 |
PDBsum entry 1ee3

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.4.17.1
- carboxypeptidase A.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Peptidyl-L-amino acid + H2O = peptide + L-amino acid
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
+
|
|
=
|
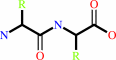
|
+
|
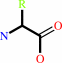
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Inorg Chem
7:490-499
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Three high-resolution crystal structures of cadmium-substituted carboxypeptidase A provide insight into the enzymatic function.
|
|
F.Jensen,
T.Bukrinsky,
J.Bjerrum,
S.Larsen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Three high-resolution crystal structures of Cd(II)-substituted carboxypeptidase
A (CPA) have been determined by X-ray diffraction from crystals prepared in
three different buffer systems to assess the effect of pH and ionic strength on
the Cd(II) coordination geometry. All crystallize in the space group P2(1) with
identical cell dimensions. Cd-CPA(7.5): Cd(II)-substituted CPA prepared at pH
7.5 with [Cl(-)]=2 mM determined to 1.70 A resolution ( R=17.4% and
R(free)=19.8%); Cd-CPA(5.5): Cd(II)-substituted CPA prepared at pH 5.5 with
[Cl(-)]=2 mM to 2.00 A resolution ( R=16.1% and R(free)=18.6%); Cd-CPA(7.5)-Cl:
Cd(II)-substituted CPA prepared at pH 7.5 with [Cl(-)]=250 mM to 1.76 A
resolution ( R=16.7% and R(free)=17.8%). No noticeable structural changes were
observed between the three structures. Two water molecules coordinate to Cd(II),
in contrast to the single water molecule coordinating to Zn(II) in the Zn-CPA
structure. No binding sites for anions could be identified, even in the
structure with a high concentration of chloride ions. It is suggested that the
anion inhibition is due to weak outer-sphere association of Cl(-) ions at
several binding sites, shielding the strong positive charge distribution at the
surface of the protein near the active site. Based on structural data and a
sequence alignment of 18 non-redundant carboxypeptidases, a more elaborate
version of the earlier reaction model is proposed that also addresses the
transport of water to and from the active site. Conserved residues whose
function was not addressed previously delineate the proposed pathways used in
the transport of water during catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Heeb,
D.Prashun,
J.H.Griffin,
and
B.N.Bouma
(2009).
Plasma protein S contains zinc essential for efficient activated protein C-independent anticoagulant activity and binding to factor Xa, but not for efficient binding to tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
|
| |
FASEB J,
23,
2244-2253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Hershfield,
N.Pattabiraman,
C.N.Madhavarao,
and
M.A.Namboodiri
(2007).
Mutational analysis of aspartoacylase: implications for Canavan disease.
|
| |
Brain Res,
1148,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Stewart,
C.A.Blindauer,
S.Berezenko,
D.Sleep,
and
P.J.Sadler
(2003).
Interdomain zinc site on human albumin.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
3701-3706.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Houborg,
P.Harris,
J.Petersen,
P.Rowland,
J.C.Poulsen,
P.Schneider,
J.Vind,
and
S.Larsen
(2003).
Impact of the physical and chemical environment on the molecular structure of Coprinus cinereus peroxidase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
989-996.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

