 |
PDBsum entry 1hcb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase(oxo-acid)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1hcb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
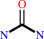 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Mol Biol
241:226-232
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Enzyme-substrate interactions. Structure of human carbonic anhydrase I complexed with bicarbonate.
|
|
V.Kumar,
K.K.Kannan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of HCAI-HCO3- complex has been refined with 10-1.6A X-ray
diffraction data to an R-value of 17.7%. The structure reveals monodentate
binding of the HCO3- anion at an apical tetrahedral position to the zinc ion.
The binding mode and interactions of HCO3- in HCAI differ from that in HCAII.
The activity linked H2O/OH- group in the free HCAI is replaced by the hydroxyl
group of the bicarbonate anion. This result rules out the rearrangement of the
bound HCO3- advocated earlier to explain the microscopic reversibility of the
catalysed reaction. From the geometry of the H-bonds between Glu106-Thr199 pair
and Glu117-His119 couple, the glutamic acids are expected to be ionized and
accept H-bonds from their partners. The product-inhibiton by HCO3- anion is
explained on the basis of proton localization on His119 in the Glu117-His119
couple. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that Glu117-His119
tunes the ionicity of the Zn2+ and the binding strength of HCO3- anion. A pi
hydrogen bond is observed between a water and phenyl ring of the Tyr114 residue.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.Alterio,
S.M.Monti,
E.Truppo,
C.Pedone,
C.T.Supuran,
and
G.De Simone
(2010).
The first example of a significant active site conformational rearrangement in a carbonic anhydrase-inhibitor adduct: the carbonic anhydrase I-topiramate complex.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
8,
3528-3533.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Sjöblom,
M.Polentarutti,
and
K.Djinovic-Carugo
(2009).
Structural study of X-ray induced activation of carbonic anhydrase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
10609-10613.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Krishnamurthy,
G.K.Kaufman,
A.R.Urbach,
I.Gitlin,
K.L.Gudiksen,
D.B.Weibel,
and
G.M.Whitesides
(2008).
Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
108,
946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Thiry,
B.Masereel,
J.M.Dogné,
C.T.Supuran,
J.Wouters,
and
C.Michaux
(2007).
Exploration of the Binding Mode of Indanesulfonamides as Selective Inhibitors of Human Carbonic Anhydrase Type VII by Targeting Lys 91.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
2,
1273-1280.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Marino,
K.Hayakawa,
K.Hatada,
M.Benfatto,
A.Rizzello,
M.Maffia,
and
L.Bubacco
(2007).
Structural features that govern enzymatic activity in carbonic anhydrase from a low-temperature adapted fish, Chionodraco hamatus.
|
| |
Biophys J,
93,
2781-2790.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Jude,
A.L.Banerjee,
M.K.Haldar,
S.Manokaran,
B.Roy,
S.Mallik,
D.K.Srivastava,
and
D.W.Christianson
(2006).
Ultrahigh resolution crystal structures of human carbonic anhydrases I and II complexed with "two-prong" inhibitors reveal the molecular basis of high affinity.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
128,
3011-3018.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Chothia,
T.Hubbard,
S.Brenner,
H.Barns,
and
A.Murzin
(1997).
Protein folds in the all-beta and all-alpha classes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
26,
597-627.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lindskog
(1997).
Structure and mechanism of carbonic anhydrase.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
74,
1.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

