 |
PDBsum entry 1gqw

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1gqw
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase from escherichia coli
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent taurine dioxygenase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: taurine dioxygenase, 2-aminoethanesulfonate dioxygenase, sulfate starvation-induced protein 3. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.281
|
R-free:
|
0.320
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.M.Elkins,M.J.Ryle,I.J.Clifton,J.C.Dunning-Hotopp,J.S.Lloyd, N.I.Burzlaff,J.E.Baldwin,R.P.Hausinger,P.L.Roach
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.M.Elkins
et al.
(2002).
X-ray crystal structure of Escherichia coli taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase complexed to ferrous iron and substrates.
Biochemistry,
41,
5185-5192.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Dec-01
|
Release date:
|
18-Apr-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P37610
(TAUD_ECOLI) -
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent taurine dioxygenase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
283 a.a.
277 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.17
- taurine dioxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
taurine + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = aminoacetaldehyde + sulfite + succinate + CO2 + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
taurine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
O2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
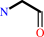 aminoacetaldehyde
aminoacetaldehyde
|
+
|
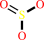 sulfite
sulfite
|
+
|
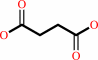 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+); L-ascorbate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(2+)
|
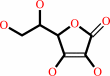 L-ascorbate
L-ascorbate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:5185-5192
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
X-ray crystal structure of Escherichia coli taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase complexed to ferrous iron and substrates.
|
|
J.M.Elkins,
M.J.Ryle,
I.J.Clifton,
J.C.Dunning Hotopp,
J.S.Lloyd,
N.I.Burzlaff,
J.E.Baldwin,
R.P.Hausinger,
P.L.Roach.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase (TauD), a non-heme Fe(II) oxygenase,
catalyses the conversion of taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonate) to sulfite and
aminoacetaldehyde concurrent with the conversion of alpha-ketoglutarate
(alphaKG) to succinate and CO(2). The enzyme allows Escherichia coli to use
taurine, widely available in the environment, as an alternative sulfur source.
Here we describe the X-ray crystal structure of TauD complexed to Fe(II) and
both substrates, alphaKG and taurine. The tertiary structure and fold of TauD
are similar to those observed in other enzymes from the broad family of
Fe(II)/alphaKG-dependent oxygenases, with closest structural similarity to
clavaminate synthase. Using the TauD coordinates, a model was determined for the
closely related enzyme 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate/alphaKG dioxygenase (TfdA),
supporting predictions derived from site-directed mutagenesis and other studies
of that biodegradative protein. The TauD structure and TfdA model define the
metal ligands and the positions of nearby aromatic residues that undergo
post-translational modifications involving self-hydroxylation reactions. The
substrate binding residues of TauD were identified and those of TfdA predicted.
These results, along with sequence alignment information, reveal how TauD
selects a tetrahedral substrate anion in preference to the planar carboxylate
selected by TfdA, providing insight into the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Saban,
S.C.Flagg,
and
M.J.Knapp
(2011).
Uncoupled O2-activation in the human HIF-asparaginyl hydroxylase, FIH, does not produce reactive oxygen species.
|
| |
J Inorg Biochem,
105,
630-636.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yang,
R.Chowdhury,
W.Ge,
R.B.Hamed,
M.A.McDonough,
T.D.Claridge,
B.M.Kessler,
M.E.Cockman,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2011).
Factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (FIH) catalyses the post-translational hydroxylation of histidinyl residues within ankyrin repeat domains.
|
| |
FEBS J,
278,
1086-1097.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Dahmani-Mardas,
C.Troadec,
A.Boualem,
S.Lévêque,
A.A.Alsadon,
A.A.Aldoss,
C.Dogimont,
and
A.Bendahmane
(2010).
Engineering melon plants with improved fruit shelf life using the TILLING approach.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e15776.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Kim,
H.L.Kim,
K.H.Kim,
d.o. .J.Kim,
S.J.Lee,
J.Y.Yoon,
H.J.Yoon,
H.Y.Lee,
S.B.Park,
S.J.Kim,
J.Y.Lee,
and
S.W.Suh
(2010).
Crystal structure of Tpa1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a component of the messenger ribonucleoprotein complex.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
38,
2099-2110.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Gazitúa,
A.W.Slater,
F.Melo,
and
B.González
(2010).
