 |
PDBsum entry 1hc7

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1hc7
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Prolyl-tRNA synthetase from thermus thermophilus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Prolyl-tRNA synthetase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: prolyl-tRNA ligase. Other_details: each monomer contains 1 zinc atom co-ordinated to cys- 427, cys432, cys-458, cys-461
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus. Organism_taxid: 274. Strain: hb-8. Other_details: purification described in reference 2
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.43Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.206
|
R-free:
|
0.234
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Yaremchuk,M.Tukalo,S.Cusack
|
Key ref:

|
 |
A.Yaremchuk
et al.
(2001).
A succession of substrate induced conformational changes ensures the amino acid specificity of Thermus thermophilus prolyl-tRNA synthetase: comparison with histidyl-tRNA synthetase.
J Mol Biol,
309,
989.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
26-Apr-01
|
Release date:
|
18-Jun-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q5SM28
(SYP_THET8) -
Proline--tRNA ligase from Thermus thermophilus (strain ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / HB8)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
477 a.a.
464 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.15
- proline--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Pro) + L-proline + ATP = L-prolyl-tRNA(Pro) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
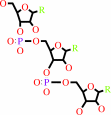 tRNA(Pro)
tRNA(Pro)
|
+
|
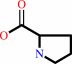 L-proline
L-proline
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
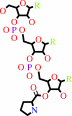 L-prolyl-tRNA(Pro)
L-prolyl-tRNA(Pro)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
309:989
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A succession of substrate induced conformational changes ensures the amino acid specificity of Thermus thermophilus prolyl-tRNA synthetase: comparison with histidyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
|
A.Yaremchuk,
M.Tukalo,
M.Grøtli,
S.Cusack.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We describe the recognition by Thermus thermophilus prolyl-tRNA synthetase
(ProRSTT) of proline, ATP and prolyl-adenylate and the sequential conformational
changes occurring when the substrates bind and the activated intermediate is
formed. Proline and ATP binding cause respectively conformational changes in the
proline binding loop and motif 2 loop. However formation of the activated
intermediate is necessary for the final conformational ordering of a ten residue
peptide ("ordering loop") close to the active site which would appear
to be essential for functional tRNA 3' end binding. These induced fit
conformational changes ensure that the enzyme is highly specific for proline
activation and aminoacylation. We also present new structures of apo and AMP
bound histidyl-tRNA synthetase (HisRS) from T. thermophilus which we compare to
our previous structures of the histidine and histidyl-adenylate bound enzyme.
Qualitatively, similar results to those observed with T. thermophilus
prolyl-tRNA synthetase are found. However histidine binding is sufficient to
induce the co-operative ordering of the topologically equivalent histidine
binding loop and ordering loop. These two examples contrast with most other
class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases whose pocket for the cognate amino acid
side-chain is largely preformed. T. thermophilus prolyl-tRNA synthetase appears
to be the second class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, after HisRS, to use a
positively charged amino acid instead of a divalent cation to catalyse the amino
acid activation reaction.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. The prolyl-adenylate complex. (a) Unbiased
positive difference electron density for the prolyl-adenylate
analogue in the active site of ProRSTT contoured at 3.0 sigma
after refinement of the structure without inclusion of the
substrate in the model. (b) Hydrogen bond interactions (red
dotted lines) of the prolyl-adenylate in the active site of
ProRSTT. Class II synthetase conserved features, the TXE loop
(gold), motif 2 (outlined in blue) and motif 3 (outlined in red)
are shown.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Induced fit recognition of histidine by HisRSTT.
The histidine bound conformation of the histidine-1 loop is
purple with white side-chains; that of the unbound form is pink
with green side-chains. The histidine substrate is in yellow.
Hydrogen bonds stabilising the position of the bound histidine
and the catalytic Arg259 are shown as dotted red lines.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2001,
309,
989-0)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Zhou,
L.Sun,
X.L.Yang,
and
P.Schimmel
(2013).
ATP-directed capture of bioactive herbal-based medicine on human tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Nature,
494,
121-124.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Merritt,
T.L.Arakaki,
J.R.Gillespie,
E.T.Larson,
A.Kelley,
N.Mueller,
A.J.Napuli,
J.Kim,
L.Zhang,
C.L.Verlinde,
E.Fan,
F.Zucker,
F.S.Buckner,
W.C.van Voorhis,
and
W.G.Hol
(2010).
Crystal structures of trypanosomal histidyl-tRNA synthetase illuminate differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic homologs.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
397,
481-494.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Srinivasan,
R.R.Sauers,
M.O.Fenley,
A.H.Boschitsch,
A.Matsumoto,
A.V.Colasanti,
and
W.K.Olson
(2009).
Properties of the Nucleic-acid Bases in Free and Watson-Crick Hydrogen-bonded States: Computational Insights into the Sequence-dependent Features of Double-helical DNA.
|
| |
Biophys Rev,
1,
13-20.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Burke,
S.An,
and
K.Musier-Forsyth
(2008).
Functional guanine-arginine interaction between tRNAPro and prolyl-tRNA synthetase that couples binding and catalysis.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1784,
1222-1225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Francklyn
(2008).
DNA polymerases and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: shared mechanisms for ensuring the fidelity of gene expression.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
11695-11703.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Shen,
M.Zhou,
B.Yang,
Y.Yu,
X.Dong,
and
J.Ding
(2008).
