 |
PDBsum entry 1ff9

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ff9
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.1.10
- saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP(+), L-glutamate-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Lysine catabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-saccharopine + NADP+ + H2O = (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate + L-glutamate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
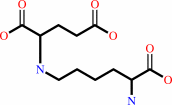 L-saccharopine
L-saccharopine
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
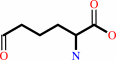 (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
|
+
|
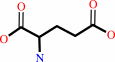 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
8:1037-1047
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of saccharopine reductase from Magnaporthe grisea, an enzyme of the alpha-aminoadipate pathway of lysine biosynthesis.
|
|
E.Johansson,
J.J.Steffens,
Y.Lindqvist,
G.Schneider.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: The biosynthesis of the essential amino acid lysine in higher fungi
and cyanobacteria occurs via the alpha-aminoadipate pathway, which is completely
different from the lysine biosynthetic pathway found in plants and bacteria. The
penultimate reaction in the alpha-aminoadipate pathway is catalysed by
NADPH-dependent saccharopine reductase. We set out to determine the structure of
this enzyme as a first step in exploring the structural biology of fungal lysine
biosynthesis. RESULTS: We have determined the three-dimensional structure of
saccharopine reductase from the plant pathogen Magnaporthe grisea in its apo
form to 2.0 A resolution and as a ternary complex with NADPH and saccharopine to
2.1 A resolution. Saccharopine reductase is a homodimer, and each subunit
consists of three domains, which are not consecutive in amino acid sequence.
Domain I contains a variant of the Rossmann fold that binds NADPH. Domain II
folds into a mixed seven-stranded beta sheet flanked by alpha helices and is
involved in substrate binding and dimer formation. Domain III is all-helical.
The structure analysis of the ternary complex reveals a large movement of domain
III upon ligand binding. The active site is positioned in a cleft between the
NADPH-binding domain and the second alpha/beta domain. Saccharopine is tightly
bound to the enzyme via a number of hydrogen bonds to invariant amino acid
residues. CONCLUSIONS: On the basis of the structure of the ternary complex of
saccharopine reductase, an enzymatic mechanism is proposed that includes the
formation of a Schiff base as a key intermediate. Despite the lack of overall
sequence homology, the fold of saccharopine reductase is similar to that
observed in some enzymes of the diaminopimelate pathway of lysine biosynthesis
in bacteria. These structural similarities suggest an evolutionary relationship
between two different major families of amino acid biosynthetic pathway, the
glutamate and aspartate families.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. Proposed Mechanism of the Reaction Catalysed by
Saccharopine Reductase

|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2000,
8,
1037-1047)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Yoneda,
J.Fukuda,
H.Sakuraba,
and
T.Ohshima
(2010).
First crystal structure of L-lysine 6-dehydrogenase as an NAD-dependent amine dehydrogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
8444-8453.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xu,
S.S.Alguindigue,
A.H.West,
and
P.F.Cook
(2007).
A proposed proton shuttle mechanism for saccharopine dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
871-882.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Siméone,
P.Constant,
C.Guilhot,
M.Daffé,
and
C.Chalut
(2007).
Identification of the missing trans-acting enoyl reductase required for phthiocerol dimycocerosate and phenolglycolipid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
4597-4602.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Lin,
S.S.Alguindigue,
J.Volkman,
K.M.Nicholas,
A.H.West,
and
P.F.Cook
(2007).
Complete kinetic mechanism of homoisocitrate dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
890-898.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Guo,
R.C.Garrad,
and
J.K.Bhattacharjee
(2006).
Functional analysis through site-directed mutations and phylogeny of the Candida albicans LYS1-encoded saccharopine dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Mol Genet Genomics,
275,
74-80.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Andi,
A.H.West,
and
P.F.Cook
(2005).
Regulatory mechanism of histidine-tagged homocitrate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Kinetic studies.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
31624-31632.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ricagno,
S.Jonsson,
N.Richards,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(2003).
Formyl-CoA transferase encloses the CoA binding site at the interface of an interlocked dimer.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
3210-3219.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Naranjo,
E.Martin de Valmaseda,
O.Bañuelos,
P.Lopez,
J.Riaño,
J.Casqueiro,
and
J.F.Martin
(2001).
Conversion of pipecolic acid into lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum requires pipecolate oxidase and saccharopine reductase: characterization of the lys7 gene encoding saccharopine reductase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
7165-7172.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