Novel α-ketoglutarate dioxygenase tfdA-related genes are found in soil DNA after exposure to phenoxyalkanoic herbicides.
|
| |
Environ Microbiol,
12,
2411-2425.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Grzyska,
E.H.Appelman,
R.P.Hausinger,
and
D.A.Proshlyakov
(2010).
Insight into the mechanism of an iron dioxygenase by resolution of steps following the FeIV=HO species.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
3982-3987.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Grzyska,
R.P.Hausinger,
and
D.A.Proshlyakov
(2010).
Metal and substrate binding to an Fe(II) dioxygenase resolved by UV spectroscopy with global regression analysis.
|
| |
Anal Biochem,
399,
64-71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Bollinger,
and
J.B.Broderick
(2009).
Frontiers in enzymatic C-H-bond activation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
13,
51-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.P.McCusker,
and
J.P.Klinman
(2009).
Modular behavior of tauD provides insight into the origin of specificity in alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent nonheme iron oxygenases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
19791-19795.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Yang,
C.Yi,
E.M.Duguid,
C.T.Sullivan,
X.Jian,
P.A.Rice,
and
C.He
(2008).
Crystal structures of DNA/RNA repair enzymes AlkB and ABH2 bound to dsDNA.
|
| |
Nature,
452,
961-965.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.G.Kovaleva,
and
J.D.Lipscomb
(2008).
Versatility of biological non-heme Fe(II) centers in oxygen activation reactions.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
4,
186-193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Singh,
P.D.Fortin,
A.Koglin,
and
C.T.Walsh
(2008).
beta-Hydroxylation of the aspartyl residue in the phytotoxin syringomycin E: characterization of two candidate hydroxylases AspH and SyrP in Pseudomonas syringae.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
11310-11320.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.C.Bruijnincx,
G.van Koten,
and
R.J.Klein Gebbink
(2008).
Mononuclear non-heme iron enzymes with the 2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad: recent developments in enzymology and modeling studies.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
37,
2716-2744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Anilkumar,
B.Bitterlich,
F.G.Gelalcha,
M.K.Tse,
and
M.Beller
(2007).
An efficient biomimetic Fe-catalyzed epoxidation of olefins using hydrogen peroxide.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
289-291.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Montero-Morán,
M.Li,
E.Rendòn-Huerta,
F.Jourdan,
D.J.Lowe,
A.W.Stumpff-Kane,
M.Feig,
C.Scazzocchio,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2007).
Purification and characterization of the FeII- and alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent xanthine hydroxylase from Aspergillus nidulans.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
5293-5304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Bursy,
A.J.Pierik,
N.Pica,
and
E.Bremer
(2007).
Osmotically induced synthesis of the compatible solute hydroxyectoine is mediated by an evolutionarily conserved ectoine hydroxylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
31147-31155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Neidig,
C.D.Brown,
K.M.Light,
D.G.Fujimori,
E.M.Nolan,
J.C.Price,
E.W.Barr,
J.M.Bollinger,
C.Krebs,
C.T.Walsh,
and
E.I.Solomon
(2007).
CD and MCD of CytC3 and taurine dioxygenase: role of the facial triad in alpha-KG-dependent oxygenases.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
129,
14224-14231.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Grzyska,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2007).
Cr(II) reactivity of taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase.
|
| |
Inorg Chem,
46,
10087-10092.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Purpero,
and
G.R.Moran
(2007).
The diverse and pervasive chemistries of the alpha-keto acid dependent enzymes.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
12,
587-601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Yu,
W.C.Edstrom,
J.Benach,
Y.Hamuro,
P.C.Weber,
B.R.Gibney,
and
J.F.Hunt
(2006).
Crystal structures of catalytic complexes of the oxidative DNA/RNA repair enzyme AlkB.
|
| |
Nature,
439,
879-884.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.D.Koehntop,
S.Marimanikkuppam,
M.J.Ryle,
R.P.Hausinger,
and
L.Que
(2006).
Self-hydroxylation of taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase: evidence for more than one oxygen activation mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
11,
63-72.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Müller,
M.I.Zavodszky,
M.Feig,
L.A.Kuhn,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2006).
Structural basis for the enantiospecificities of R- and S-specific phenoxypropionate/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenases.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
1356-1368.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Müller,
T.Fleischmann,
J.R.van der Meer,
and
H.P.Kohler
(2006).