Catalytic mechanism of the tryptophan activation reaction revealed by crystal structures of human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase in different enzymatic states.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
1288-1299.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.C.Chen,
and
C.Lim
(2008).
Predicting RNA-binding sites from the protein structure based on electrostatics, evolution and geometry.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
e29.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Guth,
and
C.S.Francklyn
(2007).
Kinetic discrimination of tRNA identity by the conserved motif 2 loop of a class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
25,
531-542.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Vasil'eva,
and
N.A.Moor
(2007).
Interaction of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases with tRNA: general principles and distinguishing characteristics of the high-molecular-weight substrate recognition.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
72,
247-263.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Krasovska,
J.Sefcikova,
K.Réblová,
B.Schneider,
N.G.Walter,
and
J.Sponer
(2006).
Cations and hydration in catalytic RNA: molecular dynamics of the hepatitis delta virus ribozyme.
|
| |
Biophys J,
91,
626-638.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Richards,
C.A.Theimer,
L.D.Finger,
and
J.Feigon
(2006).
Structure of the Tetrahymena thermophila telomerase RNA helix II template boundary element.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
34,
816-825.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Sukuru,
T.Crepin,
Y.Milev,
L.C.Marsh,
J.B.Hill,
R.J.Anderson,
J.C.Morris,
A.Rohatgi,
G.O'Mahony,
M.Grøtli,
F.Danel,
M.G.Page,
M.Härtlein,
S.Cusack,
M.A.Kron,
and
L.A.Kuhn
(2006).
Discovering new classes of Brugia malayi asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors and relating specificity to conformational change.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
20,
159-178.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Hati,
B.Ziervogel,
J.Sternjohn,
F.C.Wong,
M.C.Nagan,
A.E.Rosen,
P.G.Siliciano,
J.W.Chihade,
and
K.Musier-Forsyth
(2006).
Pre-transfer editing by class II prolyl-tRNA synthetase: role of aminoacylation active site in "selective release" of noncognate amino acids.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
27862-27872.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Crepin,
A.Yaremchuk,
M.Tukalo,
and
S.Cusack
(2006).
Structures of two bacterial prolyl-tRNA synthetases with and without a cis-editing domain.
|
| |
Structure,
14,
1511-1525.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Murayama,
M.Kato-Murayama,
K.Katsura,
T.Uchikubo-Kamo,
M.Yamaguchi-Hirafuji,
M.Kawazoe,
R.Akasaka,
K.Hanawa-Suetsugu,
C.Hori-Takemoto,
T.Terada,
M.Shirouzu,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2005).
Structure of a putative trans-editing enzyme for prolyl-tRNA synthetase from Aeropyrum pernix K1 at 1.7 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
26-29.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Champagne,
M.Sissler,
Y.Larrabee,
S.Doublié,
and
C.S.Francklyn
(2005).
Activation of the hetero-octameric ATP phosphoribosyl transferase through subunit interface rearrangement by a tRNA synthetase paralog.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
34096-34104.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Kim,
A.George,
M.Evans,
and
V.P.Conticello
(2004).
Cotranslational incorporation of a structurally diverse series of proline analogues in an Escherichia coli expression system.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
5,
928-936.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Ferré-D'Amaré
(2003).
RNA-modifying enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
13,
49-55.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.C.Wong,
P.J.Beuning,
C.Silvers,
and
K.Musier-Forsyth
(2003).
An isolated class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase insertion domain is functional in amino acid editing.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
52857-52864.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yang,
F.Jossinet,
N.Leontis,
L.Chen,
J.Westbrook,
H.Berman,
and
E.Westhof
(2003).
Tools for the automatic identification and classification of RNA base pairs.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
31,
3450-3460.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Bovee,
M.A.Pierce,
and
C.S.Francklyn
(2003).
Induced fit and kinetic mechanism of adenylation catalyzed by Escherichia coli threonyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
15102-15113.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Hughes,
J.A.Tanner,
A.D.Hindley,
A.D.Miller,
and
I.R.Gould
(2003).
Functional asymmetry in the lysyl-tRNA synthetase explored by molecular dynamics, free energy calculations and experiment.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
3,
5.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Teague
(2003).
Implications of protein flexibility for drug discovery.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
2,
527-541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kamtekar,
W.D.Kennedy,
J.Wang,
C.Stathopoulos,
D.Söll,
and
T.A.Steitz
(2003).
The structural basis of cysteine aminoacylation of tRNAPro by prolyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
1673-1678.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ambrogelly,
I.Ahel,
C.Polycarpo,
S.Bunjun-Srihari,
B.Krett,
C.Jacquin-Becker,
B.Ruan,
C.Köhrer,
C.Stathopoulos,
U.L.RajBhandary,
and
D.Söll
(2002).
Methanocaldococcus jannaschii prolyl-tRNA synthetase charges tRNA(Pro) with cysteine.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
34749-34754.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Francklyn,
J.J.Perona,
J.Puetz,
and
Y.M.Hou
(2002).
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: versatile players in the changing theater of translation.
|
| |
RNA,
8,
1363-1372.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Lemke,
and
P.L.Howell
(2002).
Substrate induced conformational changes in argininosuccinate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
13074-13081.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Ahel,
C.Stathopoulos,
A.Ambrogelly,
A.Sauerwald,
H.Toogood,
T.Hartsch,
and
D.Söll
(2002).
Cysteine activation is an inherent in vitro property of prolyl-tRNA synthetases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
34743-34748.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

