidently a stable, closed C-terminal half requires either ATP or
glucose 6-phosphate along with glucose. The crystal structure here, in
conjunction with other studies in crystallography and directed mutation, puts
the phosphate regulatory site at the N-terminal half, the site of potent product
inhibition at the C-terminal half, and a secondary site for the weak interaction
of glucose 6-phosphate at the N-terminal half of the enzyme. The relevance of
crystal structures of hexokinase I to the properties of monomeric hexokinase I
and oligomers of hexokinase I bound to the surface of mitochondria is discussed.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Stereoview of a single polypeptide chain in the
glucose/P[i] dimer of hexokinase I. Residue 465 separates the N
and C-terminal halves. The color code is as follows, yellow,
small domains (residues 75 to 209, 448 to 465 and residues 523
to 657, 896 to 913); light purple, large domains (residues 13 to
74, 210 to 447 and residues 466 to 522, 658 to 895); dark
purple, segments participating in intrachain salt links
(residues 242 to 250, 796 to 813); blue, bound glucose; red,
bound phosphate; green, bound metal ions. The view is
perpendicular to the dimer 2-fold axis. Drawing made using
MOLSCRIPT [Kraulis 1991].
|
 |
Figure 9.
Figure 9. Superposition of a model for hexokinase I with
the N-terminal half in an open conformation (bold lines) onto
the glucose/P[i] complex, using the small domain of the
N-terminal half as a basis for the superposition. The transition
from a closed to an opened conformation moves the large domain
of the N-terminal half relative to the remainder of the enzyme
and should influence contacts between the N and C-terminal
halves.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1998,
282,
345-357)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Wyatt,
R.Wu,
W.Rabeh,
H.W.Park,
M.Ghanefar,
and
H.Ardehali
(2010).
Regulation and cytoprotective role of hexokinase III.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e13823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zhang,
C.Li,
T.Shi,
K.Chen,
X.Shen,
and
H.Jiang
(2009).
Lys169 of human glucokinase is a determinant for glucose phosphorylation: implication for the atomic mechanism of glucokinase catalysis.
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e6304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.B.Iynedjian
(2009).
Molecular physiology of mammalian glucokinase.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
66,
27-42.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Molnes,
L.Bjørkhaug,
O.Søvik,
P.R.Njølstad,
and
T.Flatmark
(2008).
Catalytic activation of human glucokinase by substrate binding: residue contacts involved in the binding of D-glucose to the super-open form and conformational transitions.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
2467-2481.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Nakamura,
A.Miranda-Vizuete,
K.Miki,
C.Mori,
and
E.M.Eddy
(2008).
Cleavage of disulfide bonds in mouse spermatogenic cell-specific type 1 hexokinase isozyme is associated with increased hexokinase activity and initiation of sperm motility.
|
| |
Biol Reprod,
79,
537-545.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tinto,
A.Zagari,
M.Capuano,
A.De Simone,
V.Capobianco,
G.Daniele,
M.Giugliano,
R.Spadaro,
A.Franzese,
and
L.Sacchetti
(2008).
Glucokinase gene mutations: structural and genotype-phenotype analyses in MODY children from South Italy.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
3,
e1870.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Kuser,
F.Cupri,
L.Bleicher,
and
I.Polikarpov
(2008).
Crystal structure of yeast hexokinase PI in complex with glucose: A classical "induced fit" example revised.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
731-740.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Orlova,
E.C.Garner,
V.E.Galkin,
J.Heuser,
R.D.Mullins,
and
E.H.Egelman
(2007).
The structure of bacterial ParM filaments.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
14,
921-926.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Reisler,
and
E.H.Egelman
(2007).
Actin structure and function: what we still do not understand.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
36133-36137.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Tsai
(2007).
Function of interdomain alpha-helix in human brain hexokinase: covalent linkage and catalytic regulation between N- and C-terminal halves.
|
| |
J Biomed Sci,
14,
195-202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Nishimasu,
S.Fushinobu,
H.Shoun,
and
T.Wakagi
(2007).
Crystal structures of an ATP-dependent hexokinase with broad substrate specificity from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
9923-9931.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zhang,
C.Li,
K.Chen,
W.Zhu,
X.Shen,
and
H.Jiang
(2006).
Conformational transition pathway in the allosteric process of human glucokinase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
13368-13373.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Skaff,
C.S.Kim,
H.J.Tsai,
R.B.Honzatko,
and
H.J.Fromm
(2005).
Glucose 6-phosphate release of wild-type and mutant human brain hexokinases from mitochondria.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
38403-38409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kawai,
T.Mukai,
S.Mori,
B.Mikami,
and
K.Murata
(2005).
Hypothesis: structures, evolution, and ancestor of glucose kinases in the hexokinase family.
|
| |
J Biosci Bioeng,
99,
320-330.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Kamata,
M.Mitsuya,
T.Nishimura,
J.Eiki,
and
Y.Nagata
(2004).
Structural basis for allosteric regulation of the monomeric allosteric enzyme human glucokinase.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
429-438.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Mukai,
S.Kawai,
S.Mori,
B.Mikami,
and
K.Murata
(2004).
Crystal structure of bacterial inorganic polyphosphate/ATP-glucomannokinase. Insights into kinase evolution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
50591-50600.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.V.Lunin,
Y.Li,
J.D.Schrag,
P.Iannuzzi,
M.Cygler,
and
A.Matte
(2004).
Crystal structures of Escherichia coli ATP-dependent glucokinase and its complex with glucose.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
6915-6927.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Mukai,
S.Kawai,
S.Mori,
B.Mikami,
and
K.Murata
(2003).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of inorganic polyphosphate/ATP-glucomannokinase from Arthrobacter sp. strain KM.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1662-1664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Gottlob,
N.Majewski,
S.Kennedy,
E.Kandel,
R.B.Robey,
and
N.Hay
(2001).
Inhibition of early apoptotic events by Akt/PKB is dependent on the first committed step of glycolysis and mitochondrial hexokinase.
|
| |
Genes Dev,
15,
1406-1418.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Aleshin,
M.Malfois,
X.Liu,
C.S.Kim,
H.J.Fromm,
R.B.Honzatko,
M.H.Koch,
and
D.I.Svergun
(1999).
Nonaggregating mutant of recombinant human hexokinase I exhibits wild-type kinetics and rod-like conformations in solution.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
8359-8366.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Rosano,
E.Sabini,
M.Rizzi,
D.Deriu,
G.Murshudov,
M.Bianchi,
G.Serafini,
M.Magnani,
and
M.Bolognesi
(1999).
Binding of non-catalytic ATP to human hexokinase I highlights the structural components for enzyme-membrane association control.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
1427-1437.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ardehali,
R.L.Printz,
R.R.Whitesell,
J.M.May,
and
D.K.Granner
(1999).
Functional interaction between the N- and C-terminal halves of human hexokinase II.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
15986-15989.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Liu,
C.S.Kim,
F.T.Kurbanov,
R.B.Honzatko,
and
H.J.Fromm
(1999).
Dual mechanisms for glucose 6-phosphate inhibition of human brain hexokinase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
31155-31159.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