Purification and characterization of two enantioselective alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, RdpA and SdpA, from Sphingomonas herbicidovorans MH.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
72,
4853-4861.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Cultrone,
C.Scazzocchio,
M.Rochet,
G.Montero-Morán,
C.Drevet,
and
R.Fernández-Martín
(2005).
Convergent evolution of hydroxylation mechanisms in the fungal kingdom: molybdenum cofactor-independent hydroxylation of xanthine via alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
57,
276-290.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Haltli,
Y.Tan,
N.A.Magarvey,
M.Wagenaar,
X.Yin,
M.Greenstein,
J.A.Hucul,
and
T.M.Zabriskie
(2005).
Investigating beta-hydroxyenduracididine formation in the biosynthesis of the mannopeptimycins.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
12,
1163-1168.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Bitto,
C.A.Bingman,
S.T.Allard,
G.E.Wesenberg,
D.J.Aceti,
R.L.Wrobel,
R.O.Frederick,
H.Sreenath,
F.C.Vojtik,
W.B.Jeon,
C.S.Newman,
J.Primm,
M.R.Sussman,
B.G.Fox,
J.L.Markley,
and
G.N.Phillips
(2005).
The structure at 2.4 A resolution of the protein from gene locus At3g21360, a putative Fe(II)/2-oxoglutarate-dependent enzyme from Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
469-472.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Müller,
C.Stückl,
J.Wakeley,
M.Kertesz,
and
I.Usón
(2005).
Succinate complex crystal structures of the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase AtsK: steric aspects of enzyme self-hydroxylation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
5716-5723.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.McDonough,
K.L.Kavanagh,
D.Butler,
T.Searls,
U.Oppermann,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2005).
Structure of human phytanoyl-CoA 2-hydroxylase identifies molecular mechanisms of Refsum disease.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
41101-41110.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Neidig,
and
E.I.Solomon
(2005).
Structure-function correlations in oxygen activating non-heme iron enzymes.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
5843-5863.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Schleinitz,
S.Kleinsteuber,
T.Vallaeys,
and
W.Babel
(2004).
Localization and characterization of two novel genes encoding stereospecific dioxygenases catalyzing 2(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)propionate cleavage in Delftia acidovorans MC1.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
70,
5357-5365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Valegård,
A.C.Terwisscha van Scheltinga,
A.Dubus,
G.Ranghino,
L.M.Oster,
J.Hajdu,
and
I.Andersson
(2004).
The structural basis of cephalosporin formation in a mononuclear ferrous enzyme.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
11,
95.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Zhang,
J.S.Ren,
I.J.Clifton,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2004).
Crystal structure and mechanistic implications of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase--the ethylene-forming enzyme.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
11,
1383-1394.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.J.Clifton,
L.X.Doan,
M.C.Sleeman,
M.Topf,
H.Suzuki,
R.C.Wilmouth,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2003).
Crystal structure of carbapenem synthase (CarC).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
20843-20850.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Ryle,
K.D.Koehntop,
A.Liu,
L.Que,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2003).
Interconversion of two oxidized forms of taurine/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase, a non-heme iron hydroxylase: evidence for bicarbonate binding.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
3790-3795.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Mukherji,
C.J.Schofield,
A.S.Wierzbicki,
G.A.Jansen,
R.J.Wanders,
and
M.D.Lloyd
(2003).
The chemical biology of branched-chain lipid metabolism.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
42,
359-376.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Liu,
A.Liu,
F.Yan,
M.D.Wolfe,
J.D.Lipscomb,
and
H.W.Liu
(2003).
Biochemical and spectroscopic studies on (S)-2-hydroxypropylphosphonic acid epoxidase: a novel mononuclear non-heme iron enzyme.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
11577-11586.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Dunning Hotopp,
and
R.P.Hausinger
(2002).
Probing the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate/alpha-ketoglutarate dioxygenase substrate-binding site by site-directed mutagenesis and mechanism-based inactivation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9787-9794.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Hewitson,
L.A.McNeill,
M.V.Riordan,
Y.M.Tian,
A.N.Bullock,
R.W.Welford,
J.M.Elkins,
N.J.Oldham,
S.Bhattacharya,
J.M.Gleadle,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
C.W.Pugh,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2002).
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparagine hydroxylase is identical to factor inhibiting HIF (FIH) and is related to the cupin structural family.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
26351-26355.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

